cardiovascular systemthree
advertisement

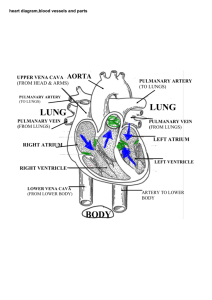
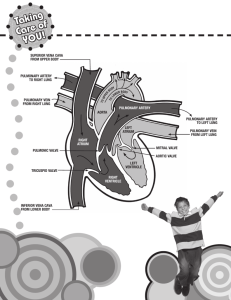
Aim # : The Cardiovascular System Do Now: How does your heart rate change? Why would your heart rate change as you sleep, walk to class, ride a roller coaster, run a marathon? The cardiovascular system • Cardio means heart • Vascular means vessel • Includes your heart, blood, vessels • Types of Blood Vessels • Arteries – moves blood away from the heart. • Veins – moves blood to the heart. Has valves. • Capillaries – microscopic blood vessels that connect arteries to veins. One cell thick. • Blood Pressure – the force blood exerts on the walls of the vessels Cardiovascular Disease • Atherosclerosis – fatty deposits on arterial walls. Clogged arteries doesn’t allow blood to flow properly • Hypertension – high blood pressure Heart • Has four chambers • 2 Upper chambers • Right Atrium • Left Atrium • 2 Lower chambers • Right Ventricle • Left Ventricle • Upper and lower chambers are separated by valves – doors that open and close to prevent and allow blood flow between chambers What happens during a heart beat? • Both atria contract at the same time • Valves open • Blood flows into ventricles • Both ventricles contract at the same time • Blood is pumped into aorta and pulmonary artery Why does your heart beat? • Moves oxygen and nutrients to cells • Removes carbon dioxide and other wastes from cells • The exchange happens through diffusion Where does the exchange occur? • Flood flows from the heart, to the lungs and back to the heart 1. Blood, high in carbon dioxide and low in oxygen, returns from the body to the heart. It enters the right atrium through the vena cava. 2. The right atrium contacts, forcing the blood into the right ventricle. 3. When the right ventricle contracts, the blood leaves the heart and goes through the pulmonary artery to the lungs. Here carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood and oxygen diffuses into the blood. 4. Oxygen rich blood travels through the pulmonary vein and into the left atrium. The pulmonary veins are the only veins to carry oxygen rich blood. 5. The left atrium contracts and forces the blood into the left ventricle. 6.The left ventricle contracts, forcing the blood out of the heart and into the aorta. • Systemic Circulation – moves oxygen rich blood to all organs and body tissues (except heart and lungs) • Coronary Circulation – the flow of blood to tissues of the heart (has its own blood vessels) Function • The main function of the respiratory system is to breathe and acquire oxygen, as well as to get rid of carbon dioxide . Breathing • A process whereby fresh air moves into and stale air moves out of lungs Path of Air • 1) Mouth or nose Nose has cilia hairs or mucus to trap dust and other particles • 2) Pharynx – back of mouth 2 tubes (back tube=esophagus Front tube=trachea) 3) Epiglottis*flap that stops food from entering airway 4) Larynx (voice box) *flexible bands of tissue*the bands vibrate when we speak, sing or whisper. 5) Trachea *tube through which air travels toward lungs 12 cm long, *C-shaped rings of cartilage 6) Bronchi *2 short branches at end of trachea *Each bronchi extends to a lung 7) Bronchioles*bronchi branch into smaller and smaller tubes called bronchioles 8) Alveoli • At end of each bronchiole • Tiny clusters of THIN sacs that can expand and contract • Capillaries surround alveoli to carry CO2 out of the blood and bring Oxygen to the blood Gas exchange occurs through diffusion Blood is a tissue • Adults have 5 Liters • Functions • Carries oxygen from lungs to all parts of the body • Removes carbon dioxide at lungs through exhaling • Carries waste products to kidneys • Transports nutrients • Materials in blood help fight infections • Helps heal wounds