Animals
advertisement

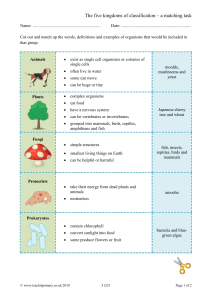
Animals ectotherm also called cold-blooded Definition: An animal whose body does not produce much internal heat Examples – reptiles, amphibians and fish endotherm Also called warm-blooded Definition: An animal whose body controls & regulates its temperature by controlling the internal heat it produces Examples: birds and mammals vertebrate Definition: An animal that has a backbone Examples – fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds & mammals invertebrate Def: An animal that does not have a backbone Examples – jellyfish, worms, snails, crabs, spiders, insects exoskeleton Definition: A waxy, waterproof outer shell (outer skeleton) Examples - arthropods endoskeleton Definition: An internal skeleton Examples – cat, mouse, dog, human, gorilla Functions of an Endoskeleton 1. Supports and protects the body 2. Helps give it shape 3. Gives muscles a place to attach How are ectotherms and endotherms different? Ectotherms need heat from their environment while endotherms make and regulate their own heat. 98.6 degrees for humans Why do animals compete? They compete for limited resources such as: food, water, space, shelter and mates Example of competition Lions stealing food from hyenas What is a territory? Definition: An area that is occupied and defended by an animal or group of animals. Maintaining their territories: 1. Scratches 2. Droppings 3. Scents 4. Calls A territory supplies: food & a safe place to raise young Animals that provide little or no care for their young Fish Amphibians Reptiles What do birds and mammals do for their young? Feed them Protect them Teach them survival skills (hunting) One positive about living in a group Protection from predators What is a society? A group of closely related animals of the same species that work together for the benefit of the whole group Animals that live in a society Ants Termites Honeybees Animal Communication Sounds Body positions Movements Scent Hibernation Definition: state of reduced body activity that occurs during winter months Benefit: so they can survive the cold weather migration Definition: regular periodic journey of an animal from one place to another and then back Benefit: to find food or to reproduce