Document
advertisement

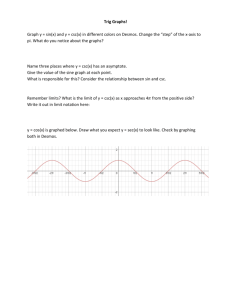
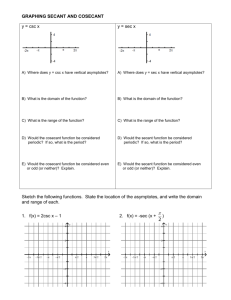
Lesson 4-6 Graphs of Secant and Cosecant Get out your graphing calculator… Graph the following y = cos x y = sec x What do you see?? 2 Graph of the Secant Function 1 sec x The graph y = sec x, use the identity . cos x At values of x for which cos x = 0, the secant function is undefined and its graph has vertical asymptotes. y y sec x Properties of y = sec x 1. domain : all real x x k (k ) 2 2. range: (–,–1] [1, +) 3. period: 2 4. vertical asymptotes: x k k 2 4 y cos x x 2 2 3 2 2 5 2 3 4 3 First graph: • y = 2cos (2x – π) + 1 Then try: • y = 2sec (2x – π) + 1 4 Graph Graph the following y = sin x y = csc x What do you see?? 5 Graph of the Cosecant Function 1 To graph y = csc x, use the identity csc x . sin x At values of x for which sin x = 0, the cosecant function is undefined and its graph has vertical asymptotes. y Properties of y = csc x 4 y csc x 1. domain : all real x x k k 2. range: (–,–1] [1, +) 3. period: 2 4. vertical asymptotes: x k k where sine is zero. x 2 2 3 2 2 5 2 y sin x 4 6 First graph: • y = -3 sin (½x + π/2) – 1 Then try: • y = -3 csc (½x + π/2) – 1 7 Key Steps in Graphing Secant and Cosecant 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Identify the key points of your reciprocal graph (sine/cosine), note the original zeros, maximums and minimums Find the new period (2π/b) Find the new beginning (bx - c = 0) Find the new end (bx - c = 2π) Find the new interval (new period / 4) to divide the new reference period into 4 equal parts to create new x values for the key points Adjust the y values of the key points by applying the change in height (a) and the vertical shift (d) Using the original zeros, draw asymptotes, maximums become minimums, minimums become maximums… Graph key points and connect the dots based upon known shape 8 Graphs of Tangent and Cotangent Functions Tangent and Cotangent Look at: Shape Key points Key features Transformations 10 Graph Set window Domain: -2π to 2π x-intervals: π/2 (leave y range) Graph y = tan x 11 Graph of the Tangent Function sin x To graph y = tan x, use the identity tan x . cos x At values of x for which cos x = 0, the tangent function is undefined and its graph has vertical asymptotes. y Properties of y = tan x 1. domain : all real x x n n 2 2. range: (–, +) 3. period: 4. vertical asymptotes: x n n 2 2 3 2 3 2 x 2 period: 12 Graph y = tan x and y = 4tan x in the same window What do you notice? y = tan x and y = tan 2x What do you notice? y = tan x and y = -tan x What do you notice? 13 Graph Set window Domain: 0 to 2π x-intervals: π/2 (leave y range) Graph y = cot x 14 Graph of the Cotangent Function cos x To graph y = cot x, use the identity cot x . sin x At values of x for which sin x = 0, the cotangent function is undefined and its graph has vertical asymptotes. y Properties of y = cot x y cot x 1. domain : all real x x n n 2. range: (–, +) 3. period: 4. vertical asymptotes: x n n vertical asymptotes 3 2 2 x x0 3 2 2 x x 2 x 2 15 Graph Cotangent y = cot x and y = 4cot x in the same window What do you notice? y = cot x and y = cot 2x What do you notice? y = cot x and y = -cot x What do you notice? y= cot x and y = -tan x 16 Key Steps in Graphing Tangent and Cotangent Identify the key points of your basic graph 1. Find the new period (π/b) 2. Find the new beginning (bx - c = 0) 3. Find the new end (bx - c = π) 4. Find the new interval (new period / 2) to divide the new reference period into 2 equal parts to create new x values for the key points 5. Adjust the y values of the key points by applying the amplitude (a) and the vertical shift (d) 6. Graph key points and connect the dots 17