File
advertisement

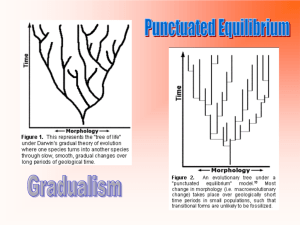
Evidence of Evolution Models of Evolution Gradualism, Punctuated Equilibrium & Endosymbiont Theory TEKS • 7B analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning any data of sudden appearance, stasis, and sequential nature of groups in the fossil record. • 7G analyze and evaluate scientific explanations concerning the complexity of the cell. “In” • Does evolution occur in rapid bursts or gradually (over time)? • This question is difficult to answer because we can't replay the past with a stopwatch in hand. • However, we can try to figure out what patterns we'd expect to observe in the fossil record if evolution did happen in bursts, or if evolution happened gradually. • Then we can check these predictions against what we observe. Lets take “A Peek at the Past” • • • • Let’s read the intro to this activity together Follow directions as stated Class discussion Answer discussion questions Lab Directions • Place the organisms in their proper layer. • If the organism does not say upper or lower just place them in the box. • If you have more than two organisms in a layer, you must look at similarities and differences between the organisms – If the organism is slightly different…place it slightly to the right of the organism below it – If the organisms is completely different ….place it to the extreme right Models of Evolution Which diagram shows gradualism and which shows punctuated equilibrium? Graduated. Why? Punctuated Equilibrium. Why? What should we observe in the fossil record if evolution is slow and steady? • If evolution is slow and steady, we'd expect to see the entire transition, from ancestor to descendent, displayed as transitional forms over a long period of time in the fossil record. In the example, the preservation of many transitional forms, through layers representing a length of time, gives a complete record of slow and steady evolution. Transitional forms in the fossil record • In the example are just a few steps in the evolution of whales from land-dwelling mammals, highlighting the transition of the walking forelimb to the flipper • Shows a slow & gradual change • Gradualism What would we observe in the fossil record if evolution happens in "quick" jumps (perhaps fewer than 100,000 years for significant change)? • If evolution happens in "quick" jumps, we'd expect to see big changes happen quickly in the fossil record, with little transition between ancestor and descendent. • Punctuated Equilibrium What happened to all the ones in the middle??? Does a jump in the fossil record necessarily mean that evolution has happened in a "quick" jump? • Sometimes a jump in the fossil record can also be explained by irregular fossil preservation. • Some fossils were not preserved….the missing link! Stasis • Stasis: a period of little or no evolutionary change in a species in the punctuated equilibrium model Stasis • Stasis: A population of mollusks is experiencing stasis, living, dying, and getting fossilized every few hundred thousand years. Little observable evolution seems to be occurring judging from these fossils. Identify which is gradualism or punctuated equilibrium Punctuated Gradualism Endosymbiont Theory • By reading the article you will be able to answer how…. – bacteria evolved to plants and animals today? – a prokaryote evolved to a eukaryote? Ticket-Out-the-Door • Answer questions