Marine Invertebrates
advertisement

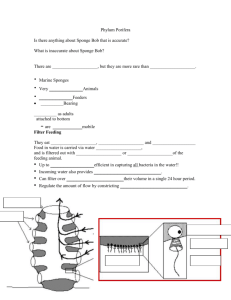
Sponges- Porifera Jellyfish, Hydroids, Corals, Sea Anemones – Cnidaria Comb Jellies- Ctenophora Chitons, Snails, Bivalves, Octopi, Squid, Nautilus, Nudibranchs, Cuttlefish- Mollusca - Sea Spider, Crabs, Shrimp, Krill, Amphipods, Copepods, Barnacles- Arthropods - Sea Stars, Ophiuroids, Sea Urchins, Sea Cucumbers, Crinoids- Echinodermata - Tunicates and Lancelets- Hemichordates - Marine Worms Considered an animal Simplest of all animals with many specialized cells Asymmetrical – no symmetry Variety of shapes and colors Evolved from a single celled Eukaryotic (Protistans) Loose aggregation of cells. Shapes may be determined by the shape of the sediment and water currents flowing by them. Calcarea are chalky sponges with calcium carbonate spicules Hexactinella includes glass sponges & the Venus flower basket with silica spicules Demospongiae include horny & bath sponges with only spongin or spongin & silica spicules Sclerospongiae are coral sponges & have spongin & silica and calcium carbonate spicule Built around a system of water canals. Body is full of tiny holes called pores or ostia, where large amounts of water circulate nutrients, oxygen, and remove waste. Water enters through the ostia -> carried to the spacious cavity called the spongocoel -> water then exits the spongocoel through a large opening called the osculum. Collar cells or choanocytes have a flagellum and when they all move it creates a great force which then moves the water through the sponge. Pinacocytes-> layer of cells that provide an outer covering for the sponge, lines the internal chambers. Archaeocytes-> resemble amoebas move throughout the sponges body can form into any cell important in repair and regeneration transport food Spicules-> Skeletal elements that give support to sponge’s body Made up of calcium carbonate, silica, or sponging (protein that allows the sponge to be flexible). Three different types The folded body has evolved to overcome the problem of water flow and surface area. The increased folds increase the surface area of the collar cells and reduce the spongocoel, which decreases the amount of water needed to be circulated. In the end it results in increased water flow and increased sponge growth. Asconoid Syconoid Simplest form First stages Clusters of body wall Tubular / folding Small Internal As it grows pockets of the collar cells. spongocoel increases. Leuconoid Highest degree of folding Largest sponges Pumps 5 gallons of water per day. Feed on bacteria, plankton, and detritus Suspension feeders-> feed on material that swims by. Filter feeders-> filter food from the water. Food is engulfed and digested by pinacocytes and archaeocytes along the canal system-> carry them-> 80% of the food gets trapped by the collar cells-> flagellum strains the food by the current created by the beating tails-> draws water in through the ostia and expels it through the osculum. Sexual and asexual Budding-> not common. Groups of cells on the outer surface of the sponge develop and grow into tiny new sponges. When it gets to a certain size the sponge drops off and either floats away or establishes itself near the parent. Fragmentation-> production of new cells that have been broken off by waves, storms, or predators. Hermaphrodites- produce both male and female gametes. Sperm cells- form from modified collar cells Eggs- archaeocytes / collar cells The stimulus that initiates the production of gametes = change in water temperature (photoperiod= amount of light / dark in 24 hours) Sperm cells-> enters-> engulfed by collar cells-> both lose flagella-> collar cell transports sperm to the egg. Amphiblastula- larval stage-> water column-> adult sponge Biggest problem- finding a suitable place to attach. They compete with corals and bryozoans. Some produce chemicals that kill corals or inhibit growth Boring Sponge – bores into corals and dead shells Crabs use pieces of sponge as camouflage -> sponge grows on the crabs shell Most are toxic to fish- few predators Sea turtles eat them yummy Hawksbill Symbiotic relationships: Mutualism- cyanobacteria-> food / nutrients / protection Commensalism- shrimp hide out in there until they are too big http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BW05vMziy2o http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T7E1rq7zHLc http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KOFFzXNYJG0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mVavqt4Sbyo