Chapter 3 - FacultyWeb
advertisement

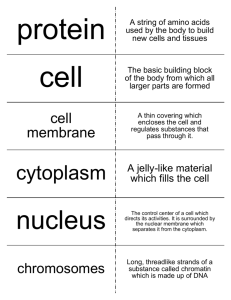
Which component of the cell membrane is primarily responsible for the membrane’s ability to form a physical barrier between the cell’s internal and external environments? 1. 2. 3. 4. Phospholipid bilayer Glycocalyx Peripheral proteins Proteoglycans Which type of integral protein allows water and small ions to pass through the cell membrane? 1. 2. 3. 4. Receptor proteins Carrier proteins Channel proteins Recognition proteins Which statement(s) correctly distinguish between cytoplasm and cytosol? 1. 2. 3. 4. Cytosol has a higher concentration of suspended proteins than cytoplasm. Cytosol is the intracellular fluid and is composed of nutrients, ions, proteins, and wastes and cytoplasm is the term for all material located between the cell membrane and nucleus. Potassium ion concentration is higher in cytoplasm than in cytosol. Cytosol and cytoplasm refer to the same substance. What is/are the major difference(s) between cytosol and extracellular fluid? 1. Cytosol has a higher concentration of sodium ions 2. ECF is a transport medium only, whereas cytosol has some carbohydrates and amino acids 3. Cytosol has a higher concentration of potassium ions 4. 2 and 3 Which of the listed organelles is nonmembranous and correctly paired with its function? 1. Microvilli/movement of materials over cell surface 2. Ribosomes/protein synthesis 3. Mitochondria/produces ATP required by cell 4. Microtubules/increase surface area for absorption What does the presence of many mitochondria imply about a cell’s energy requirements? 1. A high demand for energy 2. A low demand for energy 3. Fluctuating energy needs requiring flexibility 4. Number of mitochondria provides no implication of energy needs Certain cells in the ovaries and testes contain large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). Why? 1. 2. 3. 4. To produce large amounts of proteins To digest materials quickly To store large amounts of hormones To produce large amounts of steroid hormones Cells lining the small intestine have numerous fingerlike projections on their free surface. What are these structures, and what is their function? 1. 2. 3. 4. Microvilli; move substances across cell surface Microvilli; increase cell’s surface area and absorptive ability Cilia; increase cell’s surface area and absorptive ability Cilia; move substances across cell surface What is the genetic code? 1. 2. 3. 4. It is the method by which proteins code for amino acids. It is the “language” the cell uses in the form of triplet codons, which specify individual amino acids. It is the portion of DNA that contains instructions for the synthesis of tRNA. It is the strand of DNA containing complementary triplets used for mRNA production. What process would be affected by the lack of the enzyme RNA polymerase? 1. Nothing would be affected; DNA polymerase would take over 2. Cell’s ability to duplicate DNA 3. Cell’s ability to translate DNA 4. Cell’s ability to transcribe RNA What are two reasons that mRNA transcription so vital? 1. 2. 3. 4. Protein synthesis occurs through transcription/it occurs very quickly DNA cannot leave the nucleus/transcription ensures that mRNA exactly matches the coding strand of the gene It allows formation of chains of amino acids/the same information is presented in a different language None of these is correct Define “selectively permeable” as it applies to the cell membrane. 1. 2. 3. 4. It is a membrane through which nothing can pass. It is a membrane that allows the free passage of some molecules, but restricts the passage of others. It is a membrane through which any substance can pass without restriction. It is a membrane that only allows substances through by active transport. How would a decrease in the concentration of oxygen in the lungs affect the diffusion of oxygen into the blood? 1. 2. 3. 4. Decrease in molecule size results in decreased diffusion Decrease in distance results in increased diffusion Increase in electrical forces results in increased diffusion Decrease in gradient size results in decreased speed of diffusion What is so special about osmosis, compared with diffusion? 1. 2. 3. 4. Osmosis allows free passage of alcohol, fatty acids, and steroids through the plasma membrane. Osmosis is the movement of water rather than solute. In osmosis, water flows across a membrane toward the solution that has a higher concentration of solutes, because that is where water concentration is lower. 2 and 3 are correct. Some Pediatricians recommend the use of a 10% salt solution to relieve congestion for infants with stuffy noses. What effect would such a solution have on the cells lining the nasal cavity, and why? 1. 2. 3. 4. Cells will lose water because this is a hypertonic solution. Cells will lose water because this is a hypotonic solution. Cells will gain water because this is a hypertonic solution. Cells will gain water because this is a hypotonic solution. All methods of carrier-mediated transport have the following characteristics ___. 1. 2. 3. 4. Concentration gradients, transmembrane potential, and resting potential Specificity, saturation limits, and regulation Endocytosis, exocytosis, and pinocytosis Isotonic, hypertonic, and hypotonic solutions Which of the following methods of carriermediated transport is paired with its function? 1. 2. 3. 4. Active transport/it is dependent on a concentration gradient Facilitated diffusion/substances are bound to a receptor and passed across the cell membrane by carrier proteins Sodium-potassium pump/moves Na outside the cell and K inside the cell 2 and 3 are correct During digestion in the stomach, the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) rises to many times that of cells in the stomach. Which transport process must be operating? 1. 2. 3. 4. Facilitated diffusion Osmosis Active transport Endocytosis When they encounter bacteria, certain types of white blood cells engulf the bacteria and bring them into the cell. What is this process called? 1. 2. 3. 4. Pseudocytosis Exocytosis Pinocytosis Phagocytosis Each type of cell has a characteristic resting potential. Which is correct? 1. 2. 3. 4. Fat cells (−40 mV) Neurons (−70 mV) Cardiac muscle cells (−90 mV) All of the above are correct If the cell membrane were freely permeable to sodium ions (Na+), how would the transmembrane potential be affected? 1. 2. 3. 4. It would not change It would become more positive It would become more negative It would become unstable During the S phase, which of the following occur(s)? 1. 2. 3. 4. DNA polymerase binds to exposed nitrogenous bases DNA replication Synthesis of histone proteins in the nucleus All of the above are correct A cell is actively manufacturing enough organelles to serve two functional cells. This cell is probably in which phase of its life cycle? 1. 2. 3. 4. S G1 G2 M During DNA replication, a nucleotide is deleted from a sequence that normally codes for a polypeptide. What effect will this deletion have on the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide? 1. No effect, deletion will be skipped 2. No effect, deletion will be automatically repaired 3. Amino acid sequence will disintegrate 4. Amino acid sequence would be altered What would happen if spindle fibers failed to form in a cell during mitosis? 1. Centromeres would not appear 2. Nuclear membrane would not disintegrate 3. Chromosomes would not separate 4. Chromatin would not condense Which of the following stages of mitosis is correctly paired with the events of that stage? 1. 2. 3. 4. Anaphase/centromeres of chromatid pairs separate and daughter chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of the cell Prophase/chromatids are aligned along center of the cell Telophase/chromosomes condense and nuclear membrane fragments All of the above are correct