Chapter 13. Repeated
advertisement

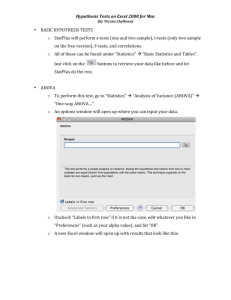
Repeated Measures ANOVA Quantitative Methods in HPELS HPELS 6210 Agenda Introduction The Repeated Measures ANOVA Hypothesis Tests with Repeated Measures ANOVA Post Hoc Analysis Instat Assumptions Introduction Recall There are two possible scenarios when obtaining two sets of data for comparison: Independent samples: The data in the first sample is completely INDEPENDENT from the data in the second sample. Dependent/Related samples: The two sets of data are DEPENDENT on one another. There is a relationship between the two sets of data. Introduction Three or more data sets? If the three or more sets of data are independent of one another Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) If the three or more sets of data are dependent on one another Repeated Measures ANOVA Agenda Introduction The Repeated Measures ANOVA Hypothesis Tests with Repeated Measures ANOVA Post Hoc Analysis Instat Assumptions Repeated Measures ANOVA Statistical Notation Recall for ANOVA: k = number of treatment conditions (levels) nx = number of samples per treatment level N = total number of samples N = kn if sample sizes are equal = SX for any given treatment level G = ST MS = mean square = variance Tx Repeated Measures ANOVA Additional Statistical Notation: P = total score for each subject (personal total) Example: If a subject was assessed three times and had scores of 3, 4, 5 P = 12 Repeated Measures ANOVA Formula Considerations Recall for ANOVA: = ST2/n – G2/N SSwithin = SSSinside each treatment SStotal = SSwithin + SSbetween SSbetween SStotal = SX2 – G2/N ANOVA Formula Considerations: =N–1 dfbetween = k – 1 dfwithin = S(n – 1) dftotal dfwithin = Sdfin each treatment ANOVA Formula Considerations: = s2between = SSbetween / dfbetween MSwithin = s2within = SSwithin / dfwithin F = MSbetween / MSwithin MSbetween Repeated Measures ANOVA New Formula Considerations: SSbetween treatments = ST2/n – G2/N SSbetween subjects = SP2/k – G2/N SSwithin SSwithin treatments = SSSinside each treatment SSerror = SSwithin treatments – SSbetween subjects SSbetween Repeated Measures ANOVA New Formula Considerations: dfbetween treatments = k – 1 dfwithin dfwithin treatments = N – k dfbetween subjects = n – 1 dferror = (N – k) – (n – 1) dfbetween Repeated Measures ANOVA MSbetween treatments=SSbetween treatments/dfbetween treatments MSerror = SSerror / dferror F = MSbetween treatments / MSerror Repeated Samples Designs One-group pretest posttest (repeated measures) design: Perform pretest on all subjects Administer treatments followed by posttests Compare pretest to posttest scores and posttest to posttest scores O X O X O Agenda Introduction The Repeated Measures ANOVA Hypothesis Tests with Repeated Measures ANOVA Post Hoc Analysis Instat Assumptions Hypothesis Test: Repeated Measuers ANOVA Example 14.1 (p 457) Overview: Researchers are interested in a behavior modification technique on outbursts in unruly children Four students (n=4) are pretested on the # of outbursts during the course of one day Teachers begin using “cost-response” technique Students are posttested one week later, one month later and 6 months later Hypothesis Test: ANOVA Questions: What is the experimental design? What is the independent variable/factor? How many levels are there? What is the dependent variable? Step 1: State Hypotheses Non-Directional H0: µpre = µ1week = µ1month = µ6months H1: At least one mean is different than the others Step 2: Set Criteria Alpha (a) = 0.05 Critical Value: Use F Distribution Table Appendix B.4 (p 693) Information Needed: dfbetween treatments = k – 1 = 4 – 1 = 3 dferror = (N-k)-(n-1) = (16-4)-(4-1) = 9 Table B.4 (p 693) Critical value = 3.86 Step 3: Collect Data and Calculate Statistic Total Sum of Squares Sum of Squares Between each Treatment SStotal = SX2 – G2/N SSbetween treatment = ST2/n – SG2/N SStotal = 222 – 442/20 SSbetween treatment = 262/4+82/4+62/4+42/4 – 442/20 SStotal = 222 - 121 SSbetween treatment = (169+16+9+4) - 121 SStotal = 101 SSbetween treatment = 77 Sum of Squares Within each Treatment Sum of Squares Error SSwithin = SSSinside each treatment SSerror = SSwithin treatments – SSbetween subjects SSwithin = 11+2+9+2 SSerror = 24 - 13 SSwithin = 24 SSwithin = 11 Sum of Squares Between each Subject SSbetween subjects = SP2/k – SG2/N SSbetween subjects = (122/4+62/4+102/4+162/4) - 442/16 SSbetween subjects = (36+9+25+64) – 121 SSbetween subjects = 13 Raw data can be found in Table14.3 (p 457) Step 