Marketing Indicator 5.06
advertisement

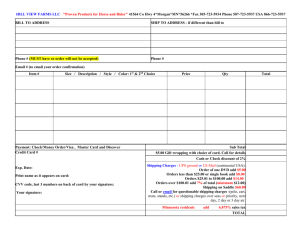
Marketing Indicator 2.11 Process the sale to complete the exchange. Types of charges and discounts associated with purchases. Credit card fee (percent of sales based on a sliding scale) Travel and entertainment cards are slightly higher than bank cards 1.79% (MC/Visa) vs. 3.25% (Am Ex) Debit card fee (flat fee no matter how much purchase is) Purchase Discount – set amount of money that a business saves on a specific order if the payment is made within a certain period of time. Ex: A purchaser brought a $100 item, with a purchase discount term 3/10, net 30. If he pays within 10 days, he will only need to pay $97. If not, the amount needs to be fully paid within 30 days. Bulk discounts – purchasing a large quantity and getting a discount on the price Tax Table Sales Tax and Example Your store ships products worldwide from one fulfillment center. You must collect a 15% sales tax on orders shipped to geographical zone A and a 7% sales tax on orders shipped to geographical zone B. You do not need to collect sales tax for orders shipped to other regions in the world. The following tables summarize the taxes that must be collected: Sales Tax Rates Geographical Zone Tax Rate A 15% B 7% Rest of World 0% Shipping/Delivery Table Shipping Charges and Example You must also charge shipping for orders shipped to geographical zone A and geographical zone B. For shipments to addresses in geographical zone A, shipping charges are $15, while shipping charges are $10 for shipments to addresses in geographical zone B. The rest of the world is subject to $25 shipping charges. Shipping Rates Geographical Zone Shipping Rate A $15 B $10 Rest of World $25 How do charges and discounts affect the price of purchases? Can increase the cost of items, overall, to cover credit card charges and frequent discounts Retailers want to make money, so they pass the charges/loss of revenue because of discount down to the customer How does technology speed up calculations of charges and discounts? Don’t have to figure “in your head” or by hand calculations of charges and/or discounts Cash register/POS (point of sale) terminal/Register does it for you, so you don’t have to make change Ex: $6.65 sale. You are given a $10 bill. How will you make change? Lessens the time taken to double check figures. What is the impact of incorrectly calculating charges/discounts? Drawer/register doesn’t balance Costs the retailer money May cost the retailer a customer Ex: Overcharging the customer Ex: Customer loses confidence in store, as the transaction wasn’t correct Takes time to redo the sale/void out the previous transaction Books/accounting don’t reconcile What is a special order? The request of an item not normally in stock or carried at a store How does accepting special orders affect retailers? Continue to meet customers’ needs and establish their loyalty Time consuming to find the item, place, track, and deliver order May lose money on an item if a price is quoted to a customer before the total cost (price, shipping, tax) is made aware to you--the retailer. What is the criteria for accepting special orders? Being able to locate the item and get it in a reasonable amount of time (ie by when the customer needs it) 20% or sometimes 50% deposit required Will the business make money on it? Or lose money on it? What paperwork is needed to process special orders? Ticket—outlining exactly what is ordered (color, size, model) Deposit money recorded on ticket Purchase order for vendor Sales receipt---paid in full Why obtain specific information when processing special orders? To insure retailer is ordering exactly what customer wants If wrong color or size is ordered, customer won’t be happy and may not do business with the retailer anymore. Vendor may not take incorrectly ordered item back. Costs money for the retailer to ship back/replace (if can) or to have at store and not sell. How can selling skills be used in relation to special orders? Ask customer open ended questions to determine their NEED If retailer doesn’t have what customer is searching for, offer them the SOLUTION—find what they want by special order If retailer is seen as a solution finder for customer’s needs, customer will be a repeat customer. Procedures for processing special orders. Ticket is created (special order form, layaway form, open order form, special order form, purchase order form) Deposit (normally 20% or 50%) is recorded on the ticket Order printed so retailer can process purchase with the correct vendor Setup inventory item with correct barcode information, after the product is added to the purchase order system. Item is flagged for open/special order Customer is called to let them know order is in Paid for, account marked paid, receipt given, item given to customer What is the nature of telephone orders in selling? Instant communication Customers calling on impulse Have sudden need and want need filled People buy where they feel comfortable Give them that feeling when they call Smile Must talk to the person as you do to someone in person Must be in control—ask the questions Must be polite and courteous—not pushy and aggressive Must have information to share with the potential customer The importance of speaking slowly and clearly when processing telephone orders. Fast talk loses listeners Customers don’t catch what was said Mistake fast talk for insecurity or dishonesty Customers want to understand what you are saying Customers want to be sure you understand what they are ordering You, want to be sure the order is processed completely and correctly, for the COMPANY’S benefit Why is accuracy necessary when processing telephone orders in selling? Inaccurate orders cost the company money The business wants the customer to get (and pay for) what they want/order Otherwise, they will be lost forever as a customer Procedures for processing telephone orders. Intro Find need Recommend product/Upselling Overcoming objections Closing sale by Customer name/customer number Phone number Address Catalog number, if they have one Items they wish to purchase Sales tax/shipping charges/total Payment method Arrival time (when they should expect the items) Thank for business