APUSH Chp. 24 Industry Comes of Age
advertisement

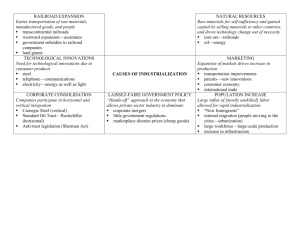
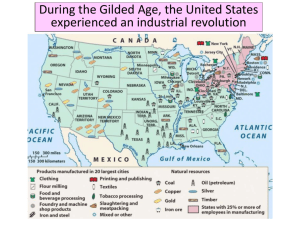
Industry Comes of Age Organizing Principle: The Gilded Age fostered the consolidation of business, the beginnings of government involvement in the economy, and the organization of disadvantage economic and social classes. APUSH Chapter 24 Causes of Rapid Industrialization 1. Steam Revolution of the 1830s-1850s. 2. The Railroad fueled the growing US economy: First big business in the US. A magnet for financial investment. The key to opening the West. Aided the development of other industries. HOW? Railroad Construction Why were times zones introduced? When did this occur? The Railroad Magnates Charles Crocker Collis Huntington Cornelius Vanderbilt “The Commodore” Mark Hopkins Leland Stanford What was the main goal of the US gov’t & the RR industry during this time? • Build a trans-continental railroad • What were the major RR companies of the day? Union Pacific - construction workers? Central Pacific - construction workers? • Which RR built more miles of track? Why? • Which RR company was involved in the Credit Mobilier scandal? “The wedding of the rails” Promontory Point, UT Where? When? (May 10, 1869) Railroad Innovation • Cornelius Vanderbilt – use of a steel rail rather than iron • Steel is safer & more economical • Pullman Palace Cars – travelling luxury hotels George Pullman “Wheeled torture chambers” & potential funeral pyres Jay Gould RR accidents become very common, yet little is done to regulate the industry. Why? Railroad Regulation • the Grange – group dedicated to helping farmers • Major RR are rife with corruption, use graft to accomplish goals • Wabash case (supreme court) • RR plutocracy seemed states had no power to to control everything regulate interstate commerce • Many late 19th century Americans are against • Implications of Wabash? gov’t intervention in • Interstate Commerce private business. Commission (ICC) WHY? • How to regulate RR? • Est by the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887 • 1st attempt by the feds to regulate business in the interest of society Causes of Rapid Industrialization 3. Technological innovations. Bessemer and open hearth process Refrigerated cars Thomas Edison o “Wizard of Menlo Park” o light bulb, phonograph, motion pictures. Bessemer Process • Cold air blown on red – hot iron creates steel • Process of making cheap steel from iron Henry Bessemer Thomas Alva Edison “Wizard of Menlo Park” The Light Bulb The Phonograph (1877) The Ediphone or Dictaphone The Motion Picture Camera Alexander Graham Bell Telephone (1876) Alternate Current George Westinghouse Alternate Current Westinghouse Lamp ad The Airplane Wilbur Wright Orville Wright Kitty Hawk, NC – December 7, 1903 Model T Automobile Henry Ford I want to pay my workers so that they can afford my product! U. S. Patents Granted 1790s 276 patents issued. 1990s 1,119,220 patents issued. Standard Oil Co. Causes of Rapid Industrialization 4. Unskilled & semi-skilled labor in abundance. 5. Abundant capital. 6. New, talented group of businessmen [entrepreneurs] and advisors. 7. Market growing as US population increased. 8. Government willing to help at all levels to stimulate economic growth. 9. Abundant natural resources. New Business Culture 1. Laissez Faire the ideology of the Industrial Age. Individual as a moral and economic ideal. Individuals should compete freely in the marketplace. The market was not man-made or invented. No room for government in the market! 2. Social Darwinism British economist. Advocate of laissez-faire. Adapted Darwin’s ideas from the “Origin of Species” to humans. Herbert Spencer Notion of “Survival of the Fittest.” Monopoly • What is it? • Exclusive control of a good or service in a given market • Problems with monopolies? Andrew Carnegie • Carnegie steel = monopoly • Used new business practice of vertical integration • Vertical = buy out all suppliers • Horizontal = buy out all competition John Rockefeller • Standard Oil Company = monopoly • Standard Oil processed 90% of nations oil by 1880 • Paid low wages and undersold competition then jacked prices up when other companies went out of business • Used horizontal integration New Type of Business Entities 1. Pool 1887 Interstate Commerce Act Interstate Commerce Commission created. 2. Trust John D. Rockefeller Standard Oil Co. √ Smaller companies stock bought by directors of Standard Oil By 1877 Rockefeller controlled 95% of all the oil refineries in the USA Standard Oil Co. New Type of Business Entities 2. Trust: Horizontal Integration John D. Rockefeller Vertical Integration: o Gustavus Swift Meat-packing o Andrew Carnegie U. S. Steel Iron & Steel Production New Type of Business Entities U. S. Corporate Mergers New Financial Businessman The Broker: J. Pierpont Morgan – eliminate wasteful competition Consolidated officers of rival businesses and put on his board of directors “interlocking directorate” Wall Street – 1867 & 1900 The Reorganization of Work The Assembly Line % of Billionaires in 1900 % of Billionaires in 1918 The Protectors of Our Industries The ‘Bosses’ of the Senate The ‘Robber Barons’ of the Past Cornelius [“Commodore”] Vanderbilt Can’t I do what I want with my money? William Vanderbilt $ The public be damned! $ What do I care about the law? H’aint I got the power? The Gospel of Wealth: Religion in the Era of Industrialization $ Wealth no longer looked upon as bad. $ Viewed as a sign of God’s approval. $ Christian duty to accumulate wealth. Russell H. Conwell “On Wealth” $ The Anglo-Saxon race $ $ $ $ Andrew Carnegie is superior. “Gospel of Wealth” (1901). Inequality is inevitable and good. Wealthy should act as “trustees” for their “poorer brethren.” It was the duty of the wealthy to leave a legacy that benefitted society Regulating the Trusts 1877 Munn. v. IL Allowed states to regulate certain businesses within their borders, including railroads 1886 Wabash, St. Louis & Pacific Railroad Company v. IL 1890 Sherman Antitrust Act in “restraint of trade” “rule of reason” loophole did not distinguish b/w good & bad trusts 1895 US v. E. C. Knight Co. limited the government's power to control monopolies Relative Share of World Manufacturing The “New South” p. 545 • Read p. 76 in The American Spirit • What is the occasion for the speech? • What problems does the south face? • Leader of the movement? Henry Grady Main goals of the New South movement?