3: Collect Data and Calculate Statistic F-Ratio F = MSbetween treatment / MSerror Mean Square Between each Treatment F = 25.67 / 1.22 MSbetween treatment = SSbetween treatment / dfbetween treatment F = 21.04 MSbetween treatment = 77 / 3 MSbetween = 25.67 Mean Square Error MSerrorn = SSerror / dferror MSerror = 11 / 9 MSwithin = 1.22 Step 4: Make Decision Agenda Introduction Repeated Measures ANOVA Hypothesis Tests with Repeated Measures ANOVA Post Hoc Analysis Instat Assumptions Post Hoc Analysis What ANOVA tells us: Rejection of the H0 tells you that there is a high PROBABILITY that AT LEAST ONE difference exists SOMEWHERE What ANOVA doesn’t tell us: Where the differences lie Post hoc analysis is needed to determine which mean(s) is(are) different Post Hoc Analysis Post Hoc Tests: Additional hypothesis tests performed after a significant ANOVA test to determine where the differences lie. Post hoc analysis IS NOT PERFORMED unless the initial ANOVA H0 was rejected! Post Hoc Analysis Type I Error Type I error: Rejection of a true H0 Pairwise comparisons: Multiple post hoc tests comparing the means of all “pairwise combinations” Problem: Each post hoc hypothesis test has chance of type I error As multiple tests are performed, the chance of type I error accumulates Experimentwise alpha level: Overall probability of type I error that accumulates over a series of pairwise post hoc hypothesis tests How is this accumulation of type I error controlled? Two Methods Bonferonni or Dunn’s Method: Perform multiple t-tests of desired comparisons or contrasts Make decision relative to a / # of tests This reduction of alpha will control for the inflation of type I error Specific post hoc tests: Note: There are many different post hoc tests that can be used Our book only covers two (Tukey and Scheffe) Repeated Measures ANOVA Bonferronni/Dunn’s method is appropriate with following consideration: Use related-samples T-tests Tukey’s and Scheffe is appropriate with following considerations: Replace MSwithin with MSerror in all formulas Replace dfwithin with dferror in all formulas Note: Statisticians are not in agreement with post hoc analysis for Repeated Measures ANOVA Agenda Introduction The Repeated Measures ANOVA Hypothesis Tests with Repeated Measures ANOVA Post Hoc Analysis Instat Assumptions Instat Label three columns as follows: Block: This groups your data by each subject. Treatment: This tells you which treatment level/condition occurred for each data point. Example: If you conducted a pretest and 2 posttests (3 total) on 5 subjects, the block column will look like: 111222333444555 Example: If each subject (n=5) received three treatments, the treatment column will look like: 123123123123123 Response: The data for each subject and treatment condition Instat Convert the “Block” and “Treatment” columns into “factors”: Choose “Manage” Choose “Column Properties” Choose “Factor” Select the appropriate column to be converted Indicate the number of levels in the factor Example: Block (5 levels, n = 5), Treatment (3 levels, k = 3) Click OK Instat Choose “Statistics” Choose “General” Response variable: Choose the Treatment variable Blocking factor: Choose the Response variable Treatment factor: Choose “Analysis of Variance” Choose the Block variable Click OK. Interpret the p-value!!! Instat Post hoc analysis: Perform multiple related samples t-Tests with the Bonferonni/Dunn correction method Reporting ANOVA Results Information to include: Value of the F statistic Degrees of freedom: Between treatments: k – 1 Error: (N – k) – (n – 1) p-value Examples: A significant treatment effect was observed (F(3, 9) = 21.03, p = 0.002) Reporting ANOVA Results An ANOVA summary table is often included Source SS df MS Between 77 3 25.67 Within Treatments 24 12 Between subjects 13 3 Error 11 9 Total 101 15 1.22 F = 21.03 Agenda Introduction The Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) Hypothesis Tests with ANOVA Post Hoc Analysis Instat Assumptions Assumptions of ANOVA Independent Observations Normal Distribution Scale of Measurement Interval or ratio Equal variances (homogeneity) Equal covariances (sphericity) If violated a penalty is incurred Violation of Assumptions Nonparametric Version Friedman Test (Not covered) When to use the Friedman Test: Related-samples design with three or more groups Scale of measurement assumption violation: Ordinal data Normality assumption violation: Regardless of scale of measurement Textbook Assignment Problems: 5, 7, 10, 23 (with post hoc)