Cheat Sheet for Intubation and Ventilation
advertisement
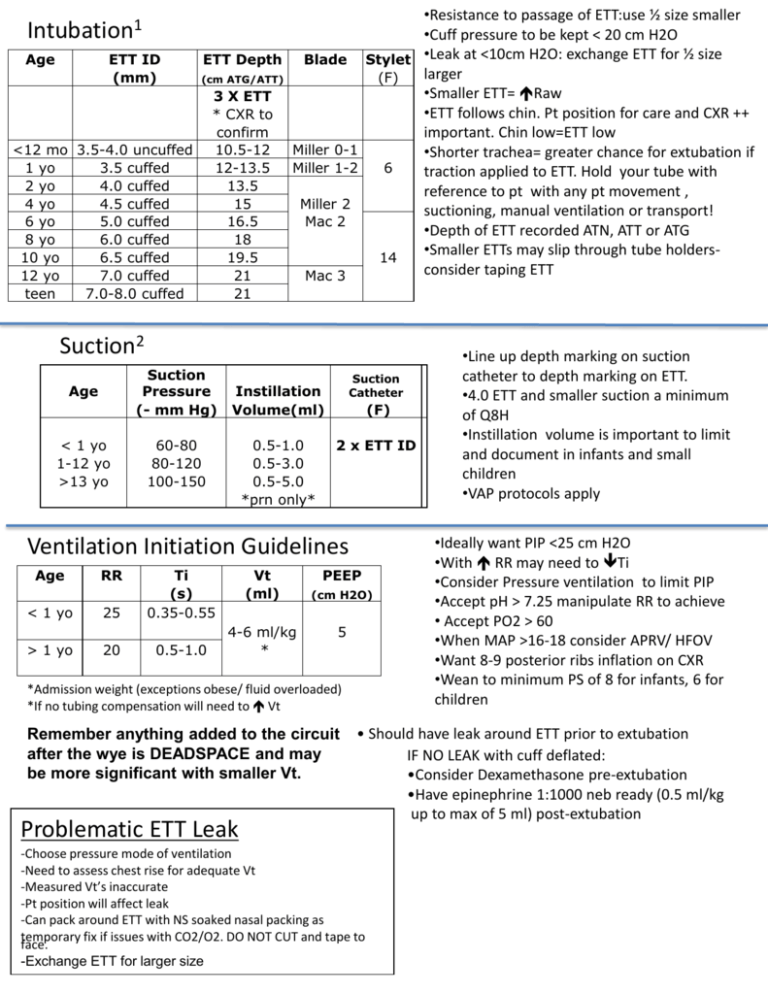
•Resistance to passage of ETT:use ½ size smaller •Cuff pressure to be kept < 20 cm H2O Age ETT ID ETT Depth Blade Stylet •Leak at <10cm H2O: exchange ETT for ½ size larger (mm) (F) (cm ATG/ATT) •Smaller ETT= Raw 3 X ETT •ETT follows chin. Pt position for care and CXR ++ * CXR to confirm important. Chin low=ETT low <12 mo 3.5-4.0 uncuffed 10.5-12 Miller 0-1 •Shorter trachea= greater chance for extubation if 1 yo 3.5 cuffed 12-13.5 Miller 1-2 6 traction applied to ETT. Hold your tube with 2 yo 4.0 cuffed 13.5 reference to pt with any pt movement , 4 yo 4.5 cuffed 15 Miller 2 suctioning, manual ventilation or transport! 6 yo 5.0 cuffed 16.5 Mac 2 •Depth of ETT recorded ATN, ATT or ATG 8 yo 6.0 cuffed 18 •Smaller ETTs may slip through tube holders10 yo 6.5 cuffed 19.5 14 consider taping ETT 12 yo 7.0 cuffed 21 Mac 3 Intubation1 teen 7.0-8.0 cuffed 21 Suction2 Suction Pressure (- mm Hg) Age < 1 yo 1-12 yo >13 yo Suction Catheter Instillation Volume(ml) 60-80 80-120 100-150 0.5-1.0 0.5-3.0 0.5-5.0 *prn only* (F) 2 x ETT ID Ventilation Initiation Guidelines Age < 1 yo > 1 yo RR 25 20 Ti (s) 0.35-0.55 0.5-1.0 Vt (ml) 4-6 ml/kg * PEEP (cm H2O) 5 *Admission weight (exceptions obese/ fluid overloaded) *If no tubing compensation will need to Vt Remember anything added to the circuit after the wye is DEADSPACE and may be more significant with smaller Vt. Problematic ETT Leak •Line up depth marking on suction catheter to depth marking on ETT. •4.0 ETT and smaller suction a minimum of Q8H •Instillation volume is important to limit and document in infants and small children •VAP protocols apply •Ideally want PIP <25 cm H2O •With RR may need to Ti •Consider Pressure ventilation to limit PIP •Accept pH > 7.25 manipulate RR to achieve • Accept PO2 > 60 •When MAP >16-18 consider APRV/ HFOV •Want 8-9 posterior ribs inflation on CXR •Wean to minimum PS of 8 for infants, 6 for children • Should have leak around ETT prior to extubation IF NO LEAK with cuff deflated: •Consider Dexamethasone pre-extubation •Have epinephrine 1:1000 neb ready (0.5 ml/kg up to max of 5 ml) post-extubation -Choose pressure mode of ventilation -Need to assess chest rise for adequate Vt -Measured Vt’s inaccurate -Pt position will affect leak -Can pack around ETT with NS soaked nasal packing as temporary fix if issues with CO2/O2. DO NOT CUT and tape