Med Term 2 test 1 review, Chapt 5
advertisement

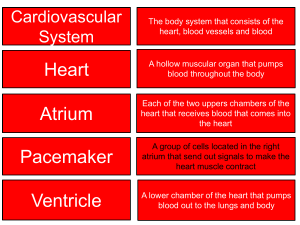
Med Term 2, Test 1 Review Chpt 5-6 Blood disorder in which RBC’s are larger than normal: megaloblastic anemia Specialist that treats disorders of the blood and blood forming tissues: hemotologist One cell thick, smallest blood vessels: capillaries Abnormally slow resting heart rate: bradycardia Pulmonary arteries carry: oxygen poor blood Balloon-like enlargement of artery wall: aneurysm Highest BP against artery walls, when ventricles contract: Systolic pressure Formed in bone marrow, most common type WBC: neutrophils Iron containing pigment of erythrocytes, transports oxygen: hemoglobin Irregular quivering of the walls of the atria: atrial fibrillation Portable EKG worn by a patient for 24 hrs: Holter monitor Total number of leukocytes is less than normal: leukopenia Medication that controls irregularities of the heartbeat; antiarrythmic Condition when the heart can’t pump all the blood it receives: Congestive Heart failure Automated External Defibrillator: for non professionals to shock patient into normal rhythm Heart Attack: Myocardial Infarction Septicemia: microorganisms and toxins in blood Embolus: foreign object (ie blood clot) circulating in the blood Vascular surgeon: specialist in treatment of blood vessels Staphylococcus Aureus: causes toxic shock syndrome and food poisoning Toxoplasmosis: pet feces T Cells: immune defense, coordinating immune defenses, kills on contact Streptococci forms chains Benign: not life threatening, doesn’t reoccur Autoimmune disorder of digestive system: crohn’s Lymphangioma: tumor of abnormal lymphatic vessels Complement: mark foreign invaders and attracts phagocytes Immunodeficiency disorder; weakened immune system Lymphoma: malignancy of lymphoid tissues Spleen; hemolytic fxn Mononucleosis; viral Myosarcoma: malignant tumor of muscle tissue Tinea Pedis: fungal infection Chickenpox: varicella Antiangoigenesis: disrupts blood supply to tumor Sarcoma: affects breasts, lymphatic, glandular tissue, not bone Metastisize; : process in which cancer spreads Ductal Carcinoma in situ: earliest stage breast cancer Mitral valve located between LA and LV Peripheral Vascular Disease; disorders of blood vessels outside heart and brain Dyscrasia: blood disorder Heart murmer; abnormal heart sound LDL bad cholesterol Serum: plasma after blood and clotting cells removed Embolism: blockage of vessel by embolus Throbocytes: known as platelets Blood gases: oxygen, Co2, nitrogen Ischemia: insufficient blood supply Cardiomyopathy: all diseases of heart muscle Palpitation; racing heart beat, may occur with a panic attack Bradycardia; slow heartbeat Coronary Artery disease: atherosclerosis of coronary arteries Hypoperfusion: deficiency of blood passing through organ or tissue Reynauds: peripheral occlusive disease, triggered by cold or stress Needle breast biopsy: xray guided needle to remove tissue Lumpectomy: removal of tumor in the breast once they have diagnosed Vermiform appendix; lymph tissue that hangs from the cecum Peyers patches; lymphoid tissue, in ileum MRSA; serious, difficult to treat Staphyococci form clusters Mastectomy: all breast tissue removed Antigen: any substance the body see’s as foreign Phagocytosis: destroying by swallowing Allergen; produces allergic rxn MATCHING: Aneurysmectomy: surgical removal of an aneurysm arteriectomy: surgical removal of part of an artery atherectomy: surgical removal of plaque carotid endarterectomy: surgical removal of the lining of the carotid artery endarterectomy: surgical removal of the lining of the artery ANEMIAS Angiitis; inflamm of blood vessel Angiospasm: spasm of blood vessels Angiostenosis: narrowing of blood vessel Arteriosclerosis: thickening and loss of elasticity of arterial walls Phlebitis;; inflamm of vein Bacterial endocarditis: inflamm of heart lining caused by bacteria Carditis: inflamm of heart Endocarditis: inflamm of lining Myocarditis: inflamm of heart muscle Pericarditis: inflamm of sac surrounding the heart Allergen: antigen capable of producing allergic response Allergy:over-reaction of the body Antibody; disease fighting protien Antigen: foreign Lymphokines: signals Bacilli: rod Rickettsia: small bacteria live on fleas and ticks Spirochetes: spiral Staphylocci: clusters Streptococci: chains