Dark Reactions ppt

Quaestio: What happens during the light-independent reactions?
Nunc Agenda:
1. Summarize the purpose of the light dependent reactions
2. What molecule is used, and what is released?
Main Idea
• The second stage of photosynthesis uses energy from the first stage to make sugars
The Dark Reactions.
• Also called light-independent reactions.
– They happen both when light is present and when light is absent.
• The dark reactions take place in the stroma.
• Carbon dioxide diffuses into the stroma through pores in a plant’s leaves (stomates) and is used to make glucose in a process known as carbon fixation.
– Uses the ATP and NADPH from light dependant reactions
The Pores in a plant’s leaf are called stomates (not to be confused with stroma)
Stomate Up Close
Carbon Dioxide Becomes Part of the
Plant After Entering the Stomates.
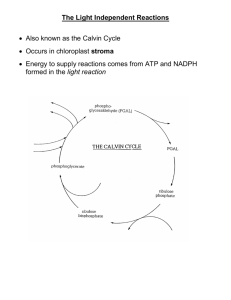
Carbon Fixation and the Calvin Cycle.
• Calvin Cycle: A series of enzyme-controlled reactions in which carbon fixation occurs.
– Named after Melvin Calvin, an American Scientist who won the Nobel prize in 1961 for his discovery of the cycle.
– Carbon Fixation: The process in which carbon dioxide is incorporated (fixed) into organic compounds by the processes of photosynthesis and chemosynthesis.
• Also called Carboxylation.
Melvin Calvin
Calvin holding a model of sucrose.
He had his own stamp!
The Specifics of the Calvin Cycle.
• The Calvin cycle starts and ends with RuBP, which is a five carbon sugar.
• RuBP stands for ribulose biphosphate.
• Carbon dioxide reacts with RuBP, creating two molecules of PGA (phosphoglyceric acid).
– This is the carbon fixation step.
Carbon Fixation
The steps of the Calvin cycle
1. 6 CO
2 enter the stroma
2. 6 CO
2
+ 6 RuBP 12 PGA (3-C)
– Catalyzed by rubisco
3. 12 PGA + ATP + NADPH 12 PGAL
4. 2 PGAL are removed and used to form glucose
5. 10 PGAL remaining are rearranged back into
6 RuBP and cycle start over with new CO
2
1.
2.
(The Dark Reaction)
3.
5.
4.
Calvin Cycle Summary.
• The Calvin cycle is part of the dark reactions.
• The Calvin cycle needs chemical energy produced in the light reactions (ATP and
NADPH)and carbon dioxide from the atmosphere to work.
• Two PGAL molecules form one glucose molecule.
– Need 6 CO
2 to make 1 glucose
• The Calvin cycle is a cycle because it starts and ends with RuBP.
Hard Questions To Answer
• Where does the O
2 from? (CO
2 or H
2
O)?
that plants release come
• Where does CO
2 go?
• Why do you think 10 PGAL molecules must be used to make 6 RuBP molecules to restore the
Calvin Cycle?
• How does the Calvin cycle build sugar molecules?
The light reactions drive the dark reactions.
Light
Reactions
Dark
Reactions
The Chemistry of the Chloroplast
The Light Reactions are also called the “Light-Dependent Reactions.”
The Dark Reactions are also called the “Light-Independent Reactions.”
Compelling Thought
• Without photosynthetic organisms, the food we eat and the air we breath would not exist. As a result, life on earth as we know it depends on the autotrophs.
• “What drives life is thus a little electric current, set up by the sunshine.”
– American biochemist and Nobel laureate Albert Szent-
Gyorgyi
Factors affecting Photosynthesis
• Can you name them?
Factors affecting Photosynthesis
• 1. Light Intensity.
• 2. Temperature.
• 3. Water Availability.
• 4. Mineral Availability.
The Carbon Cycle
• The Carbon Cycle: the pathways by which carbon is recirculated through the biosphere.
• *Not to be confused with the Calvin Cycle, which is part of a broader carbon cycle.
Critical Thinking
• Can you think of important ways human beings have altered or disrupted the carbon cycle? Think carefully and write them down.