Poetry Explication
advertisement

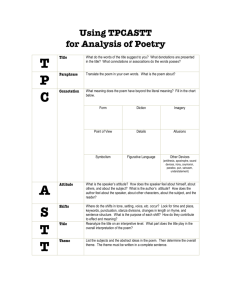
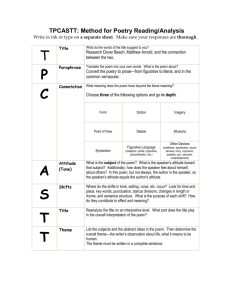
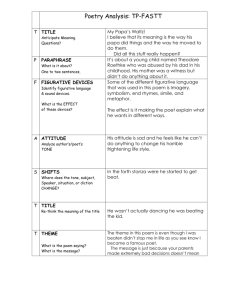
Poetry Explication The Art of Examining and Analyzing Poetry TP-CATT Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme STEP 1: Begin by Examining the Title • What images come to mind? • Examples: – “The Chimney Sweepers” by William Blake What other ideas, words, associations do you make with this image? – “I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud” by William Wordsworth *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) Examining the Title (cont’d) • What emotions come to mind? • Examples: “Never Try to Trick Me with a Kiss” by Sylvia Plath “O Captain! My Captain!” by Walt Whitman “In the Moonlight” by Thomas Hardy “When You are Old” by William Butler Yeats “The Promise of the Morning Star” by Amy Powell *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) STEP 2: Read the Poem and PARAPHRASE MORE THAN ONCE!!!! *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) Step 2: When you paraphrase ask yourself… • • • • • Who? What? Where? When? Why? • Who is the speaker? • Who does the speaker address? • What conflicts or themes does the poem present, address, or question? • What happens in the poem? Is there a “plot”? • Where is the speaker? Physical location? Setting? • When does the action occur? • Why does the speaker feel compelled to speak? *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) Who is the Speaker/Persona? • Who is doing the talking? – The speaker is the character or persona created by the poet – Describe the speaker • TITLE: “Mother to Son” • POET: Langston Hughes Step 3: Analyze your connotation with the poet’s word choice • WORD CHOICE IS EVERYTHING!!!!!! • The words the poet selects and the way they are phrased can alter the meaning of the poem • Connotation- the association we make with words -Let’s give it a try… -Again? *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) Look for the Literary Devices • Stanzas-two or more lines of poetry that together form one of the divisions of a poem – usually of the same length and follow the same pattern of meter and rhyme – almost like the poem is broken up into “paragraphs” • Rhyme Scheme -pattern of rhyme throughout the poem – Blank Verse- poetry written in iambic pentameter (10 syllabus per line) with NO RHYME – Free Verse- poetry composed of either RHYMED or UNRHYMED lines that have no set meter (pattern of syllabus) • Alliteration-repetition at the beginning -Peter Piper picked a pack of pickled peppers • Repetition- sometime the poet will repeat a specific word or phrase to emphasize an idea, feeling, or perhaps to create rhythm in the poem (beat) • Assonance-repetition of vowels -Fleet feet sweep by sleeping Greeks • Consonance-repetition of consonants sounds within the word -Rap rejects my tape deck, ejects projectile Find the Figurative Language • Metaphor- comparison of two unrelated things • Simile- same as metaphor except you use “like” or “as” and the comparison is more obvious • Personification- inanimate objects given human characteristics • Symbolism- an object comes to represent something else entirely (sometimes it’s very obvious and other times it’s left to the reader to interpret the symbolism) • Allusions- references to other works or events outside the poem (can be referring to something in history or another author/poet) • Hyperbole- an exaggeration is made for emphasis – example: “I’ve told you a million times to clean your room”) • Onomatopoeia- words are used to imitate sounds – Examples: buzz, boom, bang • Imagery- when a word or phrase that appeals directly to the reader’s senses • Step 4: Examine Speaker’s Attitude • After exploring the word choice, literary devices, and figurative language evaluate what the speaker’s attitude or tone is towards the subject of the poem • Include critical adjectives when pinpointing the attitude or tone in the poem *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) Step 5: Examine the Title (again) • Try to examine the title again on a more interpretive level • What new insight does the title provide in understanding the poem? *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) Step 6: Evaluate the Theme • What does the poem say about the human experience or human nature? • How does it relate to life? • What subject or subjects does the poem address? What do you learn about them? • What message or idea does the poet want to leave the reader with? *Title, Paraphrase, Connotation, Attitude, Title (again), Theme (TP-CATT) Step 7: Research the Poet • Research the background of the poet to see what influences or events may have inspired the poet to create a poem on the given subject Well, son, I'll tell you: Life for me ain't been no crystal stair. It's had tacks in it, And splinters, And boards torn up, And places with no carpet on the floor -Bare. But all the time I'se been a-climbin' on, And reachin' landin's, And turnin' corners, And sometimes goin' in the dark Where there ain't been no light. So boy, don't you turn back. Don't you set down on the steps 'Cause you finds it's kinder hard. Don't you fall now -For I'se still goin', honey, I'se still climbin', And life for me ain't been no crystal stair. Example 1: There once was a big brown cat a That liked to eat a lot of mice. b He got all round and fat a Because they tasted so nice.b Example 2: Whose woods these are I think I know. a His house is in the village though; a He will not see me stopping here b To watch his woods fill up with snow. a My little horse must think it queer b To stop without a farmhouse near b Between the woods and frozen lake c The darkest evening of the year. b Say the first thing that pops in your head when you hear the word… • • • • • • • • • • lemonade school wheelbarrow melancholy lifesaver money crabs brilliance prom paradise • • • • • • • • • • • • • • bug fireworks embarrassment mine creep hope umbrella garlic ring sunset blue shoelace demand glass Examples of Metaphors… “Sea of Troubles” “Time is a Thief” “Life is a Roller Coaster” I like to chat all the time I am very helpful in an emergency I often play games with my owner I sometimes interrupt when my owner is busy I can drop a beat in the middle of the street I feel important because I go everywhere my owner goes… What am I? A CELL PHONE! Imagery Example Write down the four senses the poem appeals to… “Stainless blue sky, jubilant voices of children crisp bite of a swollen apple, the afternoon sun hugs our shoulders…” We were both young when I first saw you. I close my eyes, and the flashback starts, I'm standing there... That you were Romeo, You were throwing pebbles, And my daddy said, "Stay away from Juliet." And I was crying on the staircase, Begging you, "Please don't go". And I said, "Romeo, take me somewhere we can be alone. I'll be waiting, all that's left to do is run. You be the prince, and I'll be the princess, It's a love story, baby, just say, 'yes'." Allusion Example 'Cause you were Romeo, I was a scarlet letter, And my daddy said, "Stay away from Juliet." But you were everything to me, Begging you, "Please don't go". And I said, "Romeo, take me somewhere we can be alone. I'll be waiting, all that's left to do is run. You be the prince, and I'll be the princess, It's a love story, baby, just say, 'yes'." "Romeo, save me, they're trying to tell me how to feel.