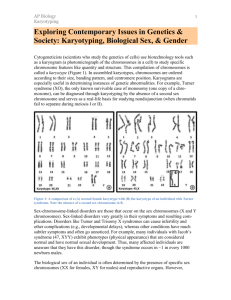
Chromsomes and karyo
advertisement
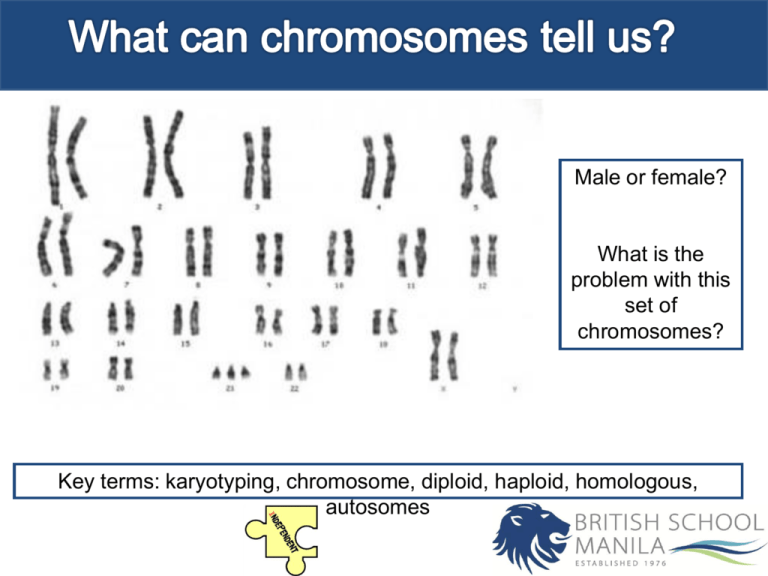
Male or female? What is the problem with this set of chromosomes? Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Objectives Outcomes Define key terminology related to chromosomes. 3: Describe karyotyping. Explore the use of karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Chromosomes are composed of DNA coiled around proteins (histones) Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes One chromosome of each homologous pair comes from the mother (called a maternal chromosome) and one comes from the father (paternal chromosome). Homologous chromosomes are similar but not identical. Each carries the same genes in the same order, but the alleles for each trait may not be the same. Outcomes 3: Describe karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes An autosome is a chromosome that is not an allosome (i.e., not a sex chromosome). Autosomes appear in pairs whose members have the same form but differ from other pairs in a diploid cell, whereas members of an allosome pair may differ from one another and thereby determine sex. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Outcomes 3: Describe karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Outcomes 3: Describe karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Outcomes 3: Describe karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Questions Outcomes 1. State the difference between a diploid and haploid cell. 3: Describe karyotyping. 2. What is an autosome? 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 3. What are homologous chromosomes? 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. 4. If a diploid cell of an organism contains 38 chromosomes how many will a gamete contain? Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Karotype and karyogram Outcomes Karyotype: A property of the cell – the number and type of chromosomes present. 3: Describe karyotyping. Karyogram: the image of this. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Non-disjunction Non-disjunction is one of the Two major occurrences of Meiosis (The other is Crossing Over) • Non-disjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes, or sister chromatids, to separate during meiosis. • Non-disjunction results with the production of zygotes with abnormal chromosome numbers…… remember…. An abnormal chromosome number (abnormal amount of DNA) is damaging to the offspring. Non-disjunctions usually occur in one of two fashions. The first is called Monosomy, the second is called Trisomy. If an organism has Trisomy 18 it has three chromosomes in the 18th set, Trisomy 21…. Three chromosomes in the 21st set. If an organism has Monosomy 23 it has only one chromosome in the 23rd set. Outcomes 3: Describe karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Outcomes 3: Describe karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Common Non-disjunction Disorders • Down’s Syndrome – Trisomy 21 • Turner’s Syndrome – Monosomy 23 (X) • Kleinfelter’s Syndrome – Trisomy 23 (XXY) • Edward’s Syndrome – Trisomy 18 Outcomes 3: Describe karyotyping. 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes Task Outcomes Carry out the karyotyping activity on: 3: Describe karyotyping. http://www.biology.arizona.edu/h uman_bio/activities/karyotyping/k aryotyping.html 5: Successfully complete the activity on karyotyping. 7: Evaluate the uses and limitations of karyotyping. Link is on Haiku Key terms: karyotyping, chromosome, diploid, haploid, homologous, autosomes