Anatomy Review 1 BackUpper
advertisement

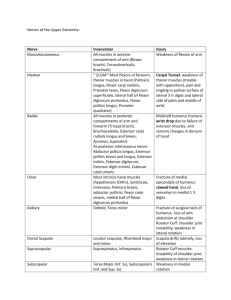
Anatomy Review #1 Brachial Plexus • See the pdf in google drive on brachial plexus • *long thoracic – Injury to this causes winged scapula – Serratus anterior • *suprascapular – Supraspinatus – infraspinatus • *thoracodorsal – Latissimus dorsi Nerve stems • • • • • Axillary: C5-6 Radial: C5-T1 Musculocutaneous: C5-7 Median: C6-T1 (C5) Ulnar: C8-T1 Spaces • Triangular space – – – – Teres minor Long head of triceps Teres major Circumflex scapular a. • Triangular interval • Teres major • Long head of radius • Shaft of humerus • Profunda brachii a. • Radial n. • Quadrangular space – – – – – – – Teres minor long head of triceps shaft of humerus teres major Axillary n. Post. circumflex humeral a. Post. circumflex humeral v. • pp. 679, 691 text Joints: Synovial Synovial – Capsule (inner synovial membrane, outer fibrous) – Hyaline covers articulating surfaces • Sternoclavicular- Modified ball and socket joint (according to the articular surfaces it is rather a saddle, but because the disk it functions like ball and socket) • • • • • • • • Acromioclavicular- plane joint (gliding) Glenohumeral- ball and socket Humeroulnar- compound (hinge-pivot) Distal radioulnar joint- pivot joint Radiocarpal- ellipsoid joint (condylar) Carpal-metacarpal- plane joints (EXCEPT: THUMB =saddle joint) Metacarpophalangeal- ball and socket Interphalangeal- hinge joint p. 20 Gray’s text Joints: Solid Fibrous joints: sutures, gomphoses, syndesmoses • Suture- skull • Gomphoses- teeth and bone • Syndesmoses- two adjacent bones linked by ligament (ligamentum flavum, interosseous membrane) Cartilaginous joints: synchondroses, symphyses • Synchondroses- where two ossification centers separated by cartilage (growth plate) • Symphyses- two separate bones are interconnected by cartilage (pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs) p. 20 Gray’s text Signs • Waiter’s tip- “Erb’s palsy” upper trunk injury – C5-6 • Claw hand- “Klumpke’s” lower trunk injury – C8-T1 – Ring and little fingers hyperextended at MCP joints, flexed at IP joints – Can’t open hand with fingers • Hand of Benediction – The ability to flex the digits 2–3 at the MCP joints is lost as is the ability to flex and extend proximal and distal interphalangeal Dupuytren’s contracture- thick palamar fascia – Can’t make fist with fingers • Volkmann’s contracture- flexion deformity caused by ischemic necrosis of • forearm flexor muscles Ape hand- flattening of thenar eminence due to injury to median n. (supracondylar fx) Odds and ends • • Guyon’s canal- formed by pisiform and hamate. Ulnar n. runs through it. “Handlebar Palsy” Cubital fossa- TAN lateral to medial – – – • • • Fracture of C2 spinous process- obliquous capitis inferior Trapezius- abd. Of humerus beyond horizontal Tight ropey muscle C7-T4=splenius capitus – • • • • • • • Biceps brachii tendon Brachial a. (splits to radial and ulnar) Median n. Innervated by C3-6 posterior ramii What inserts on radial tuberosity and radial neck? Biceps brachii Midshaft humeral fracture- supinator Carpal tunnel- lose sensation of skin of middle finger Subacromial bursitis affects suprascapular nerve Anatomical position- legs ADDucted Thoracodorsal- latissimus dorsi Touch index and middle fingers to thumb= ulnar n. More odds and ends • Bennett’s fx- fx of base of metacarpal of thumb • • • • Boxer’s fx- fx of the necks of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals (5th metacarpal in unskilled boxers) Colle’s fx- distal radius fx displaced posteriorly (dorsum of wrist) “Dinner fork deformity” Smith’s fx- opposite of Colle’s Surgical neck fx- axillary nerve and post humeral circumflex a. affected • • Midshaft of humerus fx- radial n. wrist drop Supracondylar fx- median n. ape hand Rotator cuff- SITS (Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor, Subscapularis) Shoulder most commonly dislocated anteriorly Scaphoid most commonly fractured Lunate most commonly dislocated (FOOSH) Know what makes up anatomical snuff box Lateral epicondylitis- tennis elbow Medial epicondylitis- golfer’s elbow • • • • • • • More • Mallet finger- permanent flexion of distal phalanx. Avulsion of lateral bands of extensor tendon • Boutonniere deformity- flexed middle phalanx, hyperextension of distal phalanx. Avulsion of the central band of the extensor tendon • Allen test- test ulnar, radial circulation to hand Anatomical Snuff Box • Left hand, palm facing to the right – Far left= extensor pollicis longus – Box – Next= extensor pollicis brevis – Far right= adductor pollicis longus – P.759 gray’s text