Cell Respiration Worksheet: ATP, Aerobic & Anaerobic Processes
advertisement
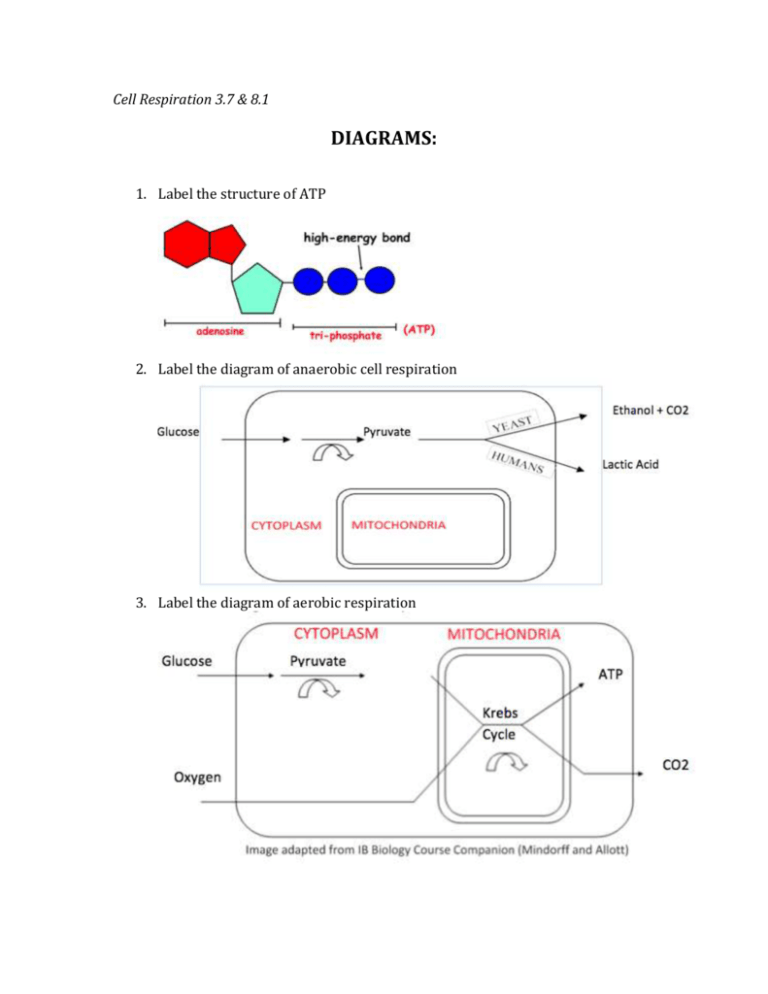
Cell Respiration 3.7 & 8.1 DIAGRAMS: 1. Label the structure of ATP 2. Label the diagram of anaerobic cell respiration 3. Label the diagram of aerobic respiration 4. Label the parts of the mitochondria including the outer membrane, inner membrane, christae, matrix, mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, and intermembrane space. State the function of these structures. Structure: Function: Outer membrane Highly permeable to ions and large molecules Site for electron transport chain and oxidative phosphorylation. Cristae maximizes the surface area for reactions Contains enzymes and solutes for the Link Reaction and Krebs Cycle Inner membrane (including christae) Matrix Mitochondrial DNA and ribosomes Protein production Inter-membrane space More efficient generation of hydrogen ion concentration gradient 5. Draw the Krebs cycle including formation of citrate, oxidation, decarboxylation, substrate-level phosphorylation (ATP formation) and production of electron carriers. 6. Complete the diagram of glycolysis (in the cytoplasm of cells) Additional Questions: 7. Write the word equation for aerobic respiration Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy 8. Complete the table below Reaction Location Purpose ATP yield Glycolysis Cytoplasm Create 2x pyruvate 2 Link reaction Matrix of the mitochondrion Convert pyruvate (3C) to acetyl CoA (2C) 0 Krebs Cycle Matrix Release hydrogen ions to electron carriers for the ETC (NADH/FADH) 2 Electron Transport Chain Inner mitochondrial membrane Energy to pump hydrogen ions to intermembrane space to generate concentration gradient 0 Oxidative phosphorylation Inner membrane of mitochondria using ATPase Uses flow of hydrogen ions through ATP Sythase to ADP to ATP 32 9. Fill in the blank a. In oxidation, electrons are lost, oxygen is gained, and hydrogen is lost b. In reduction, electrons are gained, oxygen is lost, and hydrogen is gained 10. Define phosphorylation- addition of phosphates to the glucose molecule 11. Name compounds in cell respiration that containa. 6 carbons- glucose, citric acid b. 4 carbons- oxaloacetic acid c. 3 carbons- pyruvate d. 2 carbons- acetyl CoA e. 1 carbon- CO2 f. 0 carbons- ATP, NADH, FADH 12. What is chemiosmosis? The diffusion of ions across a semi-permeable membrane through carrier proteins. In cell respiration chemiosmosis occurs in the generation of ATP when hydrogen ions are transported into the matrix through ATP synthase.



