Microscope
advertisement

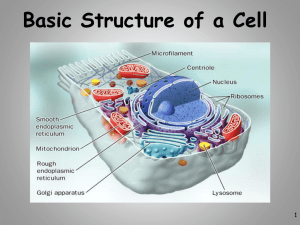
Prokaryotic Cell Key Terms 1. Cells 2. Microscope 3. Cell Theory Leaf under a microscope Microscope Infected red blood cells Frog Blood Human Blood An Overview of Cells Cell- Basic units of life. Cells and Structure •The structure of living things are determined by the amazing variety in which cells are put together. (LEGOS) Cells and Function •An organisms function are the process that enable it to stay alive and reproduce. Many and Small •One square centimeter of your skins surface contains more than 100,000 cells. Development of Cell Theory Cell Theory states the following: •All living things are composed of cells. •Cells are the basic units of structure and function in all living things. •All cells are produced from other cells. Cell Theory First Observation of Cells Vocabulary: Microscope-An instrument that makes small objects look larger. Blood under a microscope • The invention of the microscope made it possible for people to discover and learn about cells. Microscopes Robert Hooke Anton van Leeuwenhoek • Robert Hooke was an English scientist who was one of the first to observe cells. • In 1663, Hooke invented a microscope of his own, to observe the structure of a thin slice of cork. • Leeuwenhoek also began to observe tiny objects with microscopes at the same time as Robert Hooke. • Leeuwenhoek looked at drops of lake water, and scraping of teeth and gums, and water from rain gutters. 1663 microscope http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XgW1Hi V9SJs&feature=player_detailpage#t=3 Hooke’s drawings of cork cells. Plant cells under a microscope Tech and Design in History 1590 first compound microscope • Dutch eyeglass makers Zacharias and Hans Janssen made one of the first compound microscopes. First compound microscope 1981 scanning Tunneling Microscope • An STM measures electrons that leak, or “tunnel,” from the surface of a specimen. STM’s can magnify a specimen up to 1 million times. Scanning Tunneling Microscope Section 3 Assessment 1.a. Define function and structure. 1.b. Explain: Cells are the basic units of structure and function in organisms. 1.c. In what important function are the cells in your eyes involved? 2.a. What does a microscope enables people to do? 2.b. Summarize Hooke’s observation of cork under a microscope. 2.c. Why would Hooke’s discovery have been impossible without a microscope? 3.a. What are the main ideas of the cell theory? 3.b. What did Virchow contribute to the cell theory? 3.c. Use the ideas of Virchow to explain why plastic plants and stuffed animals are not alive. 4.a.What is magnification? 4.b.Contrast the way light microscopes and electron microscopes magnify objects.