The Circulatory System
advertisement

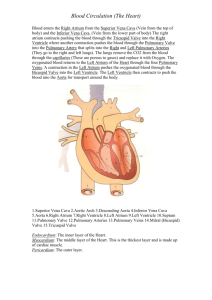
7 th Grade Health Chapter 3 Lesson 3 Circulatory System: the group of organs and tissues that act as transfer stations carrying needed materials to cells and removing their waste products Also known as the Cardiovascular System Cardio: Heart Vascular: Blood Vessels Circulatory System includes: Heart: made up of cardiac muscle Blood Vessels: made up of smooth muscle Blood Cardiac Tissue Smooth Tissue Arteries Veins Capillaries carry blood away from the heart to various parts of the body Blood rich in Oxygen Red in most diagrams carry blood from all parts of the body back to the heart Oxygen depleted blood Blue in most diagrams tiny blood vessels that carry blood to and from almost all body cells and connect arteries to veins Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide exchange takes place in the capillaries Your body contains five liters of blood Plasma: yellowish, watery part of blood which makes up over half of its volume Carries nutrients and hormones to cells Transports wastes to lungs and kidneys for removal 90% of plasma is water Red Blood Cells: carry oxygen from the lungs to all parts of the body Hemoglobin: protein that carries gases through the body White Blood Cells: fight infection in the body Create substances that destroy foreign cells Find and devour disease-causing organisms Platelets: help blood clot at the site of a wound Smallest type of blood cell Pulmonary Circulation: blood travels from the heart, through the lungs, and back to the heart Systemic Circulation: oxygen-rich blood travels to all body tissues except for the lungs The Blood from the body (low oxygen) is emptied in to the Right atrium through the Superior and Inferior Vena Cava RA Lungs LA Right Atrium Left Atrium RV Right Ventricle Lungs LV Left Ventricle Blood from Upper Body Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Blood from Lower Body RA LA RV LV From the Right Atrium, blood is emptied into the Right Ventricle through the Tricuspid valve Valve From the Right Ventricle, blood is pumped into the Pulmonary Artery through the Pulmonary valve, to the lungs, to pick up oxygen Pulmonary Artery Valve Carbon Dioxide released In the lungs, Carbon Dioxide is released and Oxygen is picked up into the blood From the lungs, blood is emptied into the Left Atrium through the Pulmonary Veins Pulmonary Vein Blood is now rich in Oxygen From the Left Atrium, blood is emptied into the Left Ventricle through the Bicuspid valve Valve From the Left Ventricle, blood is pumped into the Aorta, largest artery in the body, through the Aortic valve, then throughout the body Blood to Upper Body Aorta Valve Aorta Blood to Lower Body Atriums: store blood Ventricles: pump blood Blood from Upper Body Blood to Upper Body Superior Vena Cava Pulmonary Artery Pulmonary Vein Red: rich in O Blue: O depleted Aorta Inferior Vena Cava Blood from Lower Body Blood to Lower Body This process is repeated over and over again. When the process is interrupted, serious health conditions can occur. The force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels Systolic blood pressure: Top number; heart is contracting Diastolic blood pressure: Bottom number; heart is at rest and refills with blood Normal Blood Pressure is 120 80 There are four types of blood A, B, AB, O Used primarily in cases of blood donation Incompatible blood that is mixed, leads to clumping and blockage of vessels Type O is universal donor Problem Hypertension Heart Attack Anemia Description Abnormally high blood pressure in the arteries of the body Blood supply to the heart is stopped or reduced RBC count and hemoglobin is below normal Treatment Treated or prevented by losing weight Must be treated by a medical professional B-12 vitamin and iron supplements Sickle Cell Anemia Leukemia Hemophilia RBC’s are sickle shaped containing abnormal hemoglobin Cancer in tissues that produce WBC’s No cure; frequent hospitalization Blood doesn’t clot or clots very slowly Blood transfusions Chemotherapy