The Nitrogen Cycle
advertisement

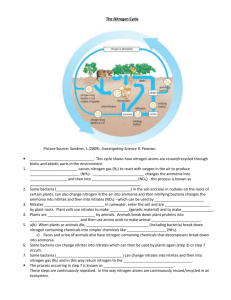
The Nitrogen Cycle: Who Cares? Nitrogen is an essential component of the amino acids that make up proteins and is a basic element of living things. Elements Essential for Life Carbon, Oxygen, and Hydrogen: needed to create sugars (C6H12O6)& carbohydrates. These are used for energy by living things Carbon, Oxygen, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen: needed to create amino acids & proteins. These are used for building tissue by living things. Nitrogen, Nitrogen Everywhere! 78% of our atmosphere is made up of nitrogen. Atmospheric nitrogen is N2 Most organisms can NOT use N2 because of its strong triple bonds (N=N) Nitrogen in the atmosphere must be chemically changed into a form that living things can absorb Nitrogen must be changed into nitrates (NO3) or ammonia (NH4) How Nitrogen is Fixed into a Usable Form Nitrogen Fixation: the process used to transform atmospheric nitrogen in to a usable form Accomplished by bacteria like (i.e. Rhizobia) and bluegreen algae A group of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in soil converts nitrogen into nitrate (NO3) Rhizobia are the most important of the nitrogenfixing bacteria that live in nodules on the roots of legumes like the pod-bearing plants such as soybeans, peas, beans, and alfalfa Rhizobia Watch this! Atmosphere Nitrogen-fixingBacteria Bacteria Nitrogen-fixing Denitrifying nitrates to change NBacteria to roots Nitrate (NO3)again… ofconvert 2on And(Rhizobia) so begins the cycle legumes nitrogen gas in(Nnodules 2) and return it back to the atmosphere (70% of air is made of N2) N2 (Nitrogen Gas) Legume Plant (Nitrogen Gas) Nitrate NO NO33 N2 Denitrifying Bacteria Atmosphere Nitrogen-fixingBacteria Bacteria Nitrogen-fixing Denitrifying nitrates to change NBacteria to roots Nitrate (NO3)again… ofconvert 2on And(Rhizobia) so begins the cycle legumes nodules gas (N return nitrogen to the 2) and in atmosphere N2 (Nitrogen Gas) Legume Plant (Nitrogen Gas) Nitrate NO NO33 N2 Denitrifying Bacteria Nitrogen Cycle Like legume plants, lightning can fix nitrogen too N2 Nitric Acid N2O Nitrifying Bacteria Other specialized bacteria convert the ammonia into nitrites (NO2 ) and then nitrates (NO3 ) Plants can only absorb nitrates or ammonium This happens through their roots and are then passed on to organisms that eat them Denitrifying Bacteria All of these activities would tend to stockpile nitrogen in the soil if it were not for another set of microorganisms Denitrifying bacteria are organisms that break down nitrogen-containing substances and return N2 gas back into the atmosphere More Bacteria in the Nitrogen Cycle! One of the major sources of nitrogen containing materials comes from waste products of animals (feces and urine) and from the decomposition of dead animals and plants. Bacteria convert these nitrogen-containing wastes into ammonia (NH3 ) and ammonium (NH4 ) Nitrogen Cycle A Smaller Cycle within the Nitrogen Cycle Legume Plant NO3 Nitrate Wastes or dead Animal animal/plant matter is/are decomposed Nitrifying Bacteria Feces & Urine (NH4) Eutrophication Watch this… Homework! Read pages 57-60 and 63 Answer the following questions What are the 5 human impacts and how do they affect the nitrogen cycle? Name three ways in which nitrogen can be fixed