GDP: What is it?
advertisement

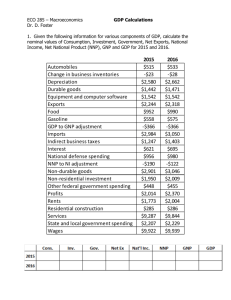
What is it? Why do we use it? Who cares? Economic growth • GDP is one of the important measures of economic growth • GDP, or gross domestic product, is the increase in the total output of an economy – “the total market value, expressed in dollars, of all final goods and services produced in an economy in a given year.” – Calculated by multiplying P x Q for ALL final goods/services produced within the borders of a country in a year The two types of GDP • Nominal GDP – GDP calculated by using the current year’s price for goods and services (also called “current-dollar GDP”) • Real GDP – GDP calculated by using a base year’s price for goods/services, so that only quantity changes over time (“constant-dollar GDP”) – Adjusted for price changes over time (inflation, deflation) – Used to compare growth of output of a country or countries over time Nominal v Real GDP, ex. 1 • Suppose in the year 2000, the economy of a country produced $100 billion worth of goods and services based on year 2000 prices. Since we're using 2000 as a basis year, the nominal and real GDP are the same. – Year 2000 Nominal GDP = $100B, Real GDP = $100B • In the year 2001, the economy produced $110B worth of goods and services based on year 2001 prices. Those same goods and services are instead valued at $105B if year 2000 prices are used. Then: – Year 2001 Nominal GDP = $110B, Real GDP = $105B Nominal GDP Growth Rate = 10% Real GDP Growth Rate = 5% Nominal v Real GDP, ex. 2 • Jim’s height is 1.95 meters • Renaldo’s height is 6 feet • Which student is taller? • If you wanted to compare their height, what would you have to do? – Convert each to a common measurement • What do you need to know in order to do this? – 1 foot= 0.30 meters • With this information, which student is taller? – 1.95/0.30= 6.5 feet tall (Jim is taller) So what? • To compare GDP over time, GDP has to be adjusted for price level changes (just like the height comparison). – (video) • Since GDP is a P x Q calculation, g/s have to be measured in constant dollars in order to calculate the real GDP. • Let’s get started by taking a look at handout 1.3 Check it: • • • • What is economic growth? What is GDP? What is GDP per capita? What is the standard of living? What is the difference in nominal and real GDP? • Which should be used to compare GDP over a series of years? Why?