PowerPoint Presentation - The Unifications of Italy and Germany
advertisement

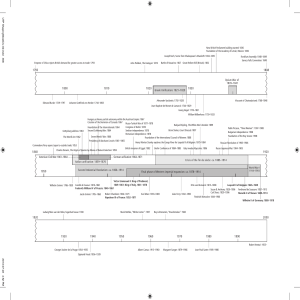
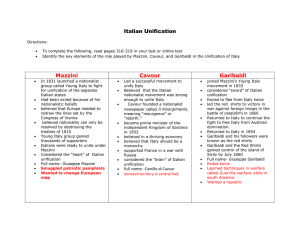
The Unifications of Italy and Germany Why Did Italy Unite • The Spread of Nationalism • Revolutions of 1848: Liberalism and Nationalism Split • Defeat of Russia in Crimean War • Isolation of Austria • Re-emergence of France under Napoleon III Italy Becomes a Nation-State • Giuseppe Mazzini (1805-1872) • Revolutionary democrat • Republican Maps Giuseppe Garibaldi (1807-1882) • • • • Republican Revolutionary Military leader guerilla fighter Count Camillo Benso di Cavour (1810-1861) • Sardinian nobleman • Prime minister of Sardinia-Piedmont • King Victor Emmanuel II (18491861) • Conservative • Ambitious • Pragmatic Before and After Napoleon III, Emperor of France (1808-1873; r. 1848-1870) • • • • Nephew of Napoleon Re-emerging French Empire Sounded democratic Believed in personal rule and a centralized state • Made a deal with Cavour: • France promised Nice and Savoy (from Piedmont) • Sardinia promised Lombardy and Venetia (from Austria) Unification Of Italy Timeline 1859 1860 1860 May 1860 1861 Austria goes to war against SardiniaPiedmont (and France) Napoleon bails, but Austria cedes Lombardy Plebescites in Tuscany, Parma, and Modena Garibaldi and thousand Red Shirts go to Sicily Kingdom of Italy declared (King Victor Emmanuel) Massimo d'Azeglio • First speaker of the new Italian Parliament: “We have made Italy, now we must make Italians!” 1.5 page essay • What makes an American different from a citizen of another nation? What makes an American have that national identity? • Is nationalism good or bad? Why? • What’s the purpose of nationalism? When can it be constructive? When can it be destructive? Unification of Germany, 1864-1871 • Otto von Bismarck (1815-1898) • Junker • Brilliant diplomat • “Blood and iron” • Not revolution • 1862 became Minister-President More on Bismarck • Social Security and Employee Welfare • Able to unify the state by promising improved economic opportunities • Leaves office when Kaiser Wilhelm II takes power The German Confederation 1815 Unification of Germany (cont.) • William I, King of Prussia (r. 1861-1888) • Schleswig-Holstein (1864) – Two disputed territories (Denmark) • Austro-Prussian war of 1866 – The Seven Weeks’ War • Austria had been the rival for the goal of German Unification Franco-Prussian War of 1870-71 • January 18, 1871: Second German Empire (Reich) declared in the Palace of Versailles, Hall of Mirrors Unification of Germany Conference of Berlin • 1884 • European leaders met together to divide up Africa peacefully • Africans had no say in the agreement • Only 2 African countries were not colonized by 1914.