AP CHEMISTRY SEMESTER ONE FINAL EXAM REVIEW MR
advertisement

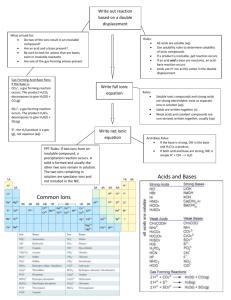
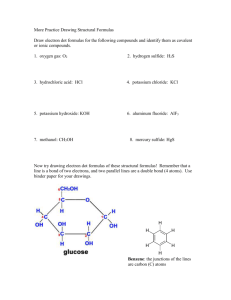
AP CHEMISTRY MR. LINARES SEMESTER ONE FINAL EXAM REVIEW 2012-2013 The first semester final exam will consist of a multiple-choice section and free-response questions. The list below identifies topics that will appear on the exam. Use previous homework problems, worksheets, and tests to prepare for your final. No calculators will be used on the multiple choice section, they will only be allowed on the free response section. Chapter 2 – Atoms, Molecules and Ions (the structure of an atom) Name and write formulas of common ions and ionic compounds The names of monatomic ions and polyatomic ions that you will need to know for test are found in figure 2.11, page 54, and on page 60, tables 2.2 and 2.3 Name the acids found on page 65….both in table 2.5 and in the text…(HNO3 etc) Name hydrates. Name and write formulas of covalent compounds (including hydrocarbons and alcohols) o Example: Hydrocarbon* Alcohol Methane CH4 methanol CH3OH Ethane C2H6 ethanol C2H5OH Propane C3H8 propanol C3H7OH *know that when combustion occurs with a hydrocarbon, it burns in air and releases H2O & CO2 Chapter 3 – Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions Molar conversions Using Avogadro’s number to find number of molecules, atoms, ions etc…from molar mass Empirical formulas and Molecular formulas Percent Mass Composition Balancing equations Stoichiometry Mole-Mole, Mole-Mass, Mass-Mass calculations Limiting reactants Excess Reactants Percent Yield Chapter 4 – Reactions in Aqueous Solutions Define solutions and know its components Electrolytes and non-electrolytes Know what a hydration shell is and how it forms Net ionic equations Properties of acids and bases. Bronstead bases and acids. Hydronium ion Mono-, di-, and triprotic acids Acid-Base neutralization reactions Know the type of redox reactions and how to perform…. Examples… Combination : S + O2 SO2 Decomposition: KClO3 KCl + O2 (unbalanced) Combustion: CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O (unbalanced) Displacement (for H, metals and halogens): Zn + HCl ZnCl2 + H2 (unbalanced) Na + CaCl2 NR Cl2 + KBr Br2 + KCl (unbalanced) Solubility…definition and rules Assigning oxidations numbers Concentration of solutions (molarity) Solution problems Titrations Chapter 5 - Gases All gas laws (including modified gas laws) from page 175-189, 192-196, and 203204 Chapter 6 - Thermochemistry Types of energy on page 224 Endo- and exothermic reactions First and second law of thermodynamics Specific heat problems Hess’s law Chapter 7 – Electronic Structure of Atoms Quantum numbers, electron orbitals and electron configurations and the periodic table (page 286-301) Chapter 8 – Periodic Properties of the Elements The five groups that elements are classified into on the periodic table (pages 318320) Trends in atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electronegativity (pages 323-335) Chapter 9 – Chemical Bonding Covalent bonding and electronegativity (pages 366-372) Drawing Lewis Structures with formal charges and resonance structures (pages 372-379) Exceptions to the octet rule Bond enthalpy Chapter 10 – Molecular Geometry Electron domain geometry and molecular geometry (along with bond angles and hybridizations). Pi and sigma bonds (pages 400-428)