Metric System Measurements
advertisement

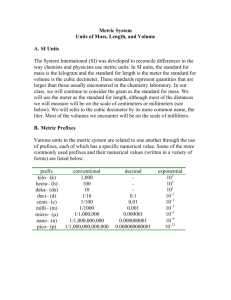
Metric System Length (L) Mass (M) Weight (W) Volume (V) Density Temperature (T) (D) 1cm 1cm Meter Stick Balance Spring Scale 1cm Graduated Cylinder Sand Mass/Volume Thermometer The Metric System ---The Universal Language of Measurement--- • Metric System – scientists & engineers use this language to communicate • The metric system is often referred to as the International System of Units (abbreviated “SI”) • The metric system is based on the number 10 and multiples of 10. Length The distance between two points • Meter – the basic unit of length in the metric system 1 meter = 1 m • Centimeter – one hundredth of a meter 1 cm = 1/100 m = 0.01 m 100 cm = 1 m • Millimeter – one thousandth of a meter 1 mm = 1/1000 m = 0.001 m = 1/10 cm = 0.1 cm 1000 mm = 1m • Kilometer – one thousand meters 1 km = 1000m 1 m = 1/1000 km • Light year –the distance light travels in one year Speed of light = 300,000 km/s Volume The amount of space an object takes up • Liter – is the basic unit of volume in the metric system 1 Liter = 1 L • Milliliter – is one thousandth of a Liter 1 mL = 1/1000 L = 0.001 L • Milliliters and Liters are used to measure the volume of • Cubic centimeters – is the metric unit used to measure the volume of • A cubic centimeter is equal to the volume of a cube that measures 1 cm by 1 cm by 1 cm (cm3). A volume of a cubic centimeter (cm3) is exactly equal to the volume of one milliliter. 1cm 1cm 1cm = 1 cm3 = 1 mL Mass a measure of the amount of matter in an object • Kilogram – the basic unit of mass in the metric system 1 kg = 1000 grams • Gram – one thousandth of a kilogram 1 g = 1/1000 kg = 0.001 kg 1000 g = 1 kg • Milligram – one thousandth of a gram 1 mg = 1/1000 g = 0.001 g 1000 mg = 1 g Weight a measure of the attraction between two objects due to gravity • Gravity - a force of attraction between two masses. • The strength of the gravitational force between two objects depends on the masses of the objects and the distance between them: a) The greater the mass, the greater the gravitational force. b) The greater the distance between the two objects, the weaker the gravitational force between them • Newton (N) - the basic unit of weight in the metric system. Mass vs. Weight • An object has a universal mass, but may have different weight depending on gravity. • The mass of an object does not change. • The weight of an object changes as a result of changes in gravity. • A pineapple on earth weighs more than on the moon because the earth’s gravity is greater. But the pineapple’s mass always remains the same wherever you go (unless you get hungry and eat it!). Density a measure of the amount of matter that occupies a unit certain volume • Density = mass/volume (units are usually g/mL) The density of water = 1.00 g/mL This means that one gram of water occupies one milliliter of volume. The density of oil = 0.91 g/mL If lighter fluids float on heavier fluids, do you expect water to float on oil? Sand grains If the human body is nearly 70% water, is it possible to float in quicksand? Should you get worried? Temperature a measure of how hot or cold something is • Celsius = a unit of temperature in the metric system • Water freezes at 0° C. • Water boils at 100° C. • Normal body temperature is 37° C • Room temperature is 21° C. Temperature (continued) • Kelvin = another unit of temperature in the metric system. • The lowest possible temperature is 0 Kelvin (-273 ° C). This is Absolute Zero. • To convert from Celsius to Kelvin: K = C + 273° Metric Prefixes Prefix Symbol Meaning kilo- k 1000 thousand hecto- h 200 hundred deka- da 10 ten deci- d 0.1 tenth centi- c 0.01 hundredth milli- m 0.001 thousandth