MarketStructures.PerfectImperfect
advertisement

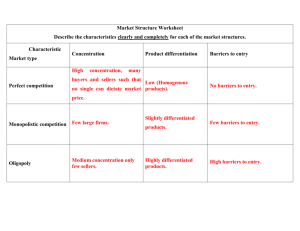
FrontPage: NNIGN LAWTON, Okla.-Strange moments for a local restaurant Friday night when one patron couldn't pay for her dinner or drinks. Police say Kristi Rhines ordered several alcoholic drinks and food at El Chico in Lawton but later said she had no way to pay for them. She told managers her husband was on his way to pick up the tab. When asked about her husband, she told them she was legally married to Jesus Christ, but had no marriage license. She also told management that Jesus would be able to walk in and produce U.S. currency to pay for her bill. Police confirmed that Rhines had no way of paying for her tab. She was booked into the Lawton City Jail on a complaint of fraud. Woman arrested claiming Jesus Christ will pay her restaurant tab The Last Word: No homework Chapter 7 • Terms used to describe the level of competition in a market. • Perfect Competition • Imperfect Competition • Monopoly • Monopolistic Competition • Oligopoly • 1. Many buyers and sellers: – A large number of buyers and sellers ensures that no one controls prices. • 2. Standardized product: – All products are essentially the same. • 3. Freedom to enter and exit markets: – Producers can enter or exit the market with no interference. • 4. Independent Buyers and Sellers: – Buyers and sellers do not band together to influence prices. • 5. Well-informed buyers and sellers: – Both buyers and sellers know the market prices and other conditions. • Monopoly – Types of monopoly • Monopolistic competition • Oligopoly • 1. Only One Seller: – A single business controls the supply of a product that has no close substitutes. • 2. A Restricted, Regulated Market: – Govt. regulations or other barriers to entry keep other firms out of the market. • 3. Control of Prices: – Monopolies act as price makers because they sell products that have no close substitutes and they face no competition. • Natural monopoly: – Occurs when the costs of production are lowest with only one producer. – May occur because of economies of scale – the avg. cost of production falls as the producer grows larger • Government monopoly: – exists when the govt. either owns and runs the business or authorizes only one producer. • Technological monopoly: – occurs when a firm controls a manufacturing method, invention, or type of technology. • Geographic monopoly: – Exists when there are no other producers within a certain region. • 1. Many buyers and sellers: – Fewer sellers than perfect comp., but still enough for meaningful competition. • 2. Similar but differentiated products: – Use brand name and advertising to differentiate from competitors Big N’ Tasty Whopper Classic • 3. Limited Control of Price: – Product differentiation gives producers some control over what they charge. • 4. Freedom to Enter or Exit Market: – Does not require huge amounts of capital; can sell off equipment and other assets if doing poorly • Five Guys Burgers with Fast Food Mania • 5 Questions for Five Guys from Forbes Oligopoly • 1. Few Sellers and Many Buyers: – A few firms dominate the market – Exists if top 4 firms control at least 40% of market Oligopoly • 2. Standardized or Differentiated Products: – Standardized: steel, aluminum, glass – Diff.: cereals, soft drinks Oligopoly • 3. More control of prices: – Because there are few sellers, they have more control than in monopolistic comp. – However, price changes will affect whole market. – Less likely to compete based on price. Oligopoly • 4. Little Freedom to Enter or Exit Market: – Start-up costs are extremely high for factories, warehouses, etc. – Existing firms may also hold patents # of Type of Product Seller’s Sellers Control over Prices Perfect Many Standardized Competition Monopolistic Many Similar, but Competition differentiated Oligopoly Few Monopoly One Barriers to Enter or Exit Market None Few Limited Few Standardized for Some Many industry, differentiated for consumers Standardized, Significant Very but no close Many substitutes • Market Structure with MJMFoodie