Formation of Gametes: Meiosis
advertisement

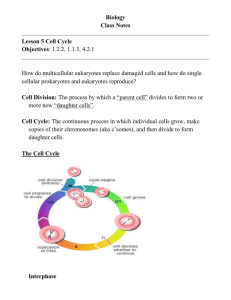
Meiosis: reduction division that results in half the number of chromosomes to make sex cells (gametes) What’s a gamete? Male = sperm consists of the nucleus (in the head), a tail, and mitochondria for energy Female = eggs Nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes and a reserve supply of food for developing organism What is ploidy when referring to cells? The number of chromosome sets within a cell Each set is designated n so one set is n is haploid, two sets is 2n is diploid, three sets is 3n is triploid, four sets is 4n is tetraploid, How are gametes different from somatic cells? Somatic cells Gamete cells Body cells Sex cells 46 c’somes 23 c’somes Diploid – 2 sets of Haploid- only 1 set of chromosomes c’somes Meiosis consists of ONE replication of c’somes followed by TWO divisions MEIOSIS I Homologous chromosomes separate This never happens in mitosis Results in two daughter cells with the same # of c’somes as parent 2n n Crossing over occurs MEIOSIS II Each of the two daughter cells again separate its chromosomes (without copying like between 2 events of mitosis) Results in 4 daughter cells with ½ the # of c’somes as the parent cell In males: all 4 cells become sperm spermatogenesis In females: one cell becomes an egg, the other 3 die oogenesis Comparison of Mitosis & Meiosis Mitosis Results in 2 daughter cells Meiosis Results in 4 daughter cells Daughter cells are diploid Daughter cells are haploid Daughter cells are identical to each other and to parent Daughter cells are different from each other and from parent Lets talk about CROSSING OVER Happens in Prophase of Meiosis I Paired Homologous chromosomes exchange genes while next to each other You don’t inherit entire chromosomes from your parents— only pieces of them Produces new combinations of genes creating more variation and diversity within a species Important for natural selection and evolution Crossovers are completely random! Determination of Sex Females: two X chromosomes (XX) Males: XY All offspring receive an X chromosome from mom and either an X or a Y from dad X chromosome: Essential for LIFE Y chromosome: Not essential for life large and contains thousands of genes Small and contains only 23 genes CHECK YOUR UNDERSTANDING What are the male and female gametes? How many chromosomes does a gamete have? What is the ploidy of a gamete? When does crossing over occur? Why is it important? How many sperm cells are formed by meiosis of one cell? How many egg cells? Summarize the differences between mitosis and meiosis What sex chromosome is always passed down by a mother? What 2 sex chromosomes may be passed down by a father?