Political Parties
advertisement

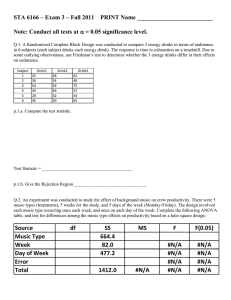
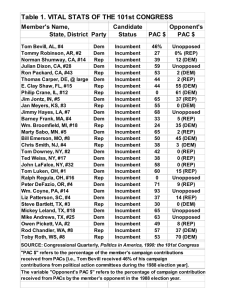
POLITICAL PARTIES I.) What is a Party? A.) Definition: 1.) 2.) B.) Not always like minded: II.) Where did Parties Come from? A.) Federalists vs. Anti-Federalists B.) Major Periods 1. Era of Democrats 2. Rise of Republicans 3. Return of Democrats 4. A Period of Reaction 5. Resurgence of Conservatives Party Eras: Modern Era 1968-Present Era of Divided Government: Dealignment • One party controls Congress and the other controls the White House = “Gridlock” • A divided government is typical of the past few decades. The usual pattern was republican President and Democratic Cong. • Ticket-Splitting Increased • Republicans dominate the Presidency until 1993 • Nixon (“Southern Strategy” and Reagan built a coalition of disenchanted white suburban middle class, Southern white Protestants and big business) • Party strength weakens – Candidate's issues and character take center stage – Republicans better candidates & more organized campaigns – Democrats → Roosevelt coalition fractures III.) What Do Parties Do? A.) Connecting Citizens to Their Government (linkage) – Necessity in representative politics WHY? – Increase efficacy → Help citizens make sense of and interact with government – Register Voters B.) Identify and publicize issues C.) electoral role D.) watchdog E.) finance political party activity F.) government by party 1.) shift IV.) Where Are They Strong? A.) Democrats B.) RepublicansC.) Battleground States D.) Swing States V.) Why Have They Weakened? A.) split ticket voting B.) technology C.) campaign finance laws D.) progressive innovations: referendum, inititiative, recall VI.)Why the Two Party System? A.) Historic tradition B.) Hasn’t failed C.) Biased rules: debates, campaign funding, getting on ballot single member districts VII.) Rise of Partisanship A.) Not new B. Effects of Partisanship B.) Why the increase of partisanship? C.) VIII.) Minor Parties A.) Minor Parties in the U.S. 1.) Ideological Parties 2.) Single-Issues Parties 3.) Economic Protest Parties 4.) Splinter Parties B.) The Key Role of Minor Parties 1.) Innovations 2.) Spoiler Role 3.) Critics and Reformers 4.) Adoption of issues by major parties Ross Perot Ralph Nader IX.) Case Study: Tea Party •Grass Roots movement started in ~2009 •Conservative/libertarian movement •Anti- stimulus, anti-healthcare, anti-bail-out • Very Decentralized • Ran as Republicans defeated established Republicans in primaries •2010 Mid-term Election effects: Rep. 239 (+60) vs. Dem. 189 •Contract For America Makeup of CongressHouse of Representatives: 246 Rep.; 188 Dem.; 1 Vacant Seat (Grimm- NY Rep) Senate: 54 Rep.; 44 Dem.; 2 Ind. Makeup of California’s Legislature Assembly: 52 Dem.; 28 Rep. Senate: 25 DEm.; 12 Rep/ 3 vacant