Digestion I Heterotroph- Consumes organic nutrients “eats food” ( ex

Digestion
I Heterotroph - Consumes organic nutrients “eats food”
( ex) animals, Fungi, some protists & monera ( bacteria)
1.
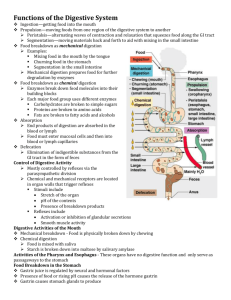
Oral cavity- mouth a) Teeth - rip, tear, grind
-------
mechanical digestion
_______________________
physical breakdown of food
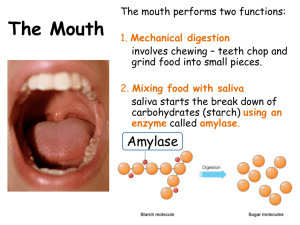
***mechanical digestion increases surface area for chemical digestion to occur b) Tongue moves food c) Salivary glands - produce saliva that contains enzymes
(ex) (amylase) starch---
sugar (carbohydrate digestion begins in mouth)
2.
Esophagus muscular tube
Chemical digestion - enzymes break down large molecules into small molecules ( hydrolysis ) a.
Connects mouth to stomach
Peristalsis wave of muscle contractions that moves food through GI tract
( digestive system) “ gastrointestinal”
3.
Stomach- a.
Muscular – churns food ( stirs) mechanical b.
Has HCL- hydrochloric acid.
Provides the optimum environment for enzymes ( pepsin digests protein) protease
HCL triggers enzymes to begin working
Mucus protects stomach lining
Protein digestion starts in the stomach
4.
Small Intestine a.
Chyme ( partially digested food) enters the small intestine b.
Secretes intestinal juice; contains enzymes to digest carbohydrates, fat and protein
Accessory Organs - secrete fluids into small intestine a.
Liverlarge organ above the stomach that produces bile b.
Bile - fluid secretion of liver- enzyme prepares fats and oils for digestion by physically breaking them down into small pieces ( emulsifier) c.
Gall bladder organ which stores bile which is produced by the liver d.
Pancreas - secretes several enzymes including intestinal protease, lipids and amalayze
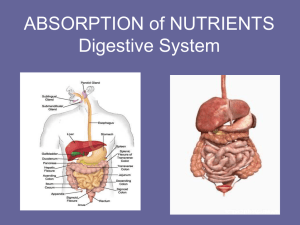
II Absorption
Food absorbed by small intestine
Villi- tiny fingerlike projections in small intestines
Includes surface area for food absorption o A) blood vessels absorb monosaccharaides ( sugar) amino acids, vitamins, minerals o Transported cells or the liver for storage as glycogen o B) lymph vessels ( lacteals)
Absorb fatty acid and glycerol
Transported to blood--
cell
1.
Large Intestine:
Absorbs H2O
Bacteria produce vitamins B&K
Eliminates feces through anus ( egestion)
Fiber: indigestible plant material ( cellulose)
Cleans out intestines
Helps prevent colon cancer ( large intestine)
III Digestive Disorders
1) Diarrhea not enough H2O absorbed by the large intestine
2) Constipation too much water absorbed by the large intestine
3) Ulcer excess gastric acid creates scars in digestive system. Some are due to bacterial infections, some are caused by acid fluids, stress, caffeine, drugs, smoking
4) Appendicitis appendix is infected and inflamed
5) Gallstones cholesterol deposits ( stored) in gall bladder
6) Anorexia nervosa psychological disorder in which a person is unable to eat or retain food