Chapter 10
advertisement

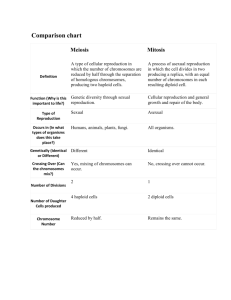
Chapter 10 Sexual Reproduction and Genetics Chapter 10.1 Meiosis Chromosomes Structures that contain the genetic material that is passed from generation to generation of cells. Homologous Chromosomes – make up a pair. Human body cells have 46 chromosomes, each parent contributes 23 chromosomes. 23 pairs of chromosomes per cell. Carry genes that control the same inherited traits. Genes – segments on the DNA that determine the characteristics and functions of the cell. Haploid vs. Diploid Cells Gametes – sex cells that have half the number of chromosomes Haploid (n) Cells – cells with only one set of chromosomes In humans this would be 23 Diploid (2n) Cells – cells with 2n number of chromosomes This is done to maintain the same number of chromosomes from generation to generation. In humans this would be 46 Fertilization – process in which a a haploid gamete combines with another haploid gamete. Sexual v. Asexual Reproduction Read the section Sexual Reproduction v. Asexual Reproduction on p. 276. Compare and contrast these types of reproduction by recreating the table in your notebook. Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction Sexual v. Asexual Reproduction Read the section Sexual Reproduction v. Asexual Reproduction on p. 276. Compare and contrast these types of reproduction by recreating the table in your notebook. Sexual Reproduction • Two parents • Offspring are genetically different from parents • Genetic variation each generation • Most Plants & Animals Asexual Reproduction • One parent • Offspring are genetically identical to parent • Bacteria (and most protists) Meiosis Process in which gametes are formed. Type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes; called a reduction division. Reduces chromosome number by the separation of homologous chromosomes. 2n n Occurs in the reproductive structures of organisms that reproduce sexually. Involves two consecutive cell divisions called meiosis I and meiosis II Animations http://www.biostudio.com/d_%20Meiosis.htm http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/celldivision/meiosis .swf http://www.sumanasinc.com/webcontent/animations/content/meiosis .html http://www.cellsalive.com/meiosis.htm http://www.johnkyrk.com/meiosis.html http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/olcweb/cgi/pluginpop.cgi?it=swf::535::535::/sites/dl/free/0072 437316/120074/bio16.swf::Unique Features of Meiosis Meiosis I Interphase and Meiosis I Meiosis II Crossing over During prophase, the homologous chromosomes exchange segments of DNA Mitosis and Meiosis Mitosis Meiosis One division Two divisions (meiosis I and II) DNA replication during interphase DNA replication during interphase Homologous chromosomes do NOT pair up Homologous chromosomes pair up Daughter cells are genetically identical Daughter cells are not genetically identical (crossing over occurs) Mitosis occurs in body cells only Meiosis occurs in reproductive cells Mitosis involved in growth and repair Meiosis involved in producing gametes and increasing genetic variation