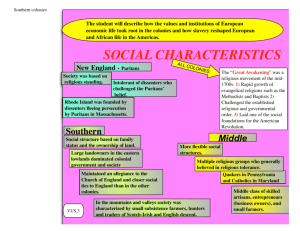
New England STORY
advertisement

NEW ENGLAND: Story with Quiz to follow New England was settled by ________ seeking freedom from _________ persecution in Europe. They formed a “______ _________” based on the principles of the _______ Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on _________ standing. In other words, leaders in the _______ were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of ______ democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from _________ persecution in Europe. They formed a “______ _________” based on the principles of the _______ Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on _________ standing. In other words, leaders in the _______ were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of ______ democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. They formed a “______ _________” based on the principles of the _______ Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on _________ standing. In other words, leaders in the _______ were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of ______ democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. They formed a “ covenant community “ based on the principles of the _______ Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on _________ standing. In other words, leaders in the _______ were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of ______ democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. They formed a “ covenant community “ based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on _________ standing. In other words, leaders in the _______ were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of ______ democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. They formed a “ covenant community “ based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on religious standing. In other words, leaders in the _______ were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of ______ democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. They formed a “ covenant community “ based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on religious standing. In other words, leaders in the church were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of ______ democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. They formed a “ covenant community “ based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on religious standing. In other words, leaders in the church were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of direct democracy through _____ ________. All male church members could vote. New England was settled by Puritans seeking freedom from religious persecution in Europe. They formed a “ covenant community “ based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact and Puritan religious beliefs. New England’s colonial society was based on religious standing. In other words, leaders in the church were also leaders in government and society. To make decisions, the Puritans practiced a form of direct democracy through town meetings. All male church members could vote. CONT... The Puritans grew increasingly intolerant of __________ who challenged their belief in the connection between religion and government. ______ _______ was founded by dissenters ________ persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts. CONT… The Puritans grew increasingly intolerant of dissenters who challenged their belief in the connection between religion and government. ______ _______ was founded by dissenters ________ persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts. CONT… The Puritans grew increasingly intolerant of dissenters who challenged their belief in the connection between religion and government. Rhode Island was founded by dissenters ________ persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts. CONT… The Puritans grew increasingly intolerant of dissenters who challenged their belief in the connection between religion and government. Rhode Island was founded by dissenters fleeing persecution by Puritans in Massachusetts. CONT… Although the Puritans were most interested in __________, they also sought __________ opportunity. The New England colonies developed an economy based on ___________, _________, ___________, _____________, and eventually ____________. The colonies prospered, reflecting the Puritans strong belief in the values of hard work and _______ (a careful management of money and possessions.) Although the Puritans were most interested in religion, they also sought __________ opportunity. The New England colonies developed an economy based on ___________, _________, ___________, _____________, and eventually ____________. The colonies prospered, reflecting the Puritans strong belief in the values of hard work and _______ (a careful management of money and possessions.) Although the Puritans were most interested in religion, they also sought economic opportunity. The New England colonies developed an economy based on ___________, _________, ___________, _____________, and eventually ____________. The colonies prospered, reflecting the Puritans strong belief in the values of hard work and _______ (a careful management of money and possessions.) Although the Puritans were most interested in religion, they also sought economic opportunity. The New England colonies developed an economy based on shipbuilding, fishing , lumbering , subsistence farming, and eventually manufacturing. The colonies prospered, reflecting the Puritans strong belief in the values of hard work and _______ (a careful management of money and possessions.) Although the Puritans were most interested in religion, they also sought economic opportunity. The New England colonies developed an economy based on shipbuilding, fishing , lumbering , subsistence farming, and eventually manufacturing. The colonies prospered, reflecting the Puritans strong belief in the values of hard work and thrift (a careful management of money and possessions.) SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Why did the Puritans come to New England? Puritans SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Why did the Puritans come to New England? Puritans Religious Freedom SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Why did the Puritans come to New England? What specific type of community did the Puritans form? Puritans Religious Freedom SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans Why did the Puritans come to New England? Religious Freedom What specific type of community did the Puritans form? “Covenant Community” based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans Why did the Puritans come to New England? Religious Freedom What specific type of community did the Puritans form? “Covenant Community” based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact What colony was settled by Puritan dissidents? SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans Why did the Puritans come to New England? Religious Freedom What specific type of community did the Puritans form? “Covenant Community” based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact What colony was settled by Puritan dissidents? Rhode Island SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans Why did the Puritans come to New England? Religious Freedom What specific type of community did the Puritans form? “Covenant Community” based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact What colony was settled by Puritan dissidents? Rhode Island What type of democracy did Puritans practice in town hall meetings? SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans Why did the Puritans come to New England? Religious Freedom What specific type of community did the Puritans form? “Covenant Community” based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact What colony was settled by Puritan dissidents? Rhode Island What type of democracy did Puritans practice in town hall meetings? Direct Democracy SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans Why did the Puritans come to New England? Religious Freedom What specific type of community did the Puritans form? “Covenant Community” based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact What colony was settled by Puritan dissidents? Rhode Island What type of democracy did Puritans practice in town hall meetings? Direct Democracy What industries existed in New England? SOL QUIZ: NEW ENGLAND What group settled New England? Puritans Why did the Puritans come to New England? Religious Freedom What specific type of community did the Puritans form? “Covenant Community” based on the principles of the Mayflower Compact What colony was settled by Puritan dissidents? Rhode Island What type of democracy did Puritans practice in town hall meetings? Direct Democracy What industries existed in New England? shipbuilding, fishing, lumbering, subsistence farming, manufacturing