innovative lesson plan
advertisement

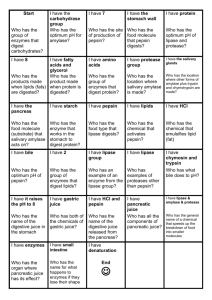
INNOVATIVE LESSON PLAN NAME OF THE TEACHER : SOUMYA. Y STANDARD : IX NAME OF THE SCHOOL : G.H.S.S. SOORANAD DIVISION : D NAME OF THE SUBJECT : BIOLOGY STRENGTH: 30/32 NAME OF THE UNIT : CHEMICAL CHANGES OF FOOD DURATION: 45 Min. NAME OF THE TOPIC : DIGESTIVE GLANDS DATE : 11.08.2014 AVERAGE AGE : 14+ AREA OF ISSUE : Lack of knowledge on health and public health PEDAGOGIC ISSUE : Lack of knowledge on digestive glands CURRICULAR STATEMENT : Creating knowledge on students about digestive glands through group discussion CONTENT ANALYSIS TERMS Salivary gland, intestinal gland, gastric gland, liver, pancreas etc. FACTS Salivary glands are situated in buccal cavity. Salivary gland secretes saliva. Saliva contains salivary amylase. Salivary amylase converts starch to maltose. Gastric glands are situated in the stomach. Gastric glands secrete gastric juice. It contains lipase and pepsin. Lipase converts lipids into fatty acids. Pepsin converts protein into poly peptides. Liver is the largest gland. Liver secrete bile. Bile emulsifies fat. Pancreas secrete pancreatic juice. Pancreatic juice contain trypsin, amylase and lipase. Trypsin acts on protein. Amylase acts on starch. Lipase acts on lipids. Intestinal glands are situated in small intestine. It secretes intestinal juice. It is a mixture of maltase, sucrase and peptidase. Maltase converts maltose into glucose. Sucrase converts sucrose into glucose and fructose. Peptidase converts peptides into amino acids. CONCEPTS MINOR CONCEPTS Salivary gland is situated in the buccal cavity, secretes saliva containing salivary amylase which converts glucose into maltose. Gastric glands are present in the stomach which secrete gastric juice, a combination of enzymes viz. lipase and pepsin. Liver secrete bile which emulsifies fat. Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which is a combination of trypsine, amylase and lipase. Intestine glands are situated in small intestine which secrete intestinal juice which is a combination of peptidase and disacharidase. MAJOR CONCEPTS Salivary gland, gastric gland, pancreas, liver and intestinal glands are the digestive glands of human digestive system which secrete digestive juices containing digestive enzymes which aids chemical process of digestion. CURRICULAR OBJECTIVES CONCEPTUAL DOMAIN: To develop remembering and understanding of the above mentioned terms such as Salivary gland, gastric gland, pancreas, liver and intestinal glands and facts and the concept of digestive glands. PROCESS DOMAIN: To develop process skills like observing, classifying, predicting, inferring etc through group activities related to the topic. CREATIVITY DOMAIN: To develop components of creativity like visualising, divergent thinking etc in pupils. ATTITUDINAL DOMAIN: To develop right attitude towards digestive glands and their importance. APPLICATIONAL DOMAIN: To develop application of the acquired knowledge, skill etc in a new or unfamiliar situation like health problems. METHODS AND TECHNIQUES USED Lecture method, group activity method. LEARNING AIDS USED Black board. EVALUATION TECHNIQUES USED Review. Continuous evaluation by asking questions. ENTRY BEHAVIOUR Pupils know that in humans digestion takesplace in digestive systems. PROCESS COMPETENCIES Observation skill, communication skill etc are developed in pupils. REFERENCES Biology text book class – IX, SCERT Teacher’s hand book. CLASS ROOM INTERACTION PROCEDURE ITRODUCING ACTIVITY: ANTICIPATED RESPONSE Students answer the questions. ACTIVITY No-1 Teacher creates a rapport in the class. Then writes the topic digestive glands on the black board. Check previous knowledge of the students by asking questions related to digestion, digestive system etc. ACTIVITY No- 2 Pupil says salivary gland. Teacher says a puzzle as Pupil actively participates in group “I am a gland. I reside in mouth. My discussion. secretion is saliva. Can you identify me”. Identify the gland and conduct group discussion using hints. HINTS Salivary amylases Carbo hydrates -> Maltose CONSOLIDATION Salivary gland is seen in buccal cavity. It secretes salivary amylase. Salivary amylase acts on carbo hydrates and converts it into maltose. ACTIVITY No- 3 Gastric gland. “My secretion is a combination of lipase and Acts on fats and protein. pepsin. My home is J shaped. Can you tell who am I?” Identify the gland and with the help of hints discuss on its site of action? HINTS Lipase : Lipids -> Fatty acids Pepsin: Protein -> Peptides CONSOLIDATION Gastric glands are situated in stomach. They secrete gastric juice which is a combination of lipase and pepsin. Lipase converts lipids into fatty acids. Pepsin converts protein into peptides. ACTIVITY No – 4 Liver “I am the largest gland. My cells have Secretion is bile which digest fat. regenerating capacity. I do the function of storage and detoxification in addition to digestion. Can you tell who am I?” Identify the gland and discuss using hints? HINTS: Bile Emulsification of fat. CONSOLIDATION Liver secretes bile which help in the emulsification of fat. ACTIVITY No- 5 Pancreas “I am pear shaped gland. My secretion is a Students participate in group discussions. combination of amylase, trypsin and lipase. Any abnormalities in my function leads to diabetes. Can you tell who am I?” Identify the gland and conduct group discussion based on hints. HINTS: Pancreatic juice. Trypsin: Protein -> Peptides. Amylase : Maltose -> Glucose and fructose. Lipase : Lipids -> Fatty acids and glycerol. CONSOLIDATION Pancreas secretes pancreatic juice which is a combination of pancreatic trypsin, pancreatic amylase and pancreatic lipase. Trypsin converts protein into peptides. Amylase converts maltose into glucose and fructose. Lipase acts on lipids and converts it into fatty acids and glycerol. ACTIVITY No- 6 Intestinal glands. “I am situated in small intestine. I secretes Group discussions have to be conducted by HCl and digestive enzymes. Can you tell who students. am I?” Conduct group discussion on my secretion based on hints. HINTS Maltase : Maltose -> Glucose. Peptidase : Peptides -> Amino acids. Disaccharidase : Disaccharides -> Mono saccharides. CONSOLIDATION Intestinal glands are situated in the small intestine secrete intestinal juice which is a combination of HCl and digestive enzymes peptidase and disaccharidase. Digestion gets completed in small intestine. BLACK BOARD SUMMARY 11.08.2014 Std: IX D Str: 30/32 BIOLOGY Digestive glands Salivary gland -> Saliva -> Salivary amylase. Gastric glands -> Gastric juice -> Lipase, pepsin. Liver -> Bile. Pancreas -> Pancreatic juice -> Lipase, trypsine, amylase. Intestinal glands -> Intestinal juice -> Peptidase, disaccharidase. REVIEW 1. Which is the largest gland? What is its secretion called? 2. Name the digestive gland? 3. Which are enzymes present in pancreatic juice? 4. What happens to carbohydrate in the mouth? 5. Which are the enzyme present in intestinal juice? FOLLOW UP ACTIVITY Draw a flow chart depicting the stepwise action of digestive enzymes as that of digestive systems. ENRICHMENT PROGRAM Pancreas is a heterochrine gland. Collect information on the statement and note down in your science diary.