Chapter 13 and 14 review
advertisement

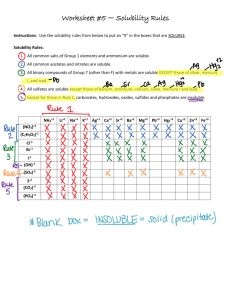
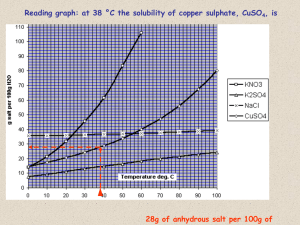
Chapter 13 and 14 review 1. Name_______________________________ Molecules whose aqueous solutions conduct electricity are called _______________________ 2. How is the solubility of a gas in a solution related to pressure? 3. The solubility of a solid solute is dependent on three things. List them: i. ii. iii. 4. Define the following terms which describe the amount of solute in a solution a. Unsaturated: b. Saturated c. Supersaturated 5. _____________________law relates _____________________ to gas-liquid solutions. 6. Define solvated (solvation): 7. . Determine whether each compound is soluble or insoluble (know your solubility rules) K2CO3 ________________________ NiPO4 ________________________ Li2S ________________________ NH4Br ________________________ CaSO4 ________________________ Mg(C2H3O2)2 ________________________ 8. Will the following pairs of solutions will form a precipitate when mixed together? (yes or no) a. Mg(NO3)2 and LiCl b. Ni(NO3)2 and Na2CO3 _______ ___________ c. Pb ( C2H3O2)2 and MgCl _______ d. NH4Cl and AgClO3 _______ 9. Write the chemical equation for each reaction in question 8 that formed a precipitate(there are three) 1. 2. 3. 10. Write the overall ionic equation for each chemical equation that you have written above 1. 2. 3. 11. Write the net ionic equation for each reaction above 1. 2. 3. 12. Identify the spectator ions for each reaction above 1. 2. 3. Use the solubility curve above to answer the following questions 13. Which of the substances on the solubility curve above is the most soluble at 40 C?_________ 14. Which is the least soluble at 90 C? ____________ 15. How many grams of potassium iodide can dissolve in 200 grams of water at 30 C?_________ 16. If 60 g of potassium nitrate dissolves in 100 g water at 30 C, then the solution is __________(super-, un- ,or saturated) 17. Describe what happens when a molecular substance ionizes in water: 18. What kinds of substances are electrolytes? 19. What kinds of substances are nonelectrolytes? 20. How do solutions of electrolytes affect colligative properties differently than those of electrolytes? 21. Define colligative properties 22. List the four colligative properties Problem Section: Constants: Kf water= -1.86 C/m olal Kb water= 0 .51 C/molal Kf Ether =-116.3C/molal K b ether 2.02 C/molal 1. What is the molarity of a solution composed of 12.210 g of MgSO4 , dissolved in enough water to make 0.750 L of solution? ________________________ 2. How many grams of ferrous nitrate (CuNO3) are needed to prepare 250.0 ml of a 0.750 M solution? ____________________________ 3. For the equation silver acetate + ammonium sulfide A)Write the balanced chemical equation B)write the overall ionic equation C) identify spectator ions D)Write the net ionic equation 4. The freezing point of an aqueous solution of cupric chlorate concentration of ferric chlorate. -5.65 C. Determine the molal 5.) Calculate the expected change in boiling point of a solution of 231.2 g of barium chloride in 200.0 g of water _____________________________