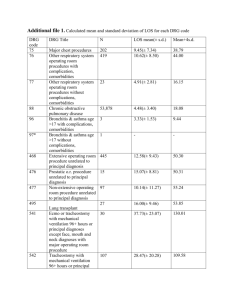
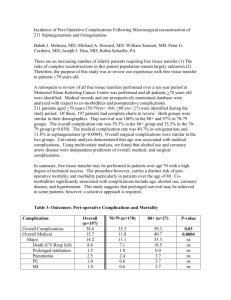
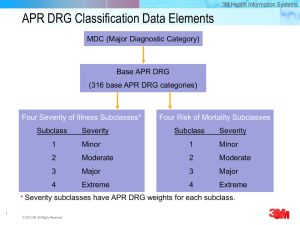
Risk-Adjusted Complications Index
advertisement

COMPANY HISTORY 1989 Staff developed and supported innovative clinical, financial, and marketing applications for SysteMetrics/McGraw-Hill (New York, NY) 1992 HCIA, Inc. (Baltimore, MD): staff responsible for HCIA’s Provider Profiling Business Unit which led company’s IPO in February 1995. 1995 The Delta Group founded by former HCIA staff to specialize in improving the clinical, financial, and market performance of healthcare organizations. Present The Delta Group offers web-based provider profiling products to leading healthcare organizations across the country. HOSPITAL ORGANIZATIONS University HealthSystem Consortium (UHC) Henry Ford Health System Baycare Health System Iowa Health System Trinity Health System SunLink Healthcare Corporation Galaxy Health Alliance Maine Health Alliance Sagamore Health Network TEACHING HOSPITALS & ACADEMIC INSTITUTIONS Massachusetts General Hospital (Harvard) Brigham & Women’s Hospital (Harvard) Yale-New Haven Hospital Mary Hitchcock Memorial Hospital (Dartmouth) Vanderbilt University Hospital Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital University of Notre Dame Medical College of Virginia Hospitals University of Alabama-Birmingham Hospital Erlanger Medical Center Oregon Health Sciences University Hospitals PHYSICIAN ORGANIZATIONS Partners Community Healthcare (Harvard) HealthCare Savings (North Carolina Medical Society) Morton Plant Mease PHO (Physicians Health Alliance) Presbyterian Medical Group Preferred Health Services Heritage Health System Mid-Valley CareNet OTHER ORGANIZATIONS Tennessee Hospital Association Oregon Association of Hospitals and Health Systems CSC Healthcare Group Cambio Health Solutions Peat Marwick Ernst & Young Physcape (MGMA) Prudential BC/BS of Alabama Ford, Chrysler & General Motors (MHA) PARADOS® Provider Profiling System Physician Hospital Practice Analysis ORYX Clinical Performance Analysis Hospital Competitive Positioning Analysis Hospital Quality Outcomes Analysis Hospital Planning and Marketing Analysis (2004) Physician Office Practice Analysis Continuum of Care Analysis APPLICATIONS ® OF PARADOS Clinical Resource Management and Quality Improvement Knowledge-Based Managed Care Contracting Provider Network Evaluation and Monitoring Strategic Planning, Marketing & Public Relations $750,000 Increase in Financial Performance $150,000 $150,000 Supplies Supplies $185,000 $185,000 Laboratory Laboratory $415,000 $415,000 Operating Operating Room Room “Using The Delta Group’s PARADOS Provider Profiling System, we were able to improve our financial performance by $750,000 by altering practice patterns and policies in laboratory, operating room, and medical/surgical supplies. Importantly, The Delta Group’s software and consulting services allowed us to achieve a favorable managed care position in the marketplace.” Jeff Judd, CEO The McDowell Hospital (65-bed general, acute care hospital) North Carolina Severity & Risk Adjustment Clinically Adjusted Data Accounts for Differences in Patient: • Severity (stage of disease) • Intensity (resource need) • Complexity (type of CCs) Adjusted Data Provides an Accurate Unit of Measure for: Peer and Benchmark Comparisons Accurate Outcome Comparisons Require Indicator-Specific Adjustment Methods ™ • Charge/Cost: APS-DRG Relative Charge/Cost Weights • Length of Stay: APS-DRG™ Relative LOS Weights • Mortality Rates: Risk-Adjusted Mortality Index™ • Complication Rates: Risk-Adjusted Complications Index™ • Readmission Rates: Risk-Adjusted Readmissions Index™ Indicator-Specific Severity & Risk-Adjustment Methods Are Required to Accurately Assess Variation in Clinical & Financial Outcomes Risk-Adjusted Readmissions Index (RARI) Standard logistic regression was used to model risk of an unanticipated readmission to the same hospital within 30 days of discharge for specific diagnoses and procedures Predictive variables used for risk of readmission were: o age o sex o presence or absence of comorbidities “and” complications o presence of cancer (except skin cancer) o DRG cluster (risk associated with principal diagnosis/procedure) o total number of comorbidities Source: “Risk-Adjusted Clinical Quality Indicators: Indices for Measuring and Monitoring Rates of Mortality, Complications, and Readmissions.” Quality Management in Health Care, Volume 9, No. 1, Fall 2000, pp. 14-22. Risk-Adjusted Mortality Index (RAMI) Standard logistic regression was used to model risk of death during a hospital stay for specific diagnoses and procedures Predictive variables used for risk of death were: o age, sex, race o presence or absence of comorbidities (not