Cells
advertisement

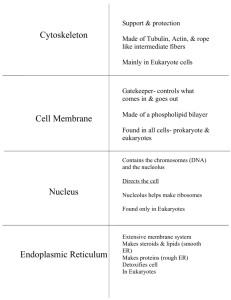
Cells Cell Theory, Prokaryotes, and Eukaryotes Cell Theory 1. 2. 3. Living organisms are composed of cells. Cells are the smallest unit of life. Cells come from pre-existing cells. Relative size of cell Types of cells Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryotes do not have a nucleus The DNA exists as a single circular chromosome Your Turn What type of organisms are prokaryotic? Can you remember what the other major type of cell is called? Eukaryotic cells complex cells with organelles Eukaryotes – Cell Parts Plasma membrane Nucleus Ribosomes Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Apparatus Lysosomes Mitochondria Centrioles Plasma Membrane Function: separates internal cell environment (cytoplasm) from exterior environment Structure: Phospholipid bi-layer that surrounds cell Contains various types of membrane proteins Selectively Permeable: allows specific substances to cross membranes but not others Plasma Membrane Fluid Mosaic Model Nucleus Location of genetic material (DNA chromosomes) Functions to separate DNA from the rest of the cell Nuclear Envelope Nuclear pores allow entry and exit of molecules mRNA between nucleus and cytoplasm Ribosomes Make proteins Composed of two subunits Located in cytoplasm or RER Endoplasmic Reticulum Two Types Rough ER (RER) and smooth Rough studded with ribosomes on outer surface site of protein synthesis Golgi Apparatus Receives vesicles from ER Modifies, sorts and packages macromolecules Sends macromolecules to final destination (via vessicles) Your Turn Make a simple diagram of a cell and highlight the pathway by which proteins are made. Protein Trafficking Proteins destined for specific cellular locations such as the plasma membrane or lysosomes are synthesized at the RER Vesicles transport proteins to Golgi apparatus From Golgi apparatus proteins are sent, via vesicles, to specified cellular location Mitochondria It is the cell’s source of energy: it makes energy from glucose (cellular respiration) ( Parts include: Double membrane DNA Lysosomes Small organelles filled with enzymes Used to breakdown macromolecules or damaged organelles WE STOP HERE FOR TODAY! Plant Cells Plant cells are eukaryotes with additional modifications Chloroplasts Cell walls Central vacuoles No centrioles Chloroplasts Location of photosynthesis Photosynthesis: the transfer of light energy into the chemical bonds of glucose Parts include: Double Membrane DNA Cell wall maintains cell shape prevents excessive water uptake holds the whole plant up against the force of gravity Composed of the polysaccharide cellulose Central Vacuole Used for storage of starch Filled with water, functions in maintaining cell pressure Eukaryotes State Three differences between plant and animal cells. Eukaryotes State Three differences between plant and animal cells. 1. Plants have chloroplasts, animals don’t 2. Plants have cell walls, animals don’t 3. Plants have large central vacuole, animals don’t Animal and Plant Cell Comparison