The Nitrogen Cycle
advertisement

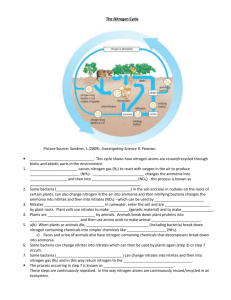
What makes fertilizer so successful in helping plants grow? Nitrogen It encourages growth of the vegetative parts of plants: • stems • leaves • roots Why is nitrogen so important to living components? •It makes up proteins, DNA and other compounds. •Without it, life wouldn’t exist The Nitrogen Cycle http://www.vtaide.com/png/nitrogenCycle.htm Explain the process of nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen gas (N2) must be “fixed” (attached) to make other compounds such as ammonium (NH3+) Explain the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria. • Bacteria that live in nodules on plant roots or in the soil which “fix” (attach) nitrogen to hydrogen so that plants can use it for growth Explain how nitrogen enters the food chain. 1. Nitrogen must first be fixed in the soil. 2. Then plants will absorb it through their roots and use it to make their tissues. 3. Primary consumers eat the plant and the nitrogen is passed on and becomes a part of the animal. 4. Producers, consumers, and their wastes are decomposed to release the nutrients to the environment once more. Explain how nitrogen can re-enter the food chain without nitrogen returning to the atmosphere. • The wastes of organisms and dead material are broken down by decomposers. • This produces ammonia which is converted to nitrate by nitrifying bacteria. • This nitrate is taken up by the plant to use again. Explain the roles of nitrifying bacteria and denitrifying bacteria. 1. Nitrifying bacteria: convert ammonium (NH3+) into nitrites (NO2-) and then nitrates (NO3-) which can be used by plants = Nitrification 2. Denitrifying bacteria: convert nitrates (NO3-) in the soil into nitrogen gas (N2) which is released to the atmosphere and oxygen (O2) which is available to the nitrifying bacteria = Denitrification