Thresholds
advertisement

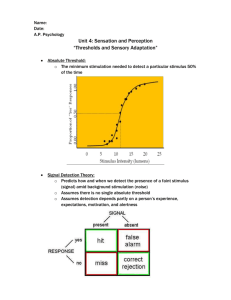
Thresholds Types of Threshold • A Threshold is an edge or a boundary • Psychologists are interested in our boundaries/thresholds when it comes to our senses. • What’s the bare minimum we can sense? Absolute Threshold •The minimum stimulation necessary for a person to detect a particular stimulus 50% of the time. (see table for examples) half an inch. Difference Threshold • The minimum difference that a person can detect between two stimuli 50% of the time. • Also called just noticeable difference Absolute Threshold vs. Difference Threshold • If you put your hand on a burner and turned it on, the first time you felt something would be Absolute Threshold and the second you noticed it getting hotter would be Difference Threshold. • • Weber’s Law Weber’s Law – detection of a stimulus depends on the original stimulus itself. Example: If a 300 lb. person loses 20 lbs and a 120 lb. Person loses 20 lbs, which one would you notice lost the weight first? (120 lbs because 20 lbs is a larger % of their body weight) Signal Detection Theory • • This theory replaced Weber’s Law Whether or not you detect a stimulus is dependent upon three kinds of variables: 1. Stimulus variables (how weak or strong the stimulus is) 2. Environmental variables (what’s going on around you) 3. Organismic variables (Your own experience, expectations, motivation and alertness) Thresholds: Signal Detection Theory • Set of formulas and principles that predict when we will detect the presence of a faint stimulus (signal) amid background stimulation (noise) • Developed out of the Cold War • Seeks to understand why people respond differently to the same stimuli and why the same person’s reactions would vary as circumstances change. • Example: Tired parents of newborns will awaken to a whimper but sleep through their alarm. Signal Detection Theory This can be used for jobs that depend on one’s ability to accurately detect a threat/stimulus. (Cold War Nuke Detection, Airport Security, Cancer Doctor) Signal Present Absent Says “No” Miss: Person did not detect signal Responder Says “Yes” Hit: False Alarm: Person correctly No signal but detected signal person said yes Correct Rejection: Person correctly noticed there was no signal Signal Detection Theory Signal Present Responder Hit Signal Absent False Alarm Present Hit Absent False Alarm Says “Yes” 30 Miss 30 Corr. Rej. 20 Miss 20 Corr. Rej. Says “No” 20 20 Liberal: Person more likely to correctly detect A signal but also more likely to falsely detect a signal. 30 30 Conservative: Person less likely to detect a signal but more likely to correctly notice when stimulus is not there. Sensory Adaptation Sensory Adaptation • Diminished sensitivity as a result of constant stimulation • If a stimulus is constant and unchanging, eventually a person may fail to respond to it • Move your watch up your wrist an inch or put your ring on a different finger. You will feel it at first but later you won’t notice it. Your senses have adapted to it. • This is why the lake water is cold at first but you “get used to it.” • Also why you don’t feel your glasses on your nose or your clothes on your body. • Remember the displacement goggles experiment from class. This showed motor adaptation to a change in vision. Selective Attention Selective Attention • Focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus to the exclusion of others • The ability to focus on one stimulus at a time • Allows a person to function in a world filled with many stimuli • People with ADD have trouble doing this. Read the following words to yourself •Did you notice that the word “the” was written twice? •If not, it shows how your brain was selectively paying attention to the meaning of what you were reading and not what was actually written. Read the following words to yourself •Did you notice that the word “the” was written twice? •If not, it shows how your brain was selectively paying attention to the meaning of what you were reading and not what was actually written. Selective Attention: An Example • View this updated version of Neisser’s Selective Attention Test basketball video clip below. Count the number of passes made by the girls in white. (click HERE to start) Did you notice the lady walk across the room with the umbrella? No! You were too busy watching & counting the passes. Try these: http://www.dothetest.co.uk/