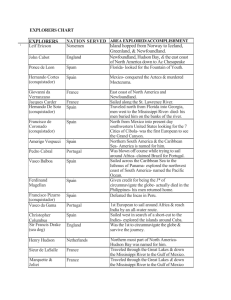
The Age of Exploration Power Point

1400s – the Renaissance begins (rebirth)
Began in Italy and spread throughout Europe
Johannes Gutenberg – printing press – books printed faster
The Travels of Marco Polo
Shared stories of the voyages of Marco Polo
Wanted to buy and resell Asian goods (silk and spices)
Gunpowder and compass
Prince Henry of Portugal
Opened a school of navigation
Aimed to make better ships, maps, and tools for navigation
New Technology
Caravel – kind of ship
Drew better maps
Improved the compass and astrolabe
Used Marco Polo’s book to learn about Asia
Never thought to travel across the Atlantic Ocean to get to Asia
Vikings
Leif Erickson – sailed west across the Atlantic, stopping in Greenland, Canada, and present-day Newfoundland
Christopher Columbus
Thought he could sail across the Atlantic to get to Asia
Risks and Rewards
Explorers had to prove themselves.
Had to prove the cost was worth it, despite risks
Hoped the benefit would be BIG
His plan was risky.
Portugal turned him down.
King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella of Spain
Said, “No!” - due to pushing the Muslims out of Spain
Reconquista – either become Catholic or leave Spain
When this ended, they finally supported his plan to travel west.
Columbus
Sailed the Nina, Pinta, and Santa Maria
October 12, 1492 – finally saw land
A Historic Meeting
Landed in San Salvador (thought it was the Indies)
Met the Taino tribe
Collected gold items, animals, and plants
Captured several Taino to bring back to Spain
When Columbus and his men returned, they were heroes.
King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella were quite pleased.
Sponsored a second expedition
Hoped to find more riches, start settlements, and convert people to the Catholic religion
Navigation Tools
Do Now Question:
How did technology help improve navigation during the time of early exploration?
DBQ 1 – How did the compass help sailors?
The compass helped sailors know in which direction they were traveling.
DBQ 2 – How might the weather affect the use of the astrolabe?
Sailors could not use the astrolabe if the weather was bad and the sun or the stars were not visible.
DBQ 3 – Why would explorers need more accurate maps?
More accurate maps would give explorers a clearer idea of where they were going and how far their journeys might be.
DBQ 4 – Why would sailors need to keep track of the time?
Sailors would keep track of the time to know how much longer it should take to get to a certain place.
Columbus’s trips inspired other European rulers to send ships west.
John Cabot Sets Sail
Sent by England’s King Henry VII to help compete with other European nations for land and wealth
Sailed west and found land – present-day
Newfoundland and Labrador (parts of Canada)
Same place the Vikings found 500 years earlier
Amerigo Vespucci
Did not believe Columbus and Cabot found the Indies
Sailed west and found land as he sailed down the coast of South America
Amerigo Vespucci’s New Idea
Looked for signs that the land was Asia – did not match
Marco Polo’s description
Thought - perhaps Earth was larger than they thought
The Naming of America
1507 – mapmaker made a new map and labeled the land of South America after Vespucci
North America was labeled later
Vasco Nunez de Balboa
Spanish explorer – first to settle in the Americas
Settled in Hispaniola -> Columbia -> Panama
Traveled west across the Isthmus of Panama (connects
North and South America) and reached the Pacific
Ocean
Proved Vespucci was right
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese explorer
Sailed around the tip of South America to the Pacific
Ocean
Named the ocean Pacific – means peaceful - his opinion of the water
Magellan’s Long Voyage
Planned to travel across the Pacific
Died in a battle in the Philippines
One ship made it back to Spain in 1522 – first to sail around the world
As more expeditions were organized, more lands were claimed.
Same countries claimed certain lands
Catholic Church settled problem with an imaginary line
Spain got land to the west; Portugal got land to the east
1494 – treaty moved the dividing line further west
Many Spanish explorers sailed west.
Dreamed of being rich, winning national glory, and/or converting Native Americans to Christianity
Juan Ponce de Leon
Sailed with Columbus on a voyage and later discovered
Puerto Rico
Heard of the land, Bimini, to the north of Puerto Rico
1513 – found present-day Florida
1521 – set up Spanish settlement, but was defeated by native tribe
First Spanish explorer to set foot on present-day U.S. soil
Hernando Cortes
Sent to find gold in land of the Aztecs
(present-day Mexico)
The Fall of the Aztecs
Aztecs believed a light-skinned god would return to rule one day – The Aztec emperor believed Cortes was this god.
Cortes captured him and fighting began.
Cortes and Spain won.
Mexico City was built on Tenochtitlan – new capital
The Seven Cities of Gold
Native American story – searched and a Spanish priest,
Marco de Niza claimed to see a city of gold
Coronado in the Southwest
Francisco Vasquez de Coronado – searched for the cities of gold
Went back to Mexico City without any gold, but did claim lands in the present-day southwestern United States for
Spain.
Lands in Florida, Mexico, and the southwestern
United States became known as New Spain
Pizarro and the Incas
Francisco Pizarro – Spanish conquistador who searched the western coast of South America.
Found the Incan empire and took control
De Soto in the Southeast
Hernando de Soto – explored the southeastern U.S.
Landed in near Tampa Bay, Florida and travelled to land near the Mississippi River
Battled Native American tribes and many died including De
Soto
More land claimed by Spain
Spain controlled much of the southern half of the U.S.
The Church forced people to follow it rules, to pay taxes, had its own court, and punished those for breaking the laws.
Religious Reforms
Martin Luther – started the Reformation – challenged the Church
Led to new churches including the Lutheran Church
Counter-Reformation – made some changes, but tried to keep power in the Catholic Church
Spread ideas to new followers in the Americas
Missionaries – converted Native Americans despite their efforts to hold onto Native American beliefs
European nations still wanted to find a shortcut to
Asia
Searching for a New Route
Thought if you sailed to and around N. America, it would be faster and easier
The first country to find it, gets control of the important new trade route.
Search lasted for hundreds of years
The French in North America
Giovanni Verrazano – sailed from North Carolina, along the Atlantic coast, and no further than Newfoundland
Did not find a passage
Jacques Cartier – During his three trips, he sailed to the mouth of the St. Lawrence River.
Claimed the land around it for France including present-day
Montreal and Quebec
Henry Hudson – English explorer who made 4 voyages in search of the Northwest Passage
During his 3 rd voyage, he explored a river in present-day
New York, named it after himself, and declared the land for the Dutch.
A Voyage Ends in Mutiny
Last voyage – searched the Hudson Bay and claimed land around it for England
Crew rebelled and sent him and 8 others on a boat – never seen or heard from again