Growth of Labor Unions - Mr. Pratt's History Class
advertisement

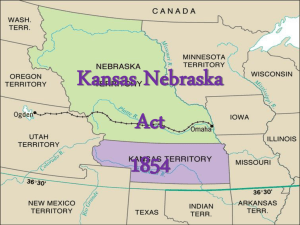
The Missouri Compromise (1820) Problems of Sectional Balance in 1850 - California statehood. - Southern “fire-eaters threatening secession. - Underground RR & fugitive slave issues: Compromise of 1850 The Compromise of 1850 1) Popular Sovereignty – Stephen Douglas 2) Slave state vs. free state 3) Fugitive Slave Act a) Uncle Tom’s Cabin (1852) b) Ableman v. Booth (1857) Harriet Beecher Stowe (1811 – 1896) So this is the lady who started the Civil War. -- Abraham Lincoln Uncle Tom’s Cabin 1852 Sold 300,000 copies in the first year. 2 million in a decade! Uncle Tom’s Cabin, 1852 The “Know-Nothings” [The American Party] ß Nativists. ß AntiCatholics. ß Antiimmigrants. 1849 Secret Order of the StarSpangled Banner created in NYC. 1852 Presidential Election √ Franklin Pierce Democrat Gen. Winfield Scott John Parker Hale Whig Free Soil 1852 Election Results Pierce & Expansionism • Mexican Territory South of the Rio Grande • Gadsden Purchase (1854) • $10 million • Caribbean Central America Expansion • Cuba - War with Spain?? • Ostend Manifesto • Slave Power Returns??? Kansas-Nebraska Act, 1854 Kansas – Nebraska Act • Causes & Motivation • Stephen Douglas • Transcontinental Railroad & opening of farmland • Initial Bill & Southern Opposition • Had the impact of repealing the Missouri Compromise • Impact • American Politics (Destruction & Rebirth) • Republican Party – New Platform Bleeding Kansas “If we win we carry slavery to the Pacific Ocean, if we fail we lose…all the territories” (pro-slavery) • • What Kansas meant for the nation Pro-slavery & free-soilers were fighting for control of Kansas. • Popular sovereignty is tested: – Voters would elect territorial leg. Who would create a constitution and pass laws on the subject – The Constitution would either permit or ban slavery – Voters would approve or reject the constitution – If approved they could apply for statehood • First election was held in Nov. 1854 – 1700 armed Missourians flooded in and threatened violence if denied voting access – Pro-slavery delegates were elected (voter fraud) – Free-soilers refused to accept this new leg and elected an anti-slavery leg & governor – Both gov. claimed legitimacy in Kansas “Bleeding Kansas” Border “Ruffians” (pro-slavery Missourians) Incidents in Kansas: Escalation • • • • • • Sack of Lawrence by 1855 Lawrence, KS was the center of anti-slavery activity Decision needed to be made on Kansas Jan 1856 Pres. Pierce condemned the free-soil gov. as rebels, supporting pro-slavery and charging free-soilers with treason May 21, 1856 pros-slavery sheriff & 800 men rode in to arrest the “rebels Destroyed offices, newspapers, businesses, etc.. Anti-slavery newspapers labeled this the “sack of Lawrence to paint a barbaric picture of pro-slavery • • • • • The Pottawatomie Massacre 56 yr. old John Brown was an abolitionist Moved to Kansas for land and promote the territory as a free state Sought revenge from the “sack of Lawrence” May 24, 1856 dragged 5 pro-slavery settlers out of their beds in Pottawatomie Creek and executed them This ignited a civil war in Kansas and guerilla war broke out in Kansas “The Crime Against Kansas” Sen. Charles Sumner (R-MA) Congr. Preston Brooks (D-SC) Birth of the Republican Party, 1854 - Northern Whigs. - Northern Democrats. - Free-Soilers. - Know-Nothings. - Other miscellaneous opponents of the Kansas-Nebraska Act. 1856 Presidential Election √ James Buchanan Democrat John C. Frémont Republican Millard Fillmore Whig “The fate of the republic hinged on the ability of President Buchanan to diffuse the passions of the past decade and devise a way of protecting free soil in the West & slavery in the South” 1856 Election Results Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857) • Background & Const. Issue • Court’s Decision (7 out of 9) & Differing Legal Opinions • Taney’s Decision & Impact • • • • • 1) Scott’s Rights 2) Fifth Amendment 3) Northwest Ord./Missouri Comp. 4) Congressional Authority 5) Republican Platform • Buchanan, Slave Power, & Kansas What caused the Panic of 1857?? What