to face. -Exchange ETT for larger size Normal Vital Signs1 Age <12 mo 1-3 years 3-5 years 6-12 years 13-18 years RR BP* HR awake HR asleep 30-60 24-40 22-34 18-30 12-16 87-105/53-66 95-105/53-66 95-110/56-70 97-112/57-71 112-128/66-80 100-190 80-160 70-140 60-110 60-90 75-160 60-90 60-90 60-90 50-90 •*Lower limit of SBP =70 + (2 x age in years) •Infants and small children don’t like strangers. RR, BP and HR will . Evaluate prior to entering room if possible •Respiratory failure is 1° cause of cardiac collapse. Intervene early. •Children have large compensation capacity. Must recognize shock early. Too late once decompensated. Signs of WOB •↑RR, Apnea •Nasal flaring •Head bobbing •Seesaw respirations •Accessory muscle use •grunting •Chest retractions •Tracheal tug CPR Guidelines1 Maneuver Adult Child Infant Adolescent and older 1 year old - adolescent < 1 year old Rescue Breathing without CPR 10-12 breaths/min (~ 1 breath every 5-6sec) 12-20 breaths/min (~ 1 breath every 3-5 sec) 12-20 breaths/min (~1 breath every 3-5 sec) Compression-ventilation ratio 30:2 for 2 rescuer 15:2 for 2 rescuer 15:2 for 2 rescuer Compression landmark Center of chest, between nipples Center of chest, between nipples Just below nipple line Compression Method 2 hands 2 hands or 1 hand: 2 thumb with encircling hands Compression Depth 1 ½-2” 1/3-1/2 depth of chest 1/3-12 depth of chest Compression rate 100 /min 100/min 100/min Airway/anatomy differences (adult pattern by ~8 years of age) Obligate Nose breather (<6 months) Poor tolerance to nasal obstruction Large Tongue -Neck extension may not relieve obstruction -More difficult to get tongue out of visual field for intubation Large head in proportion to body -Anterior flexion due to large occiput, -When supine may cause airway obstruction Large U-shaped epiglottis -More acute angle with vocal cords -More susceptible to trauma Larynx More anterior and cephalad Cricoid -Narrowest part of airway -↑ Raw with edema/infection Trachea -Small diameter, high compliance -Collapses easily with neck hyperextension or hyperflexion -↑ Raw with edema/infection Alveoli -↑ closing capacity - No pores of Kohn= ↑air trapping and ↓ collateral ventilation Chest Wall -↑ A-P diameter, horizontal ribs, rely on RR to increase VE -↑ compliance due to weak rib cage, FRC determined by elastic recoil of lungs Respiratory Muscles -Diaphragm is primary muscle used -accessory muscles weak and ineffective