Cranial Nerve Anatomy

SCRUBS – Cranial Nerves
Chun Kit Poh
08 February 2010
• Cranial nerves I – XII
• Pupillary light reflex
• Accommodation reflex
• Visual field defects
• Trigeminal Neuralgia
• Corneal reflex
• Pseudo / bulbar palsy
Objectives
• Parasympathetic
• Cranial Nerve nuclei
• Examples
• (not covering CN clinical examination)
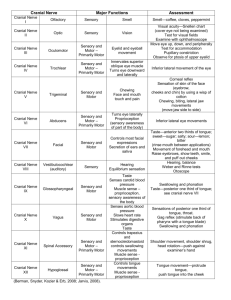
Cranial Nerves
CN I
CN II
Olfactory
Optic
CN III
CN IV
CN V
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
CN VI
CN VII
CN VIII Vestibulocochlear
CN IX Glossopharyngeal
CN X
CN XI
CN XII
Abducens
Facial
Vagus
Accessory
Hypoglossal
Sensory
Sensory
Motor
Parasympathetic
Motor
Sensory
Motor
Motor
Sensory
Motor
Parasympathetic
Sensory
Sensory
Motor
Parasympathetic
Sensory
Motor
Parasympathetic
Motor
Motor
Cranial Nerves
Cranial Nerve I (Olfactory)
CN I
• Attached to the forebrain – telencephalon (cerebral hemispheres), under the surface of the frontal lobe
• Axons from olfactory receptors in the nasal cavity enter cranial cavity through foramina of cribriform plate (of the ethmoid bone)
• Does not project via the thalamus
• Conveys olfactory information (smell)
• Damage :
• Anosmia follows damage of CN I (e.g. fracture of cribriform plate)
loss of sense of smell and also flavour of foods, but sense of taste (sweet, salt, bitter and sour) is preserved
• Can be due to head trauma or when meningiomas invade CN I
Cranial Nerve II (Optic)
CN II
• Attached to the forebrain – an outgrowth of diencephalon (thalamic structures surrounding the 3 rd ventricle)
• Axons from nasal retinal field decussate at optic chiasma and pass into contralateral optic tract
• Axons from temporal retinal field remain ipsilateral
• Mainly terminate in lateral geniculate nucleus of thalamus (some to pretectal area)
• Conveys visual information
• Damage :
• Blindness on affected side
• Relative afferent pupillary defect / Marcus Gunn pupil to subtle optic nerve defect
(observed during the Swinging Light Test)
• Pupils constrict less (hence appear to dilate) when light swings from unaffected side to affected side
Cranial Nerves II, III
Pupillary light reflex
• Tests CN II and III, midbrain function
• Direct light reflex – constriction of illuminated eye
• Consensual light reflex – constriction of non-illuminated eye
• Pathway:
Retina
Optic Nerve (CN II)
Optic chiasma
Optic tract
Some optic tract fibres (CN II) branch to
Pretectal area
Bilateral projection to Edinger-Westphal nuclei
CN III
Ciliary ganglion
Short ciliary nerve
Sphincter pupillae
Accommodation reflex
• Focussing on a near object causes pupil to constrict
• Pathway:
Retina
Optic Nerve (CN II)
Optic chiasma
Optic tract
Lateral geniculate body
Optic radiation
Visual Cortex
Association fibres
Frontal lobes
Descend via anterior limb of internal capsule
Superior colliculus
Edinger-Westphal nuclei
CN III
Ciliary ganglion
Muscles of iris and ciliary body
Visual field defects
Meyer’s loop
Where would the lesion be to produce these?
1
2
3
4
5
6
Cranial Nerves III (Oculomotor), IV (Trochlear) and VI (Abducens)
CN III
CN IV
CN VI
• Motor innervation to superior , medial and inferior rectus muscles
• Motor innervation to levator palpebrae superioris muscle
• Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons (via ciliary ganglion) to sphincter pupillae ( pupil constriction ) and ciliary muscles ( accommodation )
• Damage :
• Eye is “down and out”
• Drooping eyelid (ptosis)
• Dilatation of pupil, unresponsive to light and accommodation
• The only cranial nerve to emerge from dorsal aspect of brain stem (axons cross midline)
• Purely somatic motor innervation to superior oblique muscle
(depression, abduction and intorsion of the eye )
• Damage :
• Eye unable to look down when adducted (primary action of inferior rectus cancelled out in this position) – most notable when trying to walk down stairs!
