Progressive Mathematics Initiative www.njctl.org Mathematics
advertisement

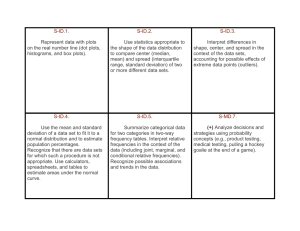
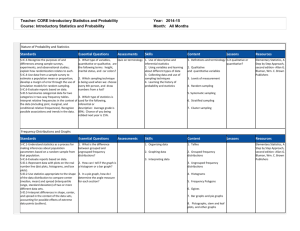
Progressive Mathematics Initiative www.njctl.org Mathematics Curriculum Unit Plan # 14 Title: Probability Subject: Algebra 1 Length of Time: 2 weeks Unit Summary: The unit looks to build on the probability learned in previous courses. The unit covers the difference between theoretical and experimental probabilities and independent and dependent events. Probabilities of mutually exclusive, overlapping, and complementary events will be calculated Learning Targets Conceptual Category: Statistics Domain: Interpreting Categorical and Quantitative Data Cluster: Summarize, represent, and interpret data on a single count or measurement variable Standard#: S-ID.2 Standard: Use statistics appropriate to the shape of the data distribution to compare center (median, mean) and spread (interquartile range, standard deviation) of two or more different data sets. Conceptual Category: Statistics Domain: Making Inferences and Justifying Conclusions Cluster: Understand and evaluate random processes underlying statistical experiments Standard#: S-IC.1 Standard: Understand statistics as a process for making inferences about population parameters based on a random sample from that population. Decide if a specified model is consistent with results from a given data-generating process, e.g., using simulation. S-IC.2 Cluster: Make inferences and justify conclusions from sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies Standard#: Standard: Recognize the purposes of and differences among sample surveys, experiments, and observational studies; S-IC.3 S-IC.5 S-IC.6 explain how randomization relates to each. Use data from a randomized experiment to compare two treatments; use simulations to decide if differences between parameters are significant. Evaluate reports based on data. Conceptual Category: Statistics Domain: Conditional Probability and the Rules of Probability Cluster: Understand independence and conditional probability and use them to interpret data Standard#: S-CP.1 S-CP.2 S-CP.4 Standard: Describe events as subsets of a sample space (the set of outcomes) using characteristics (or categories) of the outcomes, or as unions, intersections, or complements of other events (“or,” “and,” “not”). Understand that two events A and B are independent if the probability of A and B occurring together is the product of their probabilities, and use this characterization to determine if they are independent. Construct and interpret two-way frequency tables of data when two categories are associated with each object being classified. Use the two-way table as a sample space to decide if events are independent and to approximate conditional probabilities. Unit Essential Question: How can we predict the likelihood of an event occurring? Unit Enduring Understandings: Probability is the number of ways an event can happen divided by the total outcomes. Fundamental Counting Principle Permutations Combinations Mutually Exclusive events Complementary events Unit Objectives: Students will be able to describe the likelihood of an event occurring. Students will be able to apply the Fundamental Counting Principle to find combinations. Students will be able to recognize that a situation is a combination or permutation and calculate the ways in which can occur. Students will be able to calculate the probability of compound events. Students will be able to recognize mutually exclusive and overlapping events and calculate the probability of that event. Students will be able recognize complementary events. Evidence of Learning Formative Assessments: SMART Response questions used throughout the unit. 6 Quizzes Summative Assessment: Unit Test Lesson Plans Lessons Timeframe Lesson #1: Intro to Probability Lesson #2: Experimental & Theoretical Lesson #3: Word Problems Quiz 1 Experimental & Theoretical Lesson #4: Fundamental Counting Principle Quiz 2 Word Problems Lesson #5: Permutations and Combinations Quiz 3 Fundamental Counting Principle Lesson #6: Probability of Compound Events Quiz 4 Permutations and Combinations Lesson #7: Probability of Mutually Exclusive & Overlapping Events Lesson #8: Complementary Events Quiz 5 Probability of Compound Events, Mutually Exclusive, & Overlapping Events Lesson #9: Review and Unit Test Curriculum Resources: www.njctl.org/courses/math/algebra/ ½ 1⁄2 1 ½ 1½ 1 1 1