Production Possibilities Frontier

Class
4
The importance of models
International Trade
Marginal Utility
Money!
Economic models
• Economists use models to to improve our understanding of the world. Models simplify difficult concepts.
• The circular-flow diagram
• The production possibilities frontier
The circular-flow diagram
“A visual model of the economy that shows how money flows through markets amongst households and firms”
The circular-flow diagram
• Firms
– Produce and sell goods and services.
– Hire and use factors of production.
• Households
– Buy and consume goods and services.
– Own and sell factors of production .
• Markets for goods and services
– Firms sell
– Households buy
• Markets for factors of production
– Households sell
– Firms buy
The PPF
• The Production Possibilities Frontier
(PPF) is a graph that shows the various combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce given the available factors of production and the available production technology.
Quantity of computers produced
3,000
2,200
2,000
1,000
The production possibilities frontier
D
C
A
Production possibilities frontier
B
0 300 600 700 1,000 Quantity of cars produced
Copyright©2003 Southwestern/Thomson Learning
The PPF
• Concepts illustrated by the production possibilities frontier:
– efficiency
– trade-offs
– opportunity cost
– economic growth
Quantity of computers produced
4,000
3,000
2,100
2,000
A shift in the PPF
A
E
0 700 750 1,000 Quantity of cars produced
Copyright © 2004 South-Western
Consumption
“Consumption means the act of using goods and services to satisfy human wants during a given period of time”
If we had unlimited income we would satisfy unlimited wants:
But income is limited!
A. What should be buy amongst all the goods and services?
B. How much to allocate to each good and service?
Marginal Utility Analysis
Economists use the term “UTLITY” to measure happiness of satisfaction.
Economics is amoral
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Marginal Utility will not only tell me whether I am going to consume a good or service but also how much of it I will consume.
Total Utility and Marginal Utility
6
7
4
5
1
2
3
Qty Consumed
0
0
-5
10
5
25
20
15
Marginal Utility
0
75
70
70
75
25
45
60
Total Utility
0
Economic Surplus
Consumer Surplus is the utility for consumers by being able to purchase a product for less than the highest price that they would be willing to pay.
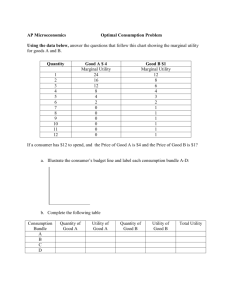
Problem 1
You purchase 4 chocolates for the price of Rs.15 per bar. You are willing to pay 25 for the bar 22 for the second 18 for the third and 15 for the
4th How much consumer surplus is derived from the 4 bars?
Problem 2
Show graphically the change in consumer surplus resulting from a rise in product price.
Budget Constraints
Paper Money
Does Paper Money have any intrinsic value?
“Intrinsic” - if your currency is not recognized will it have value?
Money that does not have intrinsic value is known as
“Fiat Money
If there was no money then we would have to barter
For barter to work – trade is said to require the double of coincidence of wants.
The history of money
Mesopotamian civilization developed a large scale economy based on “Commodity money”
Many other cultures also developed commodity money
Tobacco in America, Shells in India, Spices in
Europe, Alcohol in New South Wales
If you were in prison, what would be good forms of money to smuggle in.
3 important functions of money
Medium of exchange
Anything that facilitates trade by being generally accepted by all parties in payment for goods and services.
Unit of Account
A common unit for the measuring the value of every good and service.
Store of Value
Anything that retains its purchasing power over time.
The characteristics of Commodity money
Durable
Portable
Divisible
Uniform Quality
Gresham’s law – people tend to horde good money and trade away the rest.
Low opportunity cost
Value of money should not fluctuate erratically.
The need to specialize!
When countries specialize world output increases.
Comparative advantage.
The ability of a country to price a good at a lower opportunity cost than another country.
Absolute Advantage.
The ability of a country to produce a good using a fewer resources than another country.
Free Trade – The flow of good and services between countries without restrictions.
Fair Trade – a county should only reduce its barriers to entry if the other country does not have some sort of “unfair competitive” advantage. And also provided that the other country also reduces its trade barriers.
Type of protections
Embargo
Tariff
Quota
The infant industry argument
New domestic industries need protection because it is not yet ready to compete.
National Security argument.
A nation should not be dependent on other countries for defense.
Employment argument.
Job increases in protected industries.
Cheap foreign labor argument.
Other countries have cheaper labour, it is difficult to compete.
How do we use incentives to reduce the number of cars driving into Colombo?
The American Housing Crisis was a major component of the Global Financial Crisis.
Explain what happened.
Private Medical Colleges is a good for the country, discuss.
Up until 2000 – The Diamond Industry was run as a monopoly by South African company
De Beers. Give a history of diamonds and how they managed to maintain this monopoly.
http://www.forbes.com/athletes/list/
Athletes are paid millions of dollars. Are they being overpaid?
Using the concepts that we learned in class.
How do we ask for a salary increase?