• Causes contralateral symptoms if the trochlear nucleus in the brainstem on one side is damaged
• Purely somatic motor innervation to lateral rectus muscle
(abduction of the eye)
• Longest intracranial course for any CN – often first to be affected by fractures of base of skull / intracranial disease. Most important
CN to test!
• Abducens nucleus lies beneath floor of 4 th ventricle
• Damage :
• Eye unable to abduct (convergent squint)
• Close to Internal Carotid Artery in the cavernous sinus –
ICA aneurysm, cavernous sinus thrombosis , Tolosa-Hunt syndrome (inflammation of cavernous sinus)
Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal)
Motor innervation
CN V
• Motor innervation to
muscles of mastication
• Motor innervation to
tensor levi palatini, tensor tympani
and
digastric (anterior belly)
Sensory innervation
Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal) – sensory innervation
CN Va
CN Vb
• Forehead, eye brow, upper eyelid
• Cornea
• Upper palpebral conjunctiva
• Bulbar conjunctiva
• Nose – naris, nasal vestibule and tip
(
external nasal nerve
)
• Paranasal sinuses (except maxillary sinus)
• Lower palpebral conjunctiva
• Lower eyelid
• Mucosa in posteroinferior part of nasal cavity
• Oral mucosa posterior to incisor teeth (
nasopalatine nerve
)
• Soft palate
• Maxillary sinus
• Maxillary teeth
• Upper lip
CN Va
CN Vc • Lower lip
• Chin
• Temple
• Mandibular teeth (
inferior alveolar nerve
)
• Middle to deep part of External Acoustic Meatus (EAM)
• General sensation of anterior 2/3 of tongue
CN Vb
Cranial Nerve V (Trigeminal) – dural innervation
Meningeal branches of CN V innervates the dura mater.
CN Va
• Falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli
CN Vb
• Middle cranial fossa medially
CN Vc • Middle cranial fossa laterally
Falx cerebri - CN Va
Tentorium cerebelli - CN Va
CN Vc
CN Vb
CN Va
Trigeminal neuralgia
•
•
Common in CN Vb, less common in CN Vc, but not in CN Va
•
Management
Drugs – Carbamazepine , Lamotrigine , Phenytoin , Gabapentine , Amitriptyline
Stereotactic gamma knife
Ablative procedures ( Rhizolysis ) to destroy part of the trigeminal nerve to block the electrical activity that is causing the pain; side effect is permanent numbness to part of the face
•
•
Radiofrequency
Glycerol injection into the trigeminal cistern (subarachnoid space)
Cranial Nerve VII (Facial)
CN VII
• Sensory part ( nervus intermedius ) – smaller, more lateral roots, between CN VII and CN VIII
• Motor part – more medial roots
• From cerebellopontine angle - lateral part of pontomedullary junction
crosses posterior cranial fossa
leaves cranial cavity through internal acoustic meatus
(where motor and sensory part fuse to form CN VII)
enlarges to form geniculate ganglion
facial canal in petrous part of temporal bone
emerges through stylomastoid foramen
• Before stylomastoid foramen, branches into
• Greater petrosal nerve
• Chorda tympani
• Nerve to stapedius
• After stylomastoid foramen, enters the parotid gland (but does not supply it), branches into:
(think “TEN ZULUS BEAT MY CAT):
• Temporal
• Zygomatic
• Buccal
• Marginal mandibular
• Cervical
Cranial Nerve VII (Facial)
CN VII
• Motor innervation to muscles of facial expression
• Somatic sensory from skin around ear lobe and EAM
• Taste sensation from anterior 2/3 of tongue
• Intracranial course close to CN VIII
• Preganglionic parasympathetic neurons (via pterygopalatine ganglion) to lacrimal gland
( lacrimation ), and glands in mucosa of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses , and (via submandibular ganglion) to submandibular and submental glands ( salivation )
