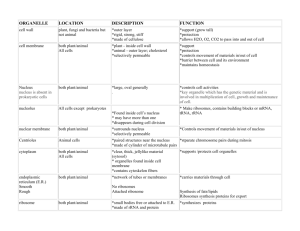
Part 2: Eukaryotic Cell
Structures
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Cytoplasm
• Location / Structure: The region of a cell
between the cell membrane and the
nucleus; made of a jelly-like watery fluid
called the cytosol
• Function: “cushions” the organelles
Cell Membrane
Location / Structure:
• Also called the plasma
membrane
• A barrier that surrounds
the cytoplasm
• Separates the inside of
cells from the outside
environment
Function:
• Regulates passage of
materials into and out of
the cell
Nucleus
Location / Structure:
• Found at the center of the
cell
• Contains DNA
• Surrounded by a doublemembrane with holes (aka
pores) to allow passage of
materials (not DNA) into
and out of the nucleus
Function: Controls the
activities of the cell
Nucleolus
Location / Structure:
• A spherical structure
found at the center of
the nucleus
Function: Creates
(synthesizes) ribosomes…
see next slide for a
description of ribosomes
Ribosomes
Location / Structure:
• Found floating in the cytoplasm and
attached to the rough ER
• Very small
• Made of RNA and protein
Function:
• Make proteins
Rough Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Location / Structure:
• Tubes and sacs made of
membrane
• Has ribosomes on its
surface
Function:
• Make proteins (due to
ribosomes)
• Transport materials (like
proteins) around the cell… it
is the highway of the cell!
Smooth Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Location / Structure:
• Tubes and sacs made of
membrane
• Does not have ribosomes on its
surface
• Attached to the Rough ER,
farther out from the nucleus
Function:
• Makes lipids
• Breaks down toxins
Golgi Apparatus
Location / Structure:
• Another system of tubes and sacs
made of membrane close to the cell
membrane
Function:
• Vesicles (spheres of membrane)
carry materials (ex: proteins from the
Rough ER) to the Golgi and from the
Golgi to release materials at the
membrane
• Called the “post office” because it
repackages materials and sends
them out of the cell
Lysosomes
Location /Structure:
• small, spherical organelles
that contain enzymes
• float in the cytoplasm
Function:
• enzymes can digest carbs,
lipids, DNA, RNA, old
organelles, viruses, bacteria
• Only found in animal cells
Mitochondria
Location / Structure: Has a
double membrane, inner
membrane is folded
Function: powerhouse of
the cell; produces energy!
Question: In what types of
cells would mitochondria be
the most numerous?
Chloroplasts
Location / Structure:
• only found in plant cells
• double membrane
• stacks of “disks” inside inner
membrane
• green due to pigment “chlorophyll”
Function:
• Sunlight energy is captured by
chlorophyll and converted to
energy stored in sugars like
glucose during photosynthesis
Vacuole
Location / Structure
• Floating in the cytoplasm,
sphere of membrane
surrounding fluid
• Found in plants and
animals, but large and in
the middle of the cell in
plants
Function: Stores waste,
water, food, etc.
Cell Wall
Location / Structure:
• Outer barrier on plant
cells
• Made of cellulose, a
tough polysaccharide
Function: supports and
protects the cell
Cytoskeleton
• Location / Structure: a
“mesh” of three types of
long protein strands
located in the cytoplasm
• Function: a structure to
maintain the shape and
size of cells (like our
skeletons!)
Cilia / Flagella
Location / Structure:
• hair-like organelles that
extend from the surface of
the cell
• cilia are shorter and more
numerous
• flagella are longer and less
numerous
Function:
• Movement
Centrioles
Location / Structure:
• Made of the same types
of proteins found in the
cytoskeleton arranged in
cylinders (look like
“churros”)
• Found only in animal cells
Function:
• Assist with cell division