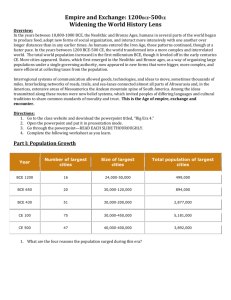
Neolithic Revolution (8000 BCE- 600 BCE) AP World History begins
advertisement

Neolithic Revolution (8000 BCE- 600 BCE) AP World History begins Domestication of plants First wheat in the Middle East Rice in East and Southeast Asia Yams in West Africa Maize in the Americas Tarot roots in New Guinea Domestication of animals Horses, cows, sheep, pigs, goats in Afro-Eurasia Llama only large domesticated animal of the Americas Early settlements not "civilizations" Jericho and Catal Huyuk Domestication of plans and animals leads to a food surplus Food surplus leads to a specialization of labor creating: Religion, writing, artisans and goods, merchants and trade, architectural advances, military and improved technologies (Ex. Wheel (3500 BCE), plow, iron) Iron metallurgy Bronze Age (3000 BCE) Iron Age (1300 BCE) Theme 1 (Interaction between humans and environment) seen with farming and irrigation Theme 2 (Development and interaction between cultures) seen as Indus and Mesopotamians trade Americas develop in isolation As “civilizations” progress, the status of women falls sharply! Mesopotamia: What are they known for (3-4 things)? Hammurabi’s code Diffusion of iron/Hittites Egypt What are they known for (4-5 things)? Ancient River Valley Civilizations Indus River Valley Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro (Pakistan): What are they known for (3-4 things)? Aryans: Indo Europeans invade, Vedas form the basis of Hinduism, caste system becomes embedded in Indian culture (Warriors, priests, merchants and workers) China: Shang Dynasty What are they known for (3-4 things)? Zhou Dynasty Mandate of Heaven used to justify rebellions Longest lasting Chinese dynasty Exceptions to the river valley rule: Chavin (Peru) and Olmec (Central America) Other Noteworthy groups of Period 1 (8000 BCE-600 BCE) o Indo European migrations (central Asia, horses, language) o Bantu migrations o Sub-Saharan Africa, impact on language, farming, iron technology o Hebrews o Monotheism, Abraham, covenant with God o Phoenicians o 22 letter alphabet Religions: Animism (spirits reside in ordinary objects) Africa, North America, Central Asia Hinduism Judaism Zoroastrianism Teachings of Zoroaster or Zarathustra, Persia, good and evil What are some big ideas that cross the whole period in all places? Period 2 Rise of classical civilizations (Rome, Han, Gupta) and the development of major world religions Big Picture Events: Rise and fall of empires Development and spread of world religions and belief systems Major development and expansion of large trade networks Rise and fall of Empires China Zhou dynasty ends in 256 BCE Qin dynasty (221 BCE-209 BCE) the warring states period Legalism Terra Cotta warriors and starts the Great Wall Standardizes weights, measurements, currencies, laws and written language Han dynasty (206 BCE to 200 CE) Golden Age of China Establish the Silk Road Buddhism spreads to China via silk road Civil Service Exam begins Technology Paper manufactured, sun dials, calendars, compass, rudder, seismograph, water powered mills India Mauryan Empire (322- 185 BCE) First to unify the Indian subcontinent Gupta Empire (320- 550 CE) Golden Age of India Not as centralized, smaller than the Mauryan Hinduism reasserted Major continuity throughout India Sati a strong example of patriarchal society in India Persian Empire Cyrus the Great Great Royal Road (1600 miles of roads comparable to eventual Roman roads) Capital Persepolis (comparable to Chang’an, Athens, Rome, Teotihuacan) Persian War and Alexander the Great of Macedonia Greece Adopted Phoenician alphabet City-states: Athens and Sparta CultureAristotle model of Greek thought by use of logic Alexander the Great Conquered Greece and spread Greek culture (Hellenism) Empire facilitated interaction and spread of culture (Greece, India, Persia, and Egypt) Library of Alexandria in Egypt center of learning (good comparison to later Timbuktu, Mali) o Geometry, medicine, anatomy, circumference of the earth, Pythagorean theorem, geocentric thought of Ptolemy Rome (Greatest achievements are law and engineering) Roman Republic What are they known for (4-5 things)? Empire Julius Caesar killed (44 BCE), Octavian Augustus becomes emperor Empire stretches from England to Middle East Pax Romana (Roman peace) Law- innocent unless proven guilty by court Engineering (Coliseum), aqueducts Roads (comparable to Persian royal road and later Incan roads) Roman culture influenced by Greek cultural diffusion Slavery- Both Greek and Roman society heavily dependent on slavery (comparison to Chinese dependency on the peasants) Silk Road: Rome traded precious metals with the Han for silk Americas Maya (300-1100 CE) What are they known for (4-5 things)? Teotihuacan City in valley of Mexico (later model for Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan) Moche of South America in the Andes (100-700 CE) Extensive irrigation, complex culture What are some comparisons across civilizations? Fall of Empires Maya- possible exhaustion of the environment Han China- (220 CE) Internal - population increases, land problems, corruption, peasant rebellion called Yellow Turban (184 CE), disease External- conflict with nomadic Xiongnu Roman Empire (Western Rome falls in 476 CE, East survives as the Byzantine Empire) Internal- tax revolts, poor leaders, division of empire, violent death of emperors, over expansion, decrease in trade, reliance on mercenaries, disease External- Huns and Goths Gupta- Invasion by the White Huns- cost weakened state and eventually overrun Hinduism and caste system survived Religions Polytheism- most early civilizations were polytheistic (belief in many gods) o Animism- Africa, Americas o Shamanism- Americas, Central Asia India Hinduism: Aryan invaders, caste system, dharma, reincarnation, moksha, Vedas, Sati Buddhism: symbols, influence of Hinduism, Siddhartha Gautama, Four Noble Truths, Eightfold path, Nirvana, Ashoka Silk Road spread Buddhism to China Also spread to Southeast Asia- Angkor Wat (both Hindu and Buddhist) China Confucianism: the Warring State period, what does it emphasize, Filial piety o Embraced by governments as ruler superior to ruled o Civil Service Exam based on Confucian Analects o Government bureaucracy based on merit o Allowed for the possibility of social mobility o Patriarchal society develops as a husband superior to wife o Eventually see foot binding o Eventually combines with Buddhism to form Neo-Confucianism during the Tang dynasty Daoism and Legalism Middle East Judaism Christianity Interactions of the Classical period Silk Road Indian Ocean Trans-Saharan Camel in first century BCE significant Camel saddle in 300’s CE greatly increases trade across the Saharan Trade connects Sub-Saharan Africa with North Africa and Mediterranean Mediterranean Carthage, Phoenicians, Greeks, Berbers, Romans and Egyptians all traded Sub-Saharan Bantus inspire trade Connect Sub-Saharan Africa with East Africa and the Indian Ocean Americas Trade during this time is limited and is regional unlike Afro-Eurasian world