• Damage :
• Parotid gland removal, mumps, parotitis, tumour may damage CN VII
• Acoustic neuroma
paralysis of facial muscles, deafness, dizziness
• Damage to nerve to stapedius
hyperacusis
Cranial Nerve VII (Facial)
CN VII
• Facial motor nucleus supplying frontalis and orbicularis oculi receive bilateral innervation from the motor cortex
• Facial motor nucleus supplying the lower facial muscles receives contralateral innervation
• Damage :
• Therefore, a unilateral Upper Motor Neurone (UMN) lesion of CN VII causes contralateral paralysis of lower facial muscles (e.g. stroke)
• A Lower Motor Neurone (LMN) lesion, either in the pons or any part of the peripheral course
complete paralysis of facial muscles on one side ( Facial palsy )
• A facial palsy of unknown aetiology
Bell’s palsy
Corneal reflex
• Tests CN Va and VII
• Pathway:
Cornea
Nasociliary nerve (branch of CN Va)
Principal sensory nucleus of CN V
(brain stem interneurons)
Facial motor nucleus
CN VII
Orbicularis oculi muscle
• Both eyes should blink if either cornea is stimulated
Cranial Nerve VIII (Vestibulocochlear)
CN VIII
• Both divisions (dendrites which make contact with hair cells of vestibular or auditory apparatus of inner ear) pass through internal auditory meatus (together with CN VII)
• Attach to brain stem at cerebellopontine angle
• Sensory , carries information related to position and movement of the head (vestibular nerve) and auditory information (cochlear nerve)
• Damage :
• Dizziness
• Deafness (profound if Lower Motor Neuron (LMN) lesion –supply is bilateral higher up, at all levels rostral to cochlear nuclei at the medulla)
Acoustic neuroma
• Benign tumour of CN VIII (Schwann cells) leading to compression of the nerve and structures at the cerebellopontine angle:
• Dizziness
• Deafness
• Paralysis of CN V-VII
facial palsy and loss of cutaneous sensation on ipsilateral face
• (Ataxia)
Cranial Nerve IX (Glossopharyngeal)
CN IX
• From lateral aspect of olive and through jugular foramen
• Descends into the neck and passes between internal and external carotid arteries to enter the pharynx (pharyngeal plexus) to supply the mucosa of pharynx and posterior tongue
• General sensory afferents end in sensory nuclei of trigeminal nerve
• Carotid body / sinus and taste fibres terminate in nucleus solitarius
• Motor from nucleus ambiguus
• Principally a sensory nerve – general sensation from pharynx, middle ear, posterior 1/3 of tongue
• Taste sensation from posterior 1/3 of tongue
• Chemoreceptors in carotid body (oxygen, CO2, and pH) and baroreceptors in carotid sinus
• Motor innervation to stylopharyngeus
• Preganglionic parasympathetic (via otic ganglion) to parotid gland
• Damage :
• Loss of sensation of taste and general sensation from posterior 1/3 of tongue
• Loss of function of stylopharyngeus (elevation of pharynx/larynx in swallowing)
• Loss of ipsilateral gag reflex
Cranial Nerve X (Vagus)
CN X
• From rootlets lateral to olive in the medulla and through jugular foramen
• Motor from nucleus ambiguus
• General sensory afferents end in sensory nuclei of trigeminal nerve whilst visceral afferents in nucleus solitarius
• Auricular branch conveys sensory fibres from
• EAM
• Tympanic membrane
• Descends in carotid sheath – pharyngeal branches and superior laryngeal nerve
• Internal ( sensory above vocal chords)
• External (motor to cricothyroid)
• Recurrent laryngeal nerves – laryngeal muscles (not cricothyroid), sensory below vocal chords
• Left related to ligamentum arteriosum
• Right related to right subclavian artery
• Forms the oesophageal plexus ….
