file
advertisement
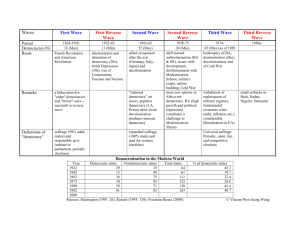
Industrialized Democracies An overview Political system • Inputs – types: support & demands – channels: interest groups and parties • Decision making – institutions & leaders of the state • Outputs – public policy Political system inputs • interest articulation – voting, participation in elections – informal group, social movement – personal interest contact – protest activity • interest groups • channels of political access Political system inputs • interest aggregation – political demands of individuals and groups are combined into policy programs • personal interest aggregation – patron-client network • central person or group • provides benefits to supporters • in exchange for their loyalty Institutional interest aggregation • associational groups – e.g. aggregation of labor and business interests • institutional groups – e.g. bureaucracy and military • political parties are the primary structures of interest aggregation – competitive vs. authoritarian party systems Competitive party system • political parties can freely form • primarily try to build electoral support • citizen support is prerequisite for controlling government • the closeness of electoral victory or even the number of political parties are not essential – e.g. the Indian or African National Congress Competitive party system • 3 stages of interest aggregation in a competitive party system • within individual parties – candidates and policy proposals • through electoral competition • through bargaining and coalition building in the legislature or executive Electoral rules • single-member district plurality rule – “first past the post” – e.g. Britain, U.S., and many other countries once influenced by Britain – the “Median Voter Theorem” • proportional representation – e.g. many countries in continental Europe Duverger’s Law • Plurality single-member district election rules tend to create two-party systems in the legislature • Proportional representation electoral systems generate multiple party systems in the legislature Three Types of Polities • Industrialized democracies – North America, European Union, Japan, and Oceania • Current and former communist regimes – East Europe, East Asia, and Cuba • The Third World – Latin America, Asia, and Africa Three Types of Polities Democracy: conceptual issues • Greek words: rule by the people • Who are “the people”? – Gender, race, and age • How to rule? – Direct versus representative democracy • Almost every government claims to be a democracy Criteria of democracy • • • • • • Institutional arrangements? Individual freedom? Economic equality? ... Necessary condition but Not sufficient condition Criteria of democracy • Democracies guarantee basic individual freedoms and rights • Democracies rely on the rule of law • Democratic governments are chosen through regular, free, and fair elections – different electoral systems • single-member district & first-past-the-post system • proportional representation system Criteria of democracy • Two uncertain and controversial criteria: • civil society and civic culture – legitimacy (the right to rule) – distinction between administration and democracy • capitalism and affluence • Historical development of democracy Origins of the Democratic State • In Europe (and North America) the way democracy developed was largely a result of the way countries handled four great transformations over the last 500 years: – The creation of the nation and state itself – The role of religion in society and government – The development of pressures for democracy – The industrial revolution Waves of Democratization • ``A group of transitions from nondemocratic to democratic regimes that occur within a specified period of time and that significantly outnumber transitions in the opposite direction during that period” The First Two Waves • A long and slow wave from 1828 to 1926 • A reverse wave of democratic breakdown from 1922 to 1942 • A wave of democratization after World War II from 1943 to 1964 • A reverse wave of democratic breakdown from 1961 to 1975 The Third Wave • Started in Portugal and Spain in mid1970s • Spread to South America from late 1970s to early 1980s • Reached Asia in late 1980s • Surge of transitions in East Europe at end of 1980s • South Africa 1990 The Third Wave Political parties in democracies • • • • • Traditional left-right political spectrum left end: communist parties left: social democratic parties right: Christian democratic parties right: conservative parties