Exploration Timeline
advertisement

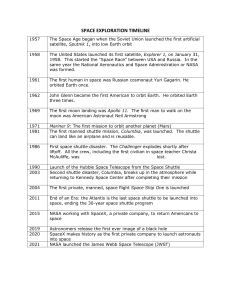
Exploration Timeline Jazzlynn Gamble Konstantin Tsiolkovsky • Born 1857; Died 1935; Lived in Russia • He did his scientific research in air balloon building, life in free space, aerodynamics and philosophy. • He wrote and published his theories of space flight and inter-planetary travels. In Kaluga he wrote his Cosmic Philosophy, and he dreamed about the far distant future of humanity, including the eventual conquest of space and our leaving the cradle of the planet Earth for the stars. Robert H. Goddard • • • • • • Born October 5, 1882(1882-10-05) in Worcester, Massachussetts Died August 10, 1945(1945-08-10) (aged 62) in Baltimore, Maryland Education: Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Clark University Occupation: Professor, rocket scientist, physicist, inventor Known for first liquid-fueled rocket, launched in Auburn, Massachussetts on March 16, 1926 The rocket, which was dubbed "Nell", rose just 41 feet during a 2.5-second flight that ended 184 feet away in a cabbage field. Sputnik • October 4, 1957 • Launched by Russia • The world's first artificial satellite • was about the size of a beach ball (58 cm.or 22.8 inches in diameter), weighed only 83.6 kg. or 183.9 pounds, and took about 98 minutes to orbit the Earth on its elliptical path. Redstone Rocket • The Mercury-Redstone rocket launch of Alan B. Shepard May 5, 1961 marked the first step in America's attempts to place a man on the moon. It also opened the door for Marshall Space Flight Center's Saturn rockets that put him there. • Took place at Cape Canaveral Moon Photograph • Five Lunar Orbiter missions were launched in 1966 through 1967 with the purpose of mapping the lunar surface before the Apollo landings. All five missions were successful, and 99% of the Moon was photographed with a resolution of 60 m or better. Neil Armstrong • • First man to walk on the moon,was born in Wapakoneta, Ohio, on August 5, 1930. He began his NASA career in Ohio. After serving as a naval aviator from 1949 to 1952, Armstrong joined the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) in 1955. His first assignment was with the NACA Lewis Research Center (now NASA Glenn) in Cleveland. Over the next 17 years, he was an engineer, test pilot, astronaut and administrator for NACA and its successor agency, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). He received a Bachelor of Science Degree in Aeronautical Engineering from Purdue University and a Master of Science in Aerospace Engineering from the University of Southern California. He holds honorary doctorates from a number of universities. Salyut 1 • Salyut 1 was the first space station put into orbit. The Soviets launched it from Baikonur Cosmodrome on April 19, 1971 using a threestage Proton launch vehicle. It completed 362 orbits before deorbiting and reentering the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean in October. It was destroyed by frictional heating during its return. Space Station • • • • A space station (also called an orbital station) is a manned satellite designed to remain in space (or most commonly low Earth orbit) for a long period of time, and which has the ability for other spacecraft to dock to it. Space stations are used to study the effects of long-term space flight on the human body as well as to provide platforms for greater number and length of scientific studies than available on other space vehicles. The first space station was Salyut 1, which was launched by the Soviet Union on April 19, 1971. The only space station currently in orbit is the International Space Station. Previous stations include the Almaz and Salyut series, Skylab and most recently Mir. Columbia Space Shuttle • The first re-useable space shuttle • Launched in 1981 by the United States. • It has three components - the orbiter space plane, rocket boosters, and external fuel tank - only the fuel tank is not recovered after a mission. Hubble Telescope • • • The Hubble Space Telescope was first scheduled for launch in 1986. But due the tragic loss of the shuttle Challenger in late January of that year, the launch was delayed four years. In April 24, 1990, the Hubble telescope was lifted into orbit aboard the shuttle Discovery. The telescope measures 13.1 m (43.5 ft) in length, 4.27 m (14.0 ft) in diameter, and weighs 11,000 kg (25,500 lb). It was launched from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Galileo • Galileo was an unmanned spacecraft sent by NASA to study the planet Jupiter and its moons. Named after the astronomer and Renaissance pioneer Galileo Galilei, it was launched on October 18, 1989 by the Space Shuttle Atlantis on the STS-34 mission. It arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, a little more than six years later