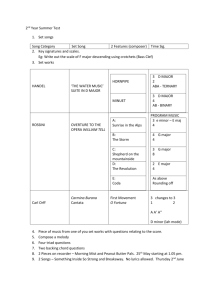
Carl orff - german composer and educator
advertisement

Born: July 10, 1895, in Munich. Died: March 29, 1982, in Munich. He was buried in the Baroque church of the beer-brewing Benedictine priory of Andechs, south of Munich "I'm a native Bavarian, born in Munich, and this city, this region, this landscape have given me so much, have shaped my very self and my work." Came from a Bavarian family that was very active in the German military. His father's regimental band supposedly had often played the compositions of young Orff. After studying at the Academy for the Musical Arts until 1914, he began his "apprenticeship with the old masters." He was especially fascinated by Monteverdi. He wrote new arrangements of Monteverdi's L'Orfeo, Lamento d'Arianna and Ballo delle Ingrate and also wrote songs for voice and piano. He served in the military during World War I. He got buried alive on the eastern front. Afterwards, he held various positions at opera houses in Mannheim and Darmstadt, later to return to Munich to further pursue his music studies. As of 1925, and for the rest of his life, Orff was the head of a department and co-founder of the Guenther School for gymnastics, music, and dance in Munich, where he worked with musical beginners. Having constant contact with children, this is where he developed his theories in music education. Orff's ideas were developed into a very innovative approach to music education for children, known as the Orff Schulwerk. The term Schulwerk is German for "school work". The music is elemental and combines movement, singing, playing and improvisation. "The goddess Fortuna must have been smiling on me when, as if by chance, she put a copy of a catalogue in my hands. It had been published by an antiquarian book dealer in Würzburg, and one title in the list attracted me as if by magic: Carmina Burana.“ The medieval poems, written in an early form of German and Latin, are often racy, but without descending into smut: “My virginity makes me frisky, my simplicity holds me back.” Orff excerpted a selection of songs of love, hedonism and drinking from the manuscript and turned them into a scenic cantata that would eventually become the most successful work in contemporary musical theater. Carmina Burana was first performed in 1937 in Frankfort. O Fortune, like the moon you are constantly changing, ever waxing and waning; hateful life now oppresses and then soothes as fancy takes it; poverty and power it melts them like ice. http://www.youtube. com/watch?v=EEHO1 iSjnSc Fate - monstrous and empty, you whirling wheel, you are malevolent, well-being is vain and always fades to nothing, shadowed and veiled you plague me too; now through the game I bring my bare back to your villainy. Fate, in health and virtue, is against me driven on and weighted down, always enslaved. So at this hour without delay pluck the vibrating strings; since Fate strikes down the strong man, everyone weep with me! Carmina Burana is one of the most popular pieces of music ever written. It's lusty lyrics, drinking songs, sinner's confessions and hymns in praise of gambling and gluttony excite singers and audiences alike and there is, around the world, at least one performance of this choral masterpiece every day. It's known to many as the background music to TV programs and commercials. After its premiere in 1937, Orff told his publisher: "Now you can take everything that I've written thus far and that you've already printed unfortunately and dump it." Carmina Burana was hugely popular in Nazi Germany after its premiere in Frankfurt in 1937. He was one of the few German composers under the Nazi regime who responded to the official call to write new music for A Midsummer Night's Dream after the music of Felix Mendelssohn had been banned — others refused to cooperate in this. But Orff had already composed music for this play as early as 1917 and 1927, long before this was a favor for the Nazi government. Orff was a personal friend of Kurt Huber, one of the founders of the resistance movement Die Weiße Rose (the White Rose), who was condemned to death by the Nazis and executed in 1943. After World War II, Orff claimed that he was a member of the group, and was himself involved in the resistance, but there was no evidence for this other than his own word, and other sources dispute his claim. Orff's assertion that he had been anti-Nazi during the war was accepted by the American de-nazification authorities, who changed his previous category of "gray unacceptable" to "gray acceptable", enabling him to continue to compose for public presentation. Founded the school with Dorothee Günther in 1924. At this school, which included gymnastics, rhythm, music and dance, Orff developed the Orff Schulwerk, a new model for teaching music and movement. The Günther-Schule initially had 17 students between the ages of 18 and 22. It began in 1924, and ran until 1944 when the Nazis confiscated it. In 1945, the building was destroyed in an Allied bomb attack, and all materials (instruments, costumes, photographs, library and archives) were destroyed. The Orff approach of music education uses very rudimentary forms of everyday activities in the purpose of music creation by young individuals. This includes singing in groups and performing voice instrumental music, rhymes and playing instruments such as the metallophone, xylophone, glockenspiel, and other percussive instruments. The music generated is largely improvisational and original tonal constructions and this builds a sense of confidence and interest in the process of creative thinking. It is not a "method". There is no systematic stepwise procedure to be followed. There are fundamental principles, clear models and basic processes that all intuitive and creative teachers use to guide their organization of musical ideas. ORFF SCHULWERK Music for Children (Carl Orff, Gunild Keetman) Volume 1: In pentatonic space Volume 2: Major: bordun patterns Volume 3: Major: dominants Volume 4: Minor: bordun patterns Volume 5: Minor: dominants Braille notation edition of volumes 1-5 24 schools throughout Europe Associations in 33 countries, including USA: NAME: American Orff-Schulwerk Association (AOSA) PRESIDENT: Judith Cole: jweloc@aol.com ADDRESS: Cindi Wobig (Executive Director), PO Box 391089, Cleveland, OH 44139 PHONE: 440-543-5366 FAX: 440-543-2687 eMail: info@aosa.org INTERNET: www.aosa.org MAGAZINE: The Orff Echo Founded the Günther-Schule and created Orff Schulwerk educational approach. Composed a fair number of works, including Carmina Burana which was an instant hit. Was married four times; had one daughter World-wide associations and scholarships founded in his name promote the “artistic estate of Carl Orff and protect and disseminate his intellectual heritage.” On his grave stone: The Latin inscription "Summus Finis" ("The ultimate goal"). http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EEHO1iSjnSc http://www.orff.de/ http://www.mvdaily.com/news/item.cgi?id=302065 http://www.classical.net/music/comp.lst/works/orff- cb/carbur3.php http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carl_orff