were its effects on the nation? • Causes Causes & Effects – declining international economy and over-expansion of the domestic economy • Effects • southern economy suffered little whereas the northern economy took a significant hit • encouraged those in the South who believed the idea that the north needed the south to keep a stabilized economy and southern threats of secession were temporarily quelled. • Southerners believed the north was now "more amenable to southern demands" and would help to keep slavery alive in the United States. The Lecompton Constitution • 1857 an election took place giving pro-slavery forces control over the writing of a state constitution – Lecompton Constitution • Knowing anti-slavery supporters would never accept it, it was never submitted • Instead they proposed voters decide on slavery alone: • If approved slavery would be allowed in Kansas • If rejected importation of slaves would be banned, but currents laves could remain as slaves • Northerners were outraged & in 1858 Free-Soilers rejected the provision and the constitution • Southerners threatened secession • Fearing secession & bowing to pressure Buchanan submitted the Lecompton Constitution (pro-slave) to Congress calling for Kansas admission as a slave state When put to the people the Lecompton Constitution was overwhelmingly rejected and the Kansas issue was put to rest.. For now • The Lincoln-Douglas (Illinois Senate) Debates, 1858 A House divided against itself, cannot stand. Lincoln Douglas Debates • • • • U.S. Senate election of 1858 Douglas (D) vs. Lincoln (R) Series of 7 debates Hot Topic: Slavery & the Territories Lincoln • “a house divided against itself cannot stand” • Equal economic opportunity for all free blacks. • Against Dred Scott Douglas “This government was made by our fathers, by white men for the benefit of white men and their posterity forever” Freeport Doctrine John Brown’s Raid “Talk! Talk! Talk! That will never free the slaves. What is needed is action – action” • Action came in the form of freeing slaves • Decided to raid a US arsenal at Harpers Ferry, Virginia • Brown planned to use these guns to arm a local slave revolt with hopes of inspiring others to follow • On October 16 Brown & 5 African Americans easily captured the arsenal, then sent out word hoping to inspire other slave revolts. • Unfortunately for Brown, no slaves followed and on Oct. 18th Marines recaptured the arsenal • Brown was captured, tried, and sentenced to hang • Died committed to abolitionism on Dec. 2, 1859 John Brown: Madman, Hero or Martyr? Mural in the Kansas Capitol building by John Steuart Curry (20c) John Brown’s Raid on Harper’s Ferry, 1859 The Emergence of Abraham Lincoln Childhood & Family Background Early Political Career Position/Stance on Slavery √ Abraham Lincoln Republican 1860 John Bell Constitutional Union Presidential Election Stephen A. Douglas Northern Democrat John C. Breckinridge Southern Democrat Republican Party Platform in 1860 - Non-extension of slavery [for the Free-Soilers. - Protective tariff [for the No. Industrialists]. - No abridgment of rights for immigrants [a disappointment for the “Know-Nothings”]. - Government aid to build a Pacific RR [for the Northwest]. - Internal improvements [for the West] at federal expense. - Free homesteads for the public domain [for farmers]. 1860 Election: 3 “Outs” & 1 ”Run!” 1860 Election: A Nation Coming Apart?! 1860 Election Results Crittenden Compromise: A Last Ditch Appeal to Sanity Senator John J. Crittenden (Know-NothingKY) Secession!: SC Dec. 20, 1860 Fort Sumter: April 12, 1861 Building Towards War • • • • • • • • • The Missouri Compromise (1820) The Compromise of 1850 Election of 1852 Pierce & Expansionism Kansas & Nebraska Act (1854) Bleeding Kansas (1854) Election of 1856 Dred-Scott Decision (1857) Election of 1860 – Abraham Lincoln becomes POTUS Names for the Civil War • • • • • • • • • The War between the States The War for Southern Independence The War for Southern Rights The Second War for Independence The War to Suppress Yankee Arrogance The War Against Slavery The War Against Northern Aggression The Yankee Invasion The War for Abolition