Vertebrates
advertisement

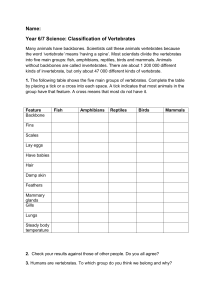
Vertebrates Karen Conlon-Riser Fall 2015 Target Audiences A homogenous group of 6th grade students at Horace Mann School, North Bergen, NJ Objectives SWBAT: identify the different characteristics of vertebrates Identify amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals cartilaginous fish Goals Students will choose vertebrates and tell their characteristic They will identify pictures of each type of vertebrate Identify vertebrates from facts about where it lives , what is eats, and if its able to keep its body temperature steady. Common Core Standards MS-LS1-5: Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how environmental and genetic factors influence the growth of organisms. [Clarification Statement: Examples of local environmental conditions could include availability of food, light, space, and water. Examples of genetic factors could include large breed cattle and species of grass affecting growth of organisms. Examples of evidence could include drought decreasing plant growth, fertilizer increasing plant growth, different varieties of plant seeds growing at different rates in different conditions, and fish growing larger in large ponds than they do in small ponds.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include genetic mechanisms, gene regulation, or biochemical processes.] Common Core Standards (cont.) MS-LS1-4: Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively. [Clarification Statement: Examples of behaviors that affect the probability of animal reproduction could include nest building to protect young from cold, herding of animals to protect young from predators, and vocalization of animals and colorful plumage to attract mates for breeding. Examples of animal behaviors that affect the probability of plant reproduction could include transferring pollen or seeds, and creating conditions for seed germination and growth. Examples of plant structures could include bright flowers attracting butterflies that transfer pollen, flower nectar and odors that attract insects that transfer pollen, and hard shells on nuts that squirrels bury.] Lesson Procedures 1. Student will be given notes from power points on the characteristics of vertebrates. Students will find pictures of each type of vertebrate based on the characteristics given. Student will play a game that they must identify the vertebrate from the clues that are given Lesson Procedures (cont.) http://www.kidscom.com/games/animal/animal.html Brain Bits Frontal lobe – problem solving in the game of identifying the animal based on clues Occipital lobe – looking at the game and well as the power point Temporal Lobe - music from both power points Parietal lobe – writing the note in notebooks – spatial orientation Learning Styles Concrete Sequential - would not like the game because they do not like to interpret abstract things Abstract Sequential would like the power point and writing the note because they like lecture and reading Learning Styles Abstract Random would love the game because they like cooperative work and assignments with interpretation. Concrete Random – would love the games because it is a hand-on experience and they love open-ending brainstorming (guessing of the animal in the game) Citations Gregorc, Anthony F. Inside Styles: Beyond the Basics : Questions and Answers on Style. Columbia, CT: Gregorc Associates, 1985. Print.