Layer(s) PDU
advertisement

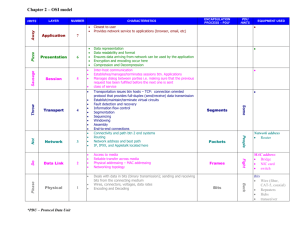
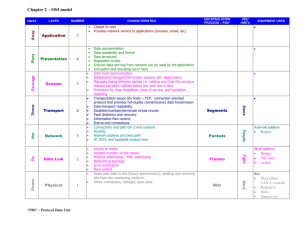
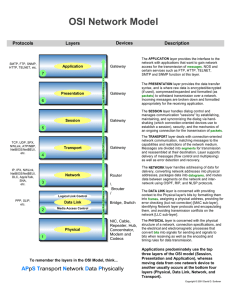
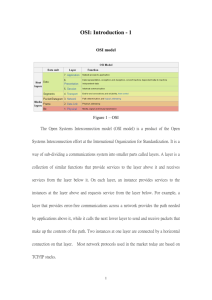
BCIS 4630 Fundamentals of IT Security NETWORKING (1) Dr. Andy Wu OSI Model • Network communications protocols are developed using the Open System Interconnection (OSI) model. • An ISO standard for worldwide communications. • The OSI model defines a framework for implementing protocols in seven distinct layers. • Each layer makes use of the services of the layer below it to provide a set of specific services to the layer above it. • Adjacent layers communicate with each other through a welldefined interface, so that in principle, we could change one layer or even completely rewrite it without affecting the others. 2 OSI Layers Layer Function Examples Application User interface Program level communication HTTP, SMTP Presentation Presentation format of data Data conversion if needed ASCII, JPEG, MP3, Encryption Session Establish and maintain communication channels OS, Application access scheduling Transport Reliable or unreliable end-to-end communication Identifies upper layer processes that will receive data TCP, UDP, SPX Network Logical addressing and routing Delivering packets from source to destination IP, IPX Data Link Transforming physical layer into a reliable link and presenting it to upper layers Includes MAC (802.3) and LLC (802.2) sublayers Ethernet Physical Transmission of bit stream over physical medium Signaling EIA/TIA 568B 3 OSI Mnemonic Away Application Pizza Presentation Sausage Session Throw Transport Not Network Do Data Link Please Physical 4 Encapsulation • When data is passed down from higher layers to lower ones, each layer creates its header and places the data given to it by the next-higher layer behind its own header, thereby encapsulating the higher layer’s data. • The Data Link layer also creates a trailer. 5 Encapsulation – Layer 4 6 Encapsulation – Layer 3 7 Encapsulation – Layer 2 8 Network Communication 9 Decomposition – Layer 2 10 Decomposition – Layer 3 11 Decomposition – Layer 4 12 Protocol Data Unit • A term that describes a set of bytes that includes the layer’s header and trailer (if any) and all data encapsulated. • From Layer X’s perspective, the higher-layer headers and the user data form one large data field. Layer(s) PDU Application, Presentation, Session Data Transport TCP Segment UDP Datagram Network IP Packet Data Link Frame Physical Bit 13