Ch 10- Cell Growth
advertisement

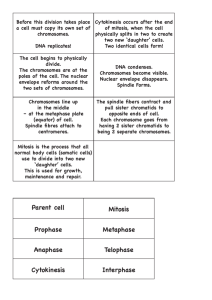
Ch 10- Cell Growth • What problems does growth cause for the cell? – Larger a cell becomes, the more demands that cell places on its DNA – The cell has more trouble moving enough nutrients and wasted across the cell membrane • Where is the information that tells cells what to do stored at? – DNA • Understanding the relationship between a cell’s volume and surface are is key to understanding why cells must divide as they grow Division of the Cell • If cell got to large, it would be more difficult to get sufficient amounts of oxygen and nutrients in and waste products out • Cell division- process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells – Copies DNA, each daughter cell gets one complete set of genetic information- solves the problem of information storage – Solves the problem of increasing size by reducing cell volume- each daughter cell has an increased ratio of surface area to volume Sec 2- Cell Division • Prokaryotes- process of cell division is simply separating the contents of the cell into two parts • Eukaryotes- process is more complex and occurs in 2 stages • Mitosis- division of cell nucleus – Asexual, cells produced are identical to parent cell – Source of new cells as multicellular organism grows and develops – Begins shortly after egg is fertilized • Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm Chromosomes • What are they? – Carries the genetic information passed from one generation to the next, made of DNA and proteins • How many chromosomes do human cells have? – 46 • • • • Fruit flies have 8 chromosomes Not visible except during cell division Before cell division, chromosomes are replicated Each chromosomes consist of 2 identical “sister” chromatids- when cell divides one chromatid goes to each of two new cells • Centromeres- area where chromatids are attached, usually located near middle Cell Cycle • During the cell cycle, a cell grows, prepares for division, and divides to form two daughter cells, each of which then begins the cycle again • Interphase- the in between time between cell division • Cell cycle- series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide • Cell cycle consists of 4 phases – Mitosis and cytokinesis take place during M phase – Chromosome replication takes place during S phase – G phases are periods of intense growth and activity Events of the Cell Cycle • Interphase- phase is quite long, made up of G₁, S, and G₂ phases • G₁ phase- where cells do most of their growing – Cells increase in size and synthesize new proteins and organelles • S phase- chromosomes are replicated and synthesis of DNA molecules takes place • G₂ phase- many of organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced • Cell is ready for the M phase and begin process of cell division Mitosis • Divided into 4 phases- prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase • May last anywhere from few minutes to several daysdepends on type of cell • Prophase- chromatin condenses into chromosomes, centrioles separate and a spindle begins to form, nuclear envelope breaks down – Centrioles- two tiny structures located in cytoplasm near nuclear envelope, separate and take position on opposite sides of nucleus – Spindle- fan-like microtubule structure that helps separate the chromosomes • Metaphase- chromosomes line up across the center of cell, each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere • Anaphase- sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are moved apart • Telophase- chromosomes gather at opposite ends of cell and lose their distinct shapes, two new nuclear envelopes will form • Mitosis is complete Cytokinesis • Result of mitosis= two nuclei each with duplicate set of chromosomes formed within cytoplasm of a single cell • Cytokinesis- division of cytoplasm, usually occurs at same time of telophase – Cytoplasm pinches in half, each daughter cell has an identical set of duplicate chromosomes • Mitosis and Cytokinesis Sec 3- Regulating the Cell Cycle • Cyclin- proteins that regulate the timing of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells • Discovered by Tim Hunt and Mark Kirschner • Many more proteins have been discovered since- 2 types of proteins- regulatory proteins in and outside of cell • Internal Regulators- allow cell cycle to proceed only when certain processes have happened inside cell – Make sure cell does not enter mitosis until all chromosomes have been replicated • External Regulators- direct cells to speed up or slow down cell cycle – Growth factors among most important external regulators Uncontrolled Cell Growth • Why is cell growth regulated so carefully? • Cancer- disorder in which some of body’s own cells lose the ability to control growth – Do not respond to the signals that regulate the growth of most cells – Divide uncontrollably and form masses of cells called tumors – May break free from tumor and spread to rest of body • What causes the loss of growth control that characterize cancer? – Smoking tobacco, radiation exposure, viral infection