Document
advertisement

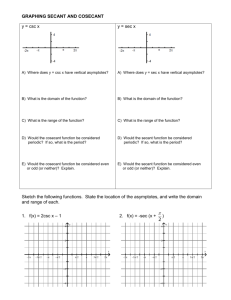
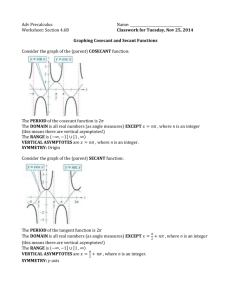
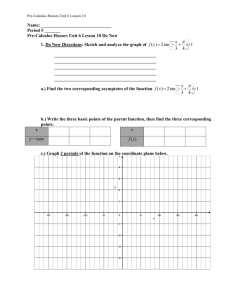
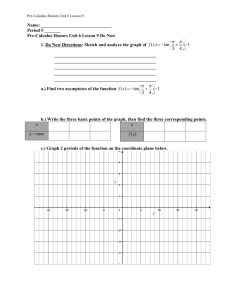
Sec. 14-2 Graphs of Other Trig Functions The ___________function is _____________ when ___________________, where n is an integer. The ______________ function is undefined when ___________. These values are excluded from the __________ and are represented by vertical _______________ on the graph. __________and __________functions have _________________or _______________ values, therefore __________ is __________. Characteristics of the Graphs of Tangent and Cotangent Function Graph Domain Range Period Amplitude y = tanx Function Graph Domain Range Period Amplitude y = cotx Like sine and cosine, you can ________________ the tangent function. For the graph of y = a tan bx, where a = 0 and x is in radians, The period is _______________ The asymptotes are located at ________________ Ex. 1 Transforming Tangent Functions Using f(x) = tan x as a guide, graph g(x) = tan2x. Identify the period, x-intercepts and asymptotes. Transformations of Cotangent Graphs For the graph of y = a cot bx, where a = 0 and x is in radians, The period is ________________ The asymptotes are located at __________________ Ex. 2 Graphing the Cotangent Function Using f(x) = cotx as a guide, graph g(x) = cot 0.5x. Identify the period, x-intercepts, and asymptotes. Recall that ____________________. So, secant is __________where __________ equals __________ and the graph will have __________asymptotes at those locations. __________will also have the same __________ as __________. __________and __________ have a similar relationship. Because secant and cosecant have ___absolute __________ or __________, amplitude is __________. Characteristics of the Graphs of Secant and Cosecant Function Graph Domain Range Period Amplitude y = secx Function y = cscx Graph Domain Range Period Amplitude Ex. 3 Graphing Secant and Cosecant Functions Using f(x) = cos x as a guide, graph g(x) = sec2x. Identify the period and asymptotes.