complications) o presence of cancer (except skin cancer) o DRG cluster (risk associated with principal diagnosis/procedure) o total number of comorbidities Source: “Risk-Adjusted Clinical Quality Indicators: Indices for Measuring and Monitoring Rates of Mortality, Complications, and Readmissions.” Quality Management in Health Care, Volume 9, No. 1, Fall 2000, pp. 14-22. Risk-Adjusted Complications Index (RACI) Standard logistic regression was used to model risk of postsurgical and post-obstetrical complications during a hospital stay for associated diagnoses and procedures Predictive variables used for risk of complications were: o age o sex o presence or absence of comorbidities (not complications) o presence of cancer (except skin cancer) o DRG cluster (risk associated with principal diagnosis/procedure) o total number of comorbidities Source: “Risk-Adjusted Clinical Quality Indicators: Indices for Measuring and Monitoring Rates of Mortality, Complications, and Readmissions.” Quality Management in Health Care, Volume 9, No. 1, Fall 2000, pp. 14-22. The Need to Clinically Adjust Inpatient Information DRG 127: Heart Failure & Shock Principle Diagnosis: Congestive Heart Failure Secondary Diagnoses: Patient #1 Acute Bronchitis Clinical Demand Index: .654 Patient #2 Stroke Clinical Demand Index: 2.154 CDI Norm: 1.000 $14,000 $11,352 $12,000 $10,000 $9,017 $8,000 $5,897 / .654 $6,000 $5,897 Actual Charge $5,270 $11,352 / 2.154 $4,000 Clinically Adjusted Charge $2,000 $0 Patient #1 Patient #2 All Payer Severity-adjusted DRGs ™ (APS-DRGs ) Developed by HSS, Inc. (participated in original Refined-DRG research with CMS—formerly HCFA) Incorporates most recent CMS severity research (SDRGs) Use principal and secondary diagnosis to indicate the severity of a patient’s illness to predict inpatient resource need Use occurrence and degree of surgery as a discriminating variable; occasionally use patient’s age and discharge status Applicable for all hospitalized patients, regardless of age, type of illness, or payer category Comprised of 1,076 clinically homogeneous statistically stable groups Reviewed by clinicians to ensure clinical integrity Source: “All Payer Severity-adjusted DRGs (APS-DRGs): A Uniform Method to Severity-adjust Discharge Data.” Topics in Health Information Management, Winter 1997. ™ APS-DRG Patient Classification System Severity Class Description Clinical Examples 0 No CC or Major CC: Heart failure & shock w/o CC 1 At least 1 CC: Heart failure & shock w/ hypertension 2 At least 1 Major CC: Heart failure & shock w/ acute renal failure Source: “All Payer Severity-adjusted DRGs (APS-DRGs): A Uniform Method to Severity-adjust Discharge Data.” Topics in Health Information Management, Winter 1997. Differences in Patient Risk for Adverse Events within the Same Severity Class DRG 107: Coronary Bypass w/Cardiac Catheterization (Severity Class 2) 34.0% Mortality Risk 11.0% Patient A Patient B 57.0% Complications Risk 68.0% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% Risk of Adverse Outcome 60% 70% 80% ® PARADOS Clinical, Financial & Market Indicators: (Includes Severity & Risk-Adjustment where Appropriate) Charges Costs Gross Margins Lengths of Stay Mortality Rates Complication Rates Readmission Rates ORYX Core Measures Market Share Patient Origin Patient Outmigration Demographics Lifestyle Characteristics Acute Morbidity Projections Acute Use Rates Planning Indicators by MD, Employer, and Health Plan PARADOS ® ORYX Core Measurement Sets*: Acute Myocardial Infarction (AMI 1-9) Heart Failure (HF 1-4) Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP 1-5) Pregnancy & Related Conditions (PR 1-3) FUNCTIONALITY OF PARADOS ® Provides online access to evidence-based guidelines (EBGs) developed by the Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement (ICSI) Easily sorts, finds, filters, graphs and trends data Compares to national benchmarks of top performing providers Compares to national, regional, or local peer groups Customizes service lines and payer groupings Drills-down to the diagnosis, procedure & patient level Creates PDF and comma-delimited files for ease of distribution & customization Consulting CONSULTING SERVICES Management consulting in executive summary format Medical management consulting led by practicing physicians Lean Six Sigma training in seminar format MEDICAL MANAGEMENT CONSULTING Dwight Wooster, MD James Kennedy, MD Michael Langley, MD William Hill, PharmD Judy Homa-Lowry, RN, MS Linda Easterly, MS, BSN Cynthia Whitaker, BS, RRA Henry Dove, PhD LEAN SIX SIGMA TRAINING Conducted by Master Black Belts certified by The George Group Integrates Lean techniques for “minimizing complexity and eliminating waste” with Six Sigma methods for “improving quality and reducing variation”