• Preganglionic parasympathetic from dorsal motor nucleus of vagus
Cranial Nerve X (Vagus)
CN X
• General sensation in the laryngopharynx, larynx, oesophagus, tympanic membrane, EAM, part of ear lobe
• Chemoreceptors in aortic bodies (oxygen, carbon dioxide – not pH) and baroreceptors in aortic arch
• Thoracic and abdominal visceral sensation
• Motor to soft palate, pharynx, larynx, upper part of oesophagus
• Preganglionic parasympathetic to cardiovascular, respiratory and GI systems
• Damage :
• Loss of ability to speak – voice changes, hoarseness
• Loss of gag reflex and other vagal reflexes such as coughing, vomiting and fainting from irritation of posterior wall of external auditory meatus
• Damage to recurrent laryngeal nerve (near inferior thyroid artery) nearly always affects abductors of vocal cords
difficulty in breathing
Cranial Nerve XI (Accessory)
CN XI
• Cranial part from lateral aspect of medulla as rootlets caudal to rootlets of vagus, joins vagus at jugular foramen to supply larynx and pharynx (hence “accessory”)
• Spinal part from motor neurons in ventral horn of spinal grey matter at C1-C5, emerge from between ventral and dorsal nerve roots and ascends through foramen magnum to enter posterior cranial fossa
• Briefly runs with cranial CN XI before emerging through jugular foramen , passes deep to SCM which it supplies
• Enters roof of posterior triangle of neck: from 1/3 down of posterior border of SCM to 1/3 up anterior border of trapezius
Cranial Nerve XI (Accessory)
CN XI
• Spinal part supplies motor innervation to sternocleidomastoid (SCM) and trapezius muscles
• Damage :
• Vulnerable in posterior triangle of the neck
paralysis of trapezius (but not SCM which it has already supplied), abduction of arms beyond 90 o (e.g. hair grooming) is impaired
• If injury is higher up (before posterior angle)
inability to tilt head on affected side, and to turn head away from affected side (remember: SCM pulls to turn head to the other side)
Cranial Nerve XII (Hypoglossal)
CN XII
• From hypoglossal nucleus (beneath floor of 4 th ventricle), emerge as a series of rootlets between the pyramid and the olive
• The hypoglossal nucleus receives afferents from nucleus solitarius and trigeminal sensory nucleus
– involved in control of reflex movements of chewing, sucking and swallowing
• Also receives corticobulbar fibres from contralateral motor cortex – voluntary movements of tongue
(e.g. speech)
• Purely motor to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue
• Damage :
• In a LMN lesion (e.g. damage to nerve in the neck), the tongue is pushed to the affected side
difficulty chewing, dysarthria
• Carotid artery surgery (e.g. endarterectomy), CN XII is near the origin of occipital artery from external carotid artery
Cranial Nerve XII (Hypoglossal)
CN XII
Lesions and motor neuron disease of CN IX-XII
• Due to:
• Motor neuron disease
• Multiple Sclerosis
• Vascular cause
• Bulbar palsy – ipsilateral LMN lesion:
• Degeneration of nucleus ambiguus and hypoglossal nucleus
• Dysphonia (difficulty in phonation)
• Dysphagia (difficulty in swallowing)
• Dysarthria (difficulty in articulation
• Weakness, wasting and fasciculation of the tongue
• Pseudobulbar palsy :
• Lesions to corticobulbar tracts projecting to nucleus ambiguus and hypoglossal nucleus
• Bilateral lesion is clinically significant
• Dysphonia, dysphagia, dysarthria
• Weakness and spasticity of the tongue
Parasympathetic supply
Cranial nerves
III
Cell in Edinger-
Westphal nucleus
( midbrain )
CN Va
Ciliary ganglion
Pupillary constriction (iris muscles), accommodation (ciliary muscles)
VII
CN VII with greater petrosal nerve
CN Vb
Lacrimal gland, glands in mucosa of nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses
Cell in superior salivatory nucleus
( pons )
CN VII with chorda tympani
Pterygopalatatine ganglion
CN Vc
Submandibular ganglion
Submandibular and sublingual glands
CN Vc
IX Parotid gland
Cell in inferior salivatory nucleus
( pons / medulla )
Otic ganglion
X
Cell in dorsal motor nucleus of vagus
( medulla )
Ganglia in wall of organ being innervated
↓ Heart rate
↑ gut activity
Constricts airways
Soft palate – motor innervation
• Tensor veli palatini
• Levator veli palatini
• Palatoglossus
• Palatopharyngeus
• Musculus uvulae
CN Vc
CN X
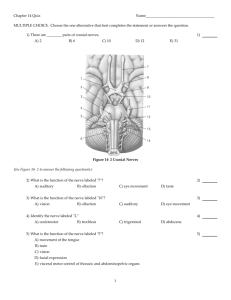
Cranial Nerve Nuclei locations
Example
1. Ramsay Hunt syndrome (type II), also called herpes zoster oticus, is a form of herpes zoster affecting the facial nerve, associated with muscle paralysis and loss of sensory modalities. Pain is experienced in the distribution of the nerve.
Describe the motor pathway of the facial nerve from the brainstem to its point of action. State and briefly explain the symptoms of the syndrome.
• From ventrolateral aspect between pons and the medulla (crosses posterior cranial fossa) , exits cranial cavity through internal acoustic, (through facial canal in petrous part of temporal bone, enlarges to form the geniculate ganglion), supplies stapedius (before going through stylomastoid foramen) and then innervates muscles of facial expression (after branching in the parotid gland into temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular and cervical) .
• Symptoms – paralysis of facial muscles unilaterally with failure to close the eye , absent corneal reflex (loss of efferent limb), hyperacusis on affected side (loss of stapedius), loss of taste sensation in anterior two-thirds of tongue, dry mouth and eyes, pain is experienced around the ear, vesicular rash in EAM and mucous membrane of oropharynx .
Example
2. Briefly describe the structures within the cavernous sinus, paying particular reference to the cranial nerves within and the surrounding structures. Cavernous sinus thrombosis may occur as a result of an infection of the any part of the head (e.g. face, ear) that drains into the cavernous sinus. Explain the clinical outcome of a cavernous sinus thrombosis.
• Draw!
• All cranial nerves passing through or in the walls affected
– CN III, CN IV, CN Va, CN Vb, CN VI.
• Abducens nerve usually affected first because it passes through the sinus – paralysis of lateral rectus resulting in medial squint.
• Involvement of ophthalmic and maxillary nerves causes severe pain in its distribution.
• Pupil may be dilated and sluggish.
• Condition may also result in visual loss (resulting from impaired venous drainage from orbit) and papilloedema.
Cranial Nerves
CN I
CN II
Olfactory
Optic
CN III
CN IV
CN V
Oculomotor
Trochlear
Trigeminal
CN VI
CN VII
CN VIII Vestibulocochlear
CN IX Glossopharyngeal
CN X
CN XI
CN XII
Abducens
Facial
Vagus
Accessory
Hypoglossal
Sensory
Sensory
Smell
Vision
Motor
Parasympathetic
Motor
Sensory
Motor
Motor
Medial, superior and inferior rectus, inferior oblique, levator palpebrae superioris
Superior oblique
Cranial dura mater; CN Va (ophthalmic), CN Vb (maxillary), CN Vc - face
CN Vc (mandibular) – muscles of mastication, tensor tympani, tensor levi palatini, digastric (anterior belly)
Lateral rectus
Sensory
Motor
Parasympathetic
Sensory
Taste (anterior tongue)
Muscles of facial expression, stapedius, stylohyoid, platysma, digastric
(posterior belly)
Hearing, balance
Sensory
Motor
Parasympathetic
Sensory
Motor
Parasympathetic
Motor
Motor
Posterior tongue, oropharynx, taste (posterior tongue), middle ear, carotid body and sinus
Stylopharyngeus
Larynx, hypopharynx, heart, lungs, (taste)
Muscles of larynx, pharynx (speech, swallowing)
Sternocleidomastoid, trapezius
Muscles of the tongue