Veal - What the World Eats
advertisement
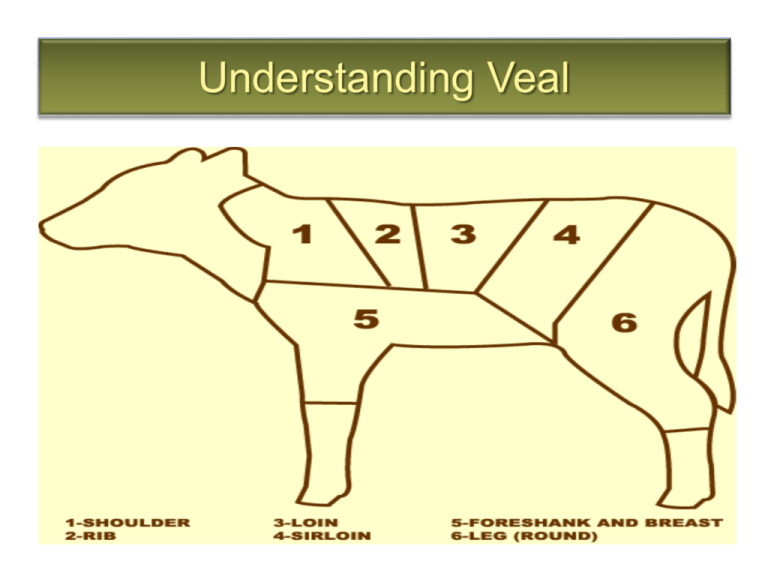
Understanding Veal The Definition of Veal • Meat of young, usually male, calves that are by-products of the dairy industry • Calves asre usually slaughtered at 8-16 weeks of age • Flavour is lighter and more delicate than beef • More tender than beef because of young age, but it is lacking in flavour • Average weight of 160kg (350lbs) 2 Feeding Procedures Free-range Veal Flyer • Free Range Veal • Calves are allowed to roam, eat grasses and other natural foods • Flesh is reddish-pink • More strongly flavoured than formula-fed veal 3 Feeding Procedures Free Range Veal Video 4 Feeding Procedures • Formula –Fed Veal – Most veal produced today is fed a nutrientrich liquid formula – Calves are tethered in pens slightly larger than their bodies in order to restrict movement – The meat is kept white by preventing them from eating grasses 5 Feeding Procedures Milk Fed Veal Video • Formula-Fed Veal 6 Skeletal Structure of a Veal 7 Primal Cuts of Veal • Foresaddle – Shoulder – Foreshank – Breast – Rib • Hindsaddle – Loin – Leg 8 Primal Cuts of Veal • Foresaddle – the anterior portion of the veal, cut between ribs 11 and 12 (front half), it contains the shoulder, foreshank/breast, and rib • Hindsaddle – the posterior portion of the veal (back half), it contains the loin and leg • Back – is the whole loin (rib+loin) that has been trimmed 9 Primal Cuts of Veal 10 Primal Cuts of Veal Shoulder/Front • This is the shoulder of the veal, it makes up 21% of the total carcass weight • It contains ribs 1 through 4, therefore it is split between ribs 4 and 5 • If boned, it can be used for roasts, stuffed or cubed • It is high in connective tissue so braising or stewing is best 11 Primal Cuts of Veal 12 Skeletal Structure of a Veal 13 Primal Cuts of Veal Foreshank & Breast • This lies beneath the shoulder and rib and is 16% of the total carcass weight • It contains cartilage and connective tissue which breaks down with low, moist heat • It can be cubed, used for fricasee, blanquette, rolled and stuffed • Fore shank is high in collagen, can be braised to make osso bucco which is garnished with gremolata 14 Primal Cuts of Veal 15 Skeletal Structure of a Veal 16 Primal Cuts of Veal Rib • The rib makes up 9% of the carcass weight and contains 7 ribs, 5 through 11 • The eye meat is very tender • The roast can be boneless to produce rib eye roast, or it can be cut into rib eye steaks • Dry heat is best used when cooking the Rib primal 17 Primal Cuts of Veal 18 Skeletal Structure of a Veal 19 Primal Cuts of Veal Loin • The loin makes up 10% of the carcass weight and contains ribs 12 and 13 • This is the primal that contains the veal tenderloin • When the loin and leg are split, the tenderloin is cut in two and the butt tenderloin stays in the leg • Often the tenderloin is removed first • * the rib + the loin = whole loin 20 Primal Cuts of Veal 21 Skeletal Structure of a Veal 22 Primal Cuts of Veal Leg • This is a very large primal making up 42% of the weight • It contains the sirloin, the leg and the hind shank • Some of the sub primals include the inside round, eye of round, knuckle, bottom round and butt tenderloin • This is used most often for making schnitzle 23 Primal Cuts of Veal 24 Skeletal Structure of a Veal 25 The Offals Cooking Sweetbreads Sweetbreads • This is the thymus gland, as the animal ages, the thymus shrinks, it should be firm and plump • To Prepare: – Cover sweetbreads in salted water overnight – Blanch them in court boullion and remove the sinew and membrane – Wrap the sweetbreads in cheesecloth, tie at both ends and press with weight to improve texture – After pressing, slice, flour/bread, and pan fry 26 The Offals Liver • It has a mild flavour, and tender in texture • It is best sauteed or broiled, and should be served medium rare • Often the liver is soaked in milk overnight to remove impurities • The membrane is always removed cooking 27 Inspection Grading The and Offals Kidneys • They are plump and firm, encased in a membrane that should be removed before cooking • The flavour is similar to liver with a hint of urine, often it is soaked in salted water overnight to remove some of this smell 28 Inspection Grading The and Offals Heart • Can be from beef or veal • The ventricals are very tough and must be removed before cooking • It can be marinated and grilled • Taste is similar to liver (irony) 29 Inspection Grading The and Offals Tripe • One of the stomachs in the beef or veal • Honeycomb tripe is the most common • The flavour is very strong so the tripe is usually blanched in 2-3 changes of water • It is typically tough and chewy 30 The Offals Inspection and Grading Chris Consentino-the offals Tongue • It is a very strong muscle, therefore it must be simmered before using • After simmering, the skin should be removed • It can be pickled and served cold, or it can be braised/stewed and finished